A1 B1 C1 D1 A2 B2 C2 D2 A1 B1 C1 A2 B2 C2
... shows the three-dimensional structure of proteins. Depending on the level of the students, the exact chemical properties of the amino acids may be discussed (hydrophobic and hydrophilic, polar and nonpolar). Because amino acids are rigidly bonded between certain parts of the amino acid itself, there ...
... shows the three-dimensional structure of proteins. Depending on the level of the students, the exact chemical properties of the amino acids may be discussed (hydrophobic and hydrophilic, polar and nonpolar). Because amino acids are rigidly bonded between certain parts of the amino acid itself, there ...
Elise Young: Animal & Range Sciences
... Elise Young: Animal & Range Sciences Mentor: David Sands -- Plant Sciences & Plant Pathology Linking common factors in the phenomenon of protein clumping observed in several diseases Proteins perform many important functions at the cellular level. However, if proteins do not fold properly, they are ...
... Elise Young: Animal & Range Sciences Mentor: David Sands -- Plant Sciences & Plant Pathology Linking common factors in the phenomenon of protein clumping observed in several diseases Proteins perform many important functions at the cellular level. However, if proteins do not fold properly, they are ...
R032 Publication Only Basic Science: Biofilm Key proteins of
... proteomic analysis revealed that the samples exhibited different protein profiles, with an increased protein expression of the strain in biofilm compared to planktonic fungal growth, being approximately 250 proteins expressed exclusively by the fungus in biofilms and others with different levels of ...
... proteomic analysis revealed that the samples exhibited different protein profiles, with an increased protein expression of the strain in biofilm compared to planktonic fungal growth, being approximately 250 proteins expressed exclusively by the fungus in biofilms and others with different levels of ...
Biotechnology Unit 3: DNA to Proteins Essential Cell Biology
... c. The tertiary structure involves all of the smaller folds interacting with each other to form the final structural conformation d. The quaternary structure is when the protein is combines with other polypeptide molecules to create a larger structure e. Proteins also have a level of organization ca ...
... c. The tertiary structure involves all of the smaller folds interacting with each other to form the final structural conformation d. The quaternary structure is when the protein is combines with other polypeptide molecules to create a larger structure e. Proteins also have a level of organization ca ...
Protein Synthesis PPT
... 3. Enzymes used for digestion and other chemical reactions are proteins (Enzymes speed up the rate of a reaction) 4. Component of all cell membranes ...
... 3. Enzymes used for digestion and other chemical reactions are proteins (Enzymes speed up the rate of a reaction) 4. Component of all cell membranes ...
ppt
... • ‘To understand the biological function of proteins we would .. Like to be able to deduce or predict the threedimensional structure from the amino acid sequence.’ • ‘This we cannot do.’ ...
... • ‘To understand the biological function of proteins we would .. Like to be able to deduce or predict the threedimensional structure from the amino acid sequence.’ • ‘This we cannot do.’ ...
Protein Synthesis
... • DNA is deoxyribonucleic acid • Composed of nucleotides • Each nucleotide contains – Deoxyribose sugar – Phosphate group (PO4-1) – Nitrogenous base (A, T, C, or G) ...
... • DNA is deoxyribonucleic acid • Composed of nucleotides • Each nucleotide contains – Deoxyribose sugar – Phosphate group (PO4-1) – Nitrogenous base (A, T, C, or G) ...
Relationship between amino acids sequences and protein structures
... regularities a new algorithm of the multiple sequences alignment was developed. The proposed method involves ‘projecting’ common supersecondary structural characteristics onto the sequence to reveal key residues. The results of the alignment revealed conserved positions. It was shown that residues a ...
... regularities a new algorithm of the multiple sequences alignment was developed. The proposed method involves ‘projecting’ common supersecondary structural characteristics onto the sequence to reveal key residues. The results of the alignment revealed conserved positions. It was shown that residues a ...
PDF - Available Technologies
... Production of recombinant protein or gene products in bacteria or other cells is dramatically increased when the TEnBOX is incorporated into the plasmid vector. The efficiency of the protein expression from the TEnBOX is much higher than reported with the best commercial vectors (pET-21 and pTriEX-3 ...
... Production of recombinant protein or gene products in bacteria or other cells is dramatically increased when the TEnBOX is incorporated into the plasmid vector. The efficiency of the protein expression from the TEnBOX is much higher than reported with the best commercial vectors (pET-21 and pTriEX-3 ...
Importance of Proteins PowerPoint
... Describe ways in which protein is used in food preparation. Identify the essential and nonessential amino acids. Compare and contrast complete and incomplete proteins. Explain what happens during the denaturation of protein and how the process occurs. Explain coagulation and apply basic principles o ...
... Describe ways in which protein is used in food preparation. Identify the essential and nonessential amino acids. Compare and contrast complete and incomplete proteins. Explain what happens during the denaturation of protein and how the process occurs. Explain coagulation and apply basic principles o ...
Document
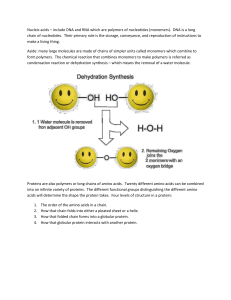
... chain of nucleotides. Their primary role is the storage, conveyance, and reproduction of instructions to make a living thing. Aside: many large molecules are made of chains of simpler units called monomers which combine to form polymers. The chemical reaction that combines monomers to make polymers ...
... chain of nucleotides. Their primary role is the storage, conveyance, and reproduction of instructions to make a living thing. Aside: many large molecules are made of chains of simpler units called monomers which combine to form polymers. The chemical reaction that combines monomers to make polymers ...
Proteins
... 20 different amino acids are found as part of proteins (8 amino acids are essential because they cannot be made by people) The 20 amino acids can be linked together in any sequence whatsoever, and in chains of varying lengths. This explains why there are so many proteins. A chain of amino acids is c ...
... 20 different amino acids are found as part of proteins (8 amino acids are essential because they cannot be made by people) The 20 amino acids can be linked together in any sequence whatsoever, and in chains of varying lengths. This explains why there are so many proteins. A chain of amino acids is c ...
Chapter 5: Biological Molecules Molecules of Life • All life made up
... o 2 monosaccharides linked to transport sugars in organisms o Sucrose: Fructose/Glucose o Maltose: Glucose/Glucose o Lactose: Glucose/Galactose ...
... o 2 monosaccharides linked to transport sugars in organisms o Sucrose: Fructose/Glucose o Maltose: Glucose/Glucose o Lactose: Glucose/Galactose ...
Hands-on Exercise: Locating Protein Information
... A variant of this protein with mutations in its amino acid sequence has been isolated (see link http://www.hsls.pitt.edu/guides/genetics/tutorials). ...
... A variant of this protein with mutations in its amino acid sequence has been isolated (see link http://www.hsls.pitt.edu/guides/genetics/tutorials). ...
TWO GENES ENCODING FUNCTIONAL PECTIN
... A proteinaceous inhibitor of pectin methylesterase (PMEI) has been reported in kiwi but to date no other proteins acting as PMEI have been found in plants. Two sequences closely related to PMEI from kiwi were identified in Arabidopsis thaliana. The corresponding cDNAs encode cell wall proteins of 17 ...
... A proteinaceous inhibitor of pectin methylesterase (PMEI) has been reported in kiwi but to date no other proteins acting as PMEI have been found in plants. Two sequences closely related to PMEI from kiwi were identified in Arabidopsis thaliana. The corresponding cDNAs encode cell wall proteins of 17 ...
Nucleic Acids and Protein Synthesis
... recognize and bind to other molecules. Examples: a. Antibody proteins must fit on bacteria and viruses to destroy them. b. Enzymes recognize and bind to specific substrates to speed up ...
... recognize and bind to other molecules. Examples: a. Antibody proteins must fit on bacteria and viruses to destroy them. b. Enzymes recognize and bind to specific substrates to speed up ...
Chapter 3
... • Single polynucleotide strand • RNA uses information in DNA to specify sequence of amino acids in proteins ...
... • Single polynucleotide strand • RNA uses information in DNA to specify sequence of amino acids in proteins ...
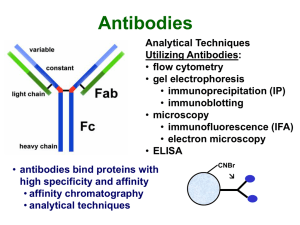
Chapter 3
... (polyclonal), or from a single B cell colony (monoclonal). • Every different antibody has a unique Fab region. • All antibodies isolated from the same species of animal have nearly identical Fc regions. ...
... (polyclonal), or from a single B cell colony (monoclonal). • Every different antibody has a unique Fab region. • All antibodies isolated from the same species of animal have nearly identical Fc regions. ...
BB 450/500 Lecture 5 Highlights
... protein. The word polypeptide refers to a polymer of amino acids. A protein may contain one or more polypeptides and is folded and may be covalently modified. 11. Hemoglobin (and many other proteins) have multiple polypeptide subunits. Interactions between the subunits include disulfide bonds, ionic ...
... protein. The word polypeptide refers to a polymer of amino acids. A protein may contain one or more polypeptides and is folded and may be covalently modified. 11. Hemoglobin (and many other proteins) have multiple polypeptide subunits. Interactions between the subunits include disulfide bonds, ionic ...
Chapter 3 (Protein structure and function)
... Surface conformation of a protein determines its chemistry Interaction of neighboring parts of the polypeptide chain may restrict the access of water molecules to the protein’s binding site - Clustering of neighboring polar amino acid side chains can alter their reactivity e.g. clustering of negativ ...
... Surface conformation of a protein determines its chemistry Interaction of neighboring parts of the polypeptide chain may restrict the access of water molecules to the protein’s binding site - Clustering of neighboring polar amino acid side chains can alter their reactivity e.g. clustering of negativ ...
Chemistry and My Body - Mrs. Jones Mrs. Jones
... blocks that make up protein. There are 20 different ‘blocks’ ...
... blocks that make up protein. There are 20 different ‘blocks’ ...
Test 2 - HCC Learning Web
... 19. What is the chemical reaction mechanism by which cells make polymers from monomers? 20. The bonding of two amino acid molecules to form a larger molecule requires ...
... 19. What is the chemical reaction mechanism by which cells make polymers from monomers? 20. The bonding of two amino acid molecules to form a larger molecule requires ...
Typical IP Protocol
... Bacterial proteins that bind IgG (Fc): • protein A (Staphylococcus aureus) • protein G (Streptococcus) • binds more species and subclasses ...
... Bacterial proteins that bind IgG (Fc): • protein A (Staphylococcus aureus) • protein G (Streptococcus) • binds more species and subclasses ...
Protein

Proteins (/ˈproʊˌtiːnz/ or /ˈproʊti.ɨnz/) are large biomolecules, or macromolecules, consisting of one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within living organisms, including catalyzing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, responding to stimuli, and transporting molecules from one location to another. Proteins differ from one another primarily in their sequence of amino acids, which is dictated by the nucleotide sequence of their genes, and which usually results in protein folding into a specific three-dimensional structure that determines its activity.A linear chain of amino acid residues is called a polypeptide. A protein contains at least one long polypeptide. Short polypeptides, containing less than about 20-30 residues, are rarely considered to be proteins and are commonly called peptides, or sometimes oligopeptides. The individual amino acid residues are bonded together by peptide bonds and adjacent amino acid residues. The sequence of amino acid residues in a protein is defined by the sequence of a gene, which is encoded in the genetic code. In general, the genetic code specifies 20 standard amino acids; however, in certain organisms the genetic code can include selenocysteine and—in certain archaea—pyrrolysine. Shortly after or even during synthesis, the residues in a protein are often chemically modified by posttranslational modification, which alters the physical and chemical properties, folding, stability, activity, and ultimately, the function of the proteins. Sometimes proteins have non-peptide groups attached, which can be called prosthetic groups or cofactors. Proteins can also work together to achieve a particular function, and they often associate to form stable protein complexes.Once formed, proteins only exist for a certain period of time and are then degraded and recycled by the cell's machinery through the process of protein turnover. A protein's lifespan is measured in terms of its half-life and covers a wide range. They can exist for minutes or years with an average lifespan of 1–2 days in mammalian cells. Abnormal and or misfolded proteins are degraded more rapidly either due to being targeted for destruction or due to being unstable.Like other biological macromolecules such as polysaccharides and nucleic acids, proteins are essential parts of organisms and participate in virtually every process within cells. Many proteins are enzymes that catalyze biochemical reactions and are vital to metabolism. Proteins also have structural or mechanical functions, such as actin and myosin in muscle and the proteins in the cytoskeleton, which form a system of scaffolding that maintains cell shape. Other proteins are important in cell signaling, immune responses, cell adhesion, and the cell cycle. Proteins are also necessary in animals' diets, since animals cannot synthesize all the amino acids they need and must obtain essential amino acids from food. Through the process of digestion, animals break down ingested protein into free amino acids that are then used in metabolism.Proteins may be purified from other cellular components using a variety of techniques such as ultracentrifugation, precipitation, electrophoresis, and chromatography; the advent of genetic engineering has made possible a number of methods to facilitate purification. Methods commonly used to study protein structure and function include immunohistochemistry, site-directed mutagenesis, X-ray crystallography, nuclear magnetic resonance and mass spectrometry.