Answers to End-of-Chapter Questions – Brooker et al ARIS site
... Answer: The AUG triplet would have shown radioactivity in the methionine test tube. Even though AUG acts as the start codon, it also codes for the amino acid methionine. The other three codons act as stop codons and do not code for an amino acid. In these cases, the researchers would not have found ...
... Answer: The AUG triplet would have shown radioactivity in the methionine test tube. Even though AUG acts as the start codon, it also codes for the amino acid methionine. The other three codons act as stop codons and do not code for an amino acid. In these cases, the researchers would not have found ...
DNA
... Translation - mRNA to Protein • The Instructions mRNA • The Reader Ribosome • The Transporter of Amino Acids Transfer RNA (tRNA) ...
... Translation - mRNA to Protein • The Instructions mRNA • The Reader Ribosome • The Transporter of Amino Acids Transfer RNA (tRNA) ...
Introductory Biology Primer - A computational tour of the human
... • Why? Every cell has same DNA but each cell expresses different proteins. • Signal transduction: One signal converted to another – Cascade has “master regulators” turning on many proteins, which in turn each turn on many proteins, ... ...
... • Why? Every cell has same DNA but each cell expresses different proteins. • Signal transduction: One signal converted to another – Cascade has “master regulators” turning on many proteins, which in turn each turn on many proteins, ... ...
nucleic acids - onlinebiosurgery
... Carries the genetic message from DNA in the nucleus to the ribosomes where proteins are synthesised (made) accordingly. ...
... Carries the genetic message from DNA in the nucleus to the ribosomes where proteins are synthesised (made) accordingly. ...
Chapter 4 • Lesson 21
... Multicellular organisms can be made up of millions or even trillions of cells. In most cases, all or most of the cells in an organism have the same DMA. However, the cells are not identical because of differences in how their genes are expressed. As you learned in Lesson 6, every gene in an organism ...
... Multicellular organisms can be made up of millions or even trillions of cells. In most cases, all or most of the cells in an organism have the same DMA. However, the cells are not identical because of differences in how their genes are expressed. As you learned in Lesson 6, every gene in an organism ...
Chapter 25: Molecular Basis of Inheritance
... DNA in the nucleus contains a triplet code; each group of three bases stands for one amino acid. During transcription, an mRNA copy of the DNA template is made. The mRNA is processed before leaving the nucleus. The mRNA joins with a ribosome, where tRNA carries the amino acids into position during t ...
... DNA in the nucleus contains a triplet code; each group of three bases stands for one amino acid. During transcription, an mRNA copy of the DNA template is made. The mRNA is processed before leaving the nucleus. The mRNA joins with a ribosome, where tRNA carries the amino acids into position during t ...
File
... 5. Explain the following and rate them in order of severity: A point mutation on the first letter in a codon A point mutation on the third letter of a codon A Frameshift mutation ...
... 5. Explain the following and rate them in order of severity: A point mutation on the first letter in a codon A point mutation on the third letter of a codon A Frameshift mutation ...
Chapter 12 Notes - White Plains Public Schools
... Anticodon- the 3 bases (AUGC) on mRNA are paired with ones on tRNA o Examples: AGU-UCC-AAG (codon) UCA-AGG-CGA (Anticodon) RNA and DNA DNA= “Master plan” -Stays in the nucleus RNA= “Blueprint” – Leaves the nucleus to go to protein building sites (Ribosomes) in cytoplasm Chapter 12 Lesson 4 Mutat ...
... Anticodon- the 3 bases (AUGC) on mRNA are paired with ones on tRNA o Examples: AGU-UCC-AAG (codon) UCA-AGG-CGA (Anticodon) RNA and DNA DNA= “Master plan” -Stays in the nucleus RNA= “Blueprint” – Leaves the nucleus to go to protein building sites (Ribosomes) in cytoplasm Chapter 12 Lesson 4 Mutat ...
Chapter 17 and 19: Review Questions
... 6. Which of the following processes occurs in the cytoplasm of a eukaryotic cell? DNA replication translation transcription DNA replication and translation translation and transcription 7. Cells are able to distinguish proteins destined for secretion or compartmentation from those to be used in the ...
... 6. Which of the following processes occurs in the cytoplasm of a eukaryotic cell? DNA replication translation transcription DNA replication and translation translation and transcription 7. Cells are able to distinguish proteins destined for secretion or compartmentation from those to be used in the ...
Lecture 17 Functional Genetics III Basic Approaches
... Functional genomics: Identify the function of each and every gene in the genome. Since the characterization of the function of a protein domain in one organism generally provides hint to its function in another organism, the first goal of functional genomics is to identify as many genes as possible ...
... Functional genomics: Identify the function of each and every gene in the genome. Since the characterization of the function of a protein domain in one organism generally provides hint to its function in another organism, the first goal of functional genomics is to identify as many genes as possible ...
DNA & THE GENETIC CODE (protein synthesis)
... RNA polymerase joins the sugarphosphate backbone of the mRNA by condensation reactions. The completed mRNA molecule passes through the nuclear pores in the nuclear membrane into the cytoplasm. There are only 2 copies of each gene in the nucleus, but transcription allows many copies of mRNA to be av ...
... RNA polymerase joins the sugarphosphate backbone of the mRNA by condensation reactions. The completed mRNA molecule passes through the nuclear pores in the nuclear membrane into the cytoplasm. There are only 2 copies of each gene in the nucleus, but transcription allows many copies of mRNA to be av ...
13.2 Ribosomes and Protein Synthesis
... The methionine codon AUG serves as the “start” codon for protein synthesis. There are three “stop” codons. UAA, UAG, and UGA are “stop” codons ...
... The methionine codon AUG serves as the “start” codon for protein synthesis. There are three “stop” codons. UAA, UAG, and UGA are “stop” codons ...
DNA Functions
... create the amino acids and then the protein. The ribosome has to take the nucleotide bases and equate it with codons that specify amino acids. Each amino acid is represented by certain ...
... create the amino acids and then the protein. The ribosome has to take the nucleotide bases and equate it with codons that specify amino acids. Each amino acid is represented by certain ...
ppt slides
... the ribosome incorporates amino acids into a polypeptide chain • RNA is decoded by tRNA (transfer RNA) molecules, which each transport specific amino acids to the growing chain • Translation ends when a stop codon (UAA, UAG, UGA) is reached ...
... the ribosome incorporates amino acids into a polypeptide chain • RNA is decoded by tRNA (transfer RNA) molecules, which each transport specific amino acids to the growing chain • Translation ends when a stop codon (UAA, UAG, UGA) is reached ...
AP Protein Synthesis
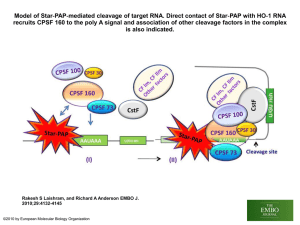
... RNA processing1. 5' cap with a modified guanine nucleotide is added. 2. At the 3' end 30-200 adenine nucleotides are added (poly-Atail). -These modifications prevent the mRNA from being degraded and signal the ribosome where to attach. 3. There are noncoding regions (introns) that are removed in eu ...
... RNA processing1. 5' cap with a modified guanine nucleotide is added. 2. At the 3' end 30-200 adenine nucleotides are added (poly-Atail). -These modifications prevent the mRNA from being degraded and signal the ribosome where to attach. 3. There are noncoding regions (introns) that are removed in eu ...
What_I_need_to_know_about_Protein_Synthesis_2013
... 20. Protein synthesis is the process of making _________ A gene is the instructions to make a _____________ The protein is the expressed __________ of the organism. 21. Where does protein synthesis occur in the cell? _________________ 22. The process of protein synthesis begins with one ____________ ...
... 20. Protein synthesis is the process of making _________ A gene is the instructions to make a _____________ The protein is the expressed __________ of the organism. 21. Where does protein synthesis occur in the cell? _________________ 22. The process of protein synthesis begins with one ____________ ...
File
... RNA Structure and Types • RNA is the bridge between gene and protein • Bases of an RNA sequence are complementary to those of one strand of the double helix, called the template strand • RNA polymerase builds an RNA molecule • Nontemplate strand of the DNA double helix is called the coding strand ...
... RNA Structure and Types • RNA is the bridge between gene and protein • Bases of an RNA sequence are complementary to those of one strand of the double helix, called the template strand • RNA polymerase builds an RNA molecule • Nontemplate strand of the DNA double helix is called the coding strand ...
The Translators
... codon of the mRNA (here, that codon is GUG, so the tRNA that binds carries the amino acid valine). ...
... codon of the mRNA (here, that codon is GUG, so the tRNA that binds carries the amino acid valine). ...
RNA & Protein Synthesis
... RNA – 3 Types • Transfer RNA (tRNA): brings amino acids to the ribosome to be added to the protein chain that is being made – There is 1 tRNA for each of the 20 amino acids. ...
... RNA – 3 Types • Transfer RNA (tRNA): brings amino acids to the ribosome to be added to the protein chain that is being made – There is 1 tRNA for each of the 20 amino acids. ...
Inquiry into Life Twelfth Edition
... Genes Cloning a gene permits • Production of large quantities of a particular DNA sequence for detailed study • Large quantities of the gene’s product (protein or RNA) can also be obtained for further use ...
... Genes Cloning a gene permits • Production of large quantities of a particular DNA sequence for detailed study • Large quantities of the gene’s product (protein or RNA) can also be obtained for further use ...
Protein Synthesis
... • Messenger RNA (mRNA) copies DNA’s code & carries the genetic information to the ribosomes • Ribosomal RNA (rRNA), along with protein, makes up the ribosomes • Transfer RNA (tRNA) transfers amino acids to the ribosomes where proteins are synthesized ...
... • Messenger RNA (mRNA) copies DNA’s code & carries the genetic information to the ribosomes • Ribosomal RNA (rRNA), along with protein, makes up the ribosomes • Transfer RNA (tRNA) transfers amino acids to the ribosomes where proteins are synthesized ...
Gene expression
Gene expression is the process by which information from a gene is used in the synthesis of a functional gene product. These products are often proteins, but in non-protein coding genes such as transfer RNA (tRNA) or small nuclear RNA (snRNA) genes, the product is a functional RNA.The process of gene expression is used by all known life - eukaryotes (including multicellular organisms), prokaryotes (bacteria and archaea), and utilized by viruses - to generate the macromolecular machinery for life.Several steps in the gene expression process may be modulated, including the transcription, RNA splicing, translation, and post-translational modification of a protein. Gene regulation gives the cell control over structure and function, and is the basis for cellular differentiation, morphogenesis and the versatility and adaptability of any organism. Gene regulation may also serve as a substrate for evolutionary change, since control of the timing, location, and amount of gene expression can have a profound effect on the functions (actions) of the gene in a cell or in a multicellular organism.In genetics, gene expression is the most fundamental level at which the genotype gives rise to the phenotype, i.e. observable trait. The genetic code stored in DNA is ""interpreted"" by gene expression, and the properties of the expression give rise to the organism's phenotype. Such phenotypes are often expressed by the synthesis of proteins that control the organism's shape, or that act as enzymes catalysing specific metabolic pathways characterising the organism.