Case Studies
... The basic structural and functional unit of the kidney is the nephron. Each kidney has about 1 million nephrons, all packed into an area of the kidney called the cortex. The nephron's primary function is to filter blood, but as you can see from the diagram, this is not a simple process. The nephron ...
... The basic structural and functional unit of the kidney is the nephron. Each kidney has about 1 million nephrons, all packed into an area of the kidney called the cortex. The nephron's primary function is to filter blood, but as you can see from the diagram, this is not a simple process. The nephron ...
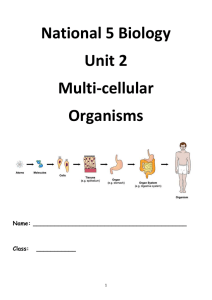
Cells, tissues and organs
... A neuron consists of a cell body attached to nerve fibres. An electrical impulse is carried towards the cell body of a neuron by a sensory fibre and away from it by an axon fibre. ...
... A neuron consists of a cell body attached to nerve fibres. An electrical impulse is carried towards the cell body of a neuron by a sensory fibre and away from it by an axon fibre. ...
Organization of Living Organisms cell: basic unit of life all living
... longitudinal muscles: allow expansion & contraction circular muscles: enlarge or decrease the diameter diagonal muscles: allow twisting what kind of movements can planaria make? ...
... longitudinal muscles: allow expansion & contraction circular muscles: enlarge or decrease the diameter diagonal muscles: allow twisting what kind of movements can planaria make? ...
HUMAN PHYSIOLOGY MODULE: 3 CIRCULATION
... under attack by bacteria, viruses, fungi, or other parasites. Some white cells (macrophages) are the blood's disposal units. They have the function of getting rid of old, unneeded blood cells as well as foreign matter (dust and bacteria). A total WBC count above 11,000 cells/cm3 is referred to as le ...
... under attack by bacteria, viruses, fungi, or other parasites. Some white cells (macrophages) are the blood's disposal units. They have the function of getting rid of old, unneeded blood cells as well as foreign matter (dust and bacteria). A total WBC count above 11,000 cells/cm3 is referred to as le ...
Circulatory and Respiratory System Review
... What happens to your heartrate when you increase physical activity? During sustained physical activity the heartrate increases because the body needs more oxygen and nutrients. ...
... What happens to your heartrate when you increase physical activity? During sustained physical activity the heartrate increases because the body needs more oxygen and nutrients. ...
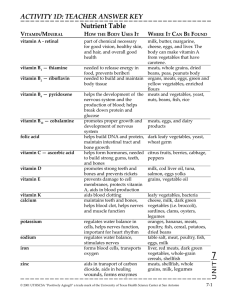
Nutrient Table ACTIVITY 1D: TEACHER ANSWER KEY
... vitamin B1 — thiamine vitamin B2 — riboflavin vitamin B6 — pyridoxene ...
... vitamin B1 — thiamine vitamin B2 — riboflavin vitamin B6 — pyridoxene ...
Annelids Powerpoint
... • Prostomium or lip digs through soil as earthworm feeds on organic matter (detritus) • Pharynx is a muscular organ behind the mouth to help suck in food • Food temporarily stored in crop, ground in gizzard, and digested & absorbed in intestine • Wastes called castings pass out through anus ...
... • Prostomium or lip digs through soil as earthworm feeds on organic matter (detritus) • Pharynx is a muscular organ behind the mouth to help suck in food • Food temporarily stored in crop, ground in gizzard, and digested & absorbed in intestine • Wastes called castings pass out through anus ...
Understanding Blood
... Blood also contains substances that dissolve clots. Occasionally a clot will occur where it is not needed, such as in an artery. The clot disrupts blood flow and can result in disease and death, especially if the clot results in a heart attack or stroke. B. Organisms that lose blood in an accident o ...
... Blood also contains substances that dissolve clots. Occasionally a clot will occur where it is not needed, such as in an artery. The clot disrupts blood flow and can result in disease and death, especially if the clot results in a heart attack or stroke. B. Organisms that lose blood in an accident o ...
The Human Body - Paramedic Association of Manitoba
... the walls of tubelike organs, ducts, and blood vessels. It also forms much of the intestinal wall. A person has little or no control over this type of muscle. ...
... the walls of tubelike organs, ducts, and blood vessels. It also forms much of the intestinal wall. A person has little or no control over this type of muscle. ...
arteries, veins and capillaries. Human circulatory
... Arteries are thick blood vessels that you can easily feel in the form of a pulse. They transport oxygenated blood to the cells. As they are full of oxygen, they appear to be a deep red colour. ...
... Arteries are thick blood vessels that you can easily feel in the form of a pulse. They transport oxygenated blood to the cells. As they are full of oxygen, they appear to be a deep red colour. ...
Circulatory System - Total Care International
... of the male’s reproductive system is to manufacture sperm and then to deliver them to the female’s reproductive tract where fertilization may occur. The role of the female’s reproductive system is basically the same except that it goes further if the sperm meets an egg. If fertilization occurs the ...
... of the male’s reproductive system is to manufacture sperm and then to deliver them to the female’s reproductive tract where fertilization may occur. The role of the female’s reproductive system is basically the same except that it goes further if the sperm meets an egg. If fertilization occurs the ...
The Circulatory System
... Erythrocytes, leukocytes and platelets all develop from a common source ...
... Erythrocytes, leukocytes and platelets all develop from a common source ...
GuideSheet unit 9 “the human Body” (SyStemS)
... 1. What are the four tissue types that are found in the integumentary system? (Pg. 936) 2. What are the functions of the integumentary system? (Pg. 938-939) 3. What are the two layers of skin composed of? (Pg. 936-937) 4. What are the events that occur when skin is repaired? (Pg. 939-940) 5. What ar ...
... 1. What are the four tissue types that are found in the integumentary system? (Pg. 936) 2. What are the functions of the integumentary system? (Pg. 938-939) 3. What are the two layers of skin composed of? (Pg. 936-937) 4. What are the events that occur when skin is repaired? (Pg. 939-940) 5. What ar ...
Perfusion
... Perfusion is the flow of blood through arteries and capillaries delivering nutrients and oxygen to cells and removing cellular wastes. Exemplars Tetralogy of Fallot (Congenital) Patent Ductus Arteriosus (PDA) Septal Defects (VSD) Coarctation of Aorta Dysrhythmias Myocardial Infarction (MI) Sudden De ...
... Perfusion is the flow of blood through arteries and capillaries delivering nutrients and oxygen to cells and removing cellular wastes. Exemplars Tetralogy of Fallot (Congenital) Patent Ductus Arteriosus (PDA) Septal Defects (VSD) Coarctation of Aorta Dysrhythmias Myocardial Infarction (MI) Sudden De ...
Slide 1
... • The two upper chambers are called the right and left atriums • The two lower chambers are called the right and left ventricles ...
... • The two upper chambers are called the right and left atriums • The two lower chambers are called the right and left ventricles ...
Biol 2402 - Northeast Texas Community College
... - respiration refers to breathing or ventilation and the exchange of gases between the atmosphere, the blood and individuals cells - the respiratory system provides oxygen to the bloodstream and removes carbon dioxide; it also allows vocalization - metabolic needs for oxygen are great; few reserves ...
... - respiration refers to breathing or ventilation and the exchange of gases between the atmosphere, the blood and individuals cells - the respiratory system provides oxygen to the bloodstream and removes carbon dioxide; it also allows vocalization - metabolic needs for oxygen are great; few reserves ...
CA Circulatory L
... • When a crocodilian is above water and breathing air, the semilunar valve in the right aorta remains closed because of higher pressure in the left & right aorta (higher than in the right ventricle). • As a result, the right aorta receives blood from the left aorta (so both aortas carry oxygenated b ...
... • When a crocodilian is above water and breathing air, the semilunar valve in the right aorta remains closed because of higher pressure in the left & right aorta (higher than in the right ventricle). • As a result, the right aorta receives blood from the left aorta (so both aortas carry oxygenated b ...
Cardiovascular System
... blood in the single ventricle means the organs are not getting blood saturated with oxygen. This is not as efficient as a four-chambered system, which keeps the two circuits separate, but it is sufficient for these cold-blooded organisms. The heart rate of amphibians and reptiles is very dependent ...
... blood in the single ventricle means the organs are not getting blood saturated with oxygen. This is not as efficient as a four-chambered system, which keeps the two circuits separate, but it is sufficient for these cold-blooded organisms. The heart rate of amphibians and reptiles is very dependent ...
Key Questions for Understanding Respiratory Physiology
... 3. Respiratory gas transport: oxygen and carbon dioxide must be transported to and from lungs and cells by the blood 4. Internal respiration: at systemic capillaries, gas exchange occurs between blood and tissue cells ...
... 3. Respiratory gas transport: oxygen and carbon dioxide must be transported to and from lungs and cells by the blood 4. Internal respiration: at systemic capillaries, gas exchange occurs between blood and tissue cells ...
Circulatory and Respiratory Systems Notes
... • Nutrients and oxygen reach body tissues by diffusing across thin walls of capillaries, the smallest blood vessels. • Blood that is completely contained within blood vessels can be pumped under higher pressure and circulated more efficiently than can blood in an open system. ...
... • Nutrients and oxygen reach body tissues by diffusing across thin walls of capillaries, the smallest blood vessels. • Blood that is completely contained within blood vessels can be pumped under higher pressure and circulated more efficiently than can blood in an open system. ...
Subject: Cardiovascular System Language: Russian
... supply to a restricted area of the brain, resulting in brief neurologic dysfunction that usually persists for less than 24 hours. It may be a warning sign of an imminent full-blown stroke. are most often caused by defective heart valves. A stenotic heart valve has a smaller-than-normal opening and c ...
... supply to a restricted area of the brain, resulting in brief neurologic dysfunction that usually persists for less than 24 hours. It may be a warning sign of an imminent full-blown stroke. are most often caused by defective heart valves. A stenotic heart valve has a smaller-than-normal opening and c ...
Practice Exam 5
... 20) High-flying birds are able to obtain enough oxygen even when the air is very thin because a. they have more efficient lungs than other vertebrates. b. they have reduced amounts of hemoglobin in their blood. c. their mitochondria are more efficient than those of other vertebrates. d. their heart ...
... 20) High-flying birds are able to obtain enough oxygen even when the air is very thin because a. they have more efficient lungs than other vertebrates. b. they have reduced amounts of hemoglobin in their blood. c. their mitochondria are more efficient than those of other vertebrates. d. their heart ...
BIOLOGY 206 CHAPTER 20: BLOOD VESSELS
... Fluids leave the capillary when CHP is greater than COP and fluids enter the capillary from the interstitial fluid when COP is greater than CHP. ...
... Fluids leave the capillary when CHP is greater than COP and fluids enter the capillary from the interstitial fluid when COP is greater than CHP. ...
cetacean behaviour - Mater Academy Lakes High School
... 40oC – humpback dolphins in the Arabian Gulf -1.9oC – cetaceans in Antarctic ...
... 40oC – humpback dolphins in the Arabian Gulf -1.9oC – cetaceans in Antarctic ...
Homeostasis

Homeostasis or homoeostasis (homeo- + -stasis) is the property of a system in which variables are regulated so that internal conditions remain stable and relatively constant. Examples of homeostasis include the regulation of temperature and the balance between acidity and alkalinity (pH). It is a process that maintains the stability of the human body's internal environment in response to changes in external conditions.The concept was described by French physiologist Claude Bernard in 1865 and the word was coined by Walter Bradford Cannon in 1926. Although the term was originally used to refer to processes within living organisms, it is frequently applied to automatic control systems such as thermostats. Homeostasis requires a sensor to detect changes in the condition to be regulated, an effector mechanism that can vary that condition, and a negative feedback connection between the two.