Prestained Protein Molecular Weight Marker
... Prestained Protein Molecular Weight Marker is a mixture of purified proteins covalently coupled to a blue chromophore. It consists of 6 proteins ranging in apparent molecular weight from approximately 20kDa to 120kDa. The protein concentrations are optimized to yield 6 well-defined blue bands after ...
... Prestained Protein Molecular Weight Marker is a mixture of purified proteins covalently coupled to a blue chromophore. It consists of 6 proteins ranging in apparent molecular weight from approximately 20kDa to 120kDa. The protein concentrations are optimized to yield 6 well-defined blue bands after ...
Sonac introduces new natural products for aqua feed
... MucoPro80 has many benefits in aqua feeds. MucoPro80 reinforces the natural gut defense system and is a very palatable and hypo-allergenic source of protein. No limitations are imposed on the export of the end product to Europe. This makes MucoPro one of the few animal proteins which can be used in ...
... MucoPro80 has many benefits in aqua feeds. MucoPro80 reinforces the natural gut defense system and is a very palatable and hypo-allergenic source of protein. No limitations are imposed on the export of the end product to Europe. This makes MucoPro one of the few animal proteins which can be used in ...
Short Answer – Answer briefly and completely on your answer sheet.
... Major kinds of proteins embedded in the plasma membrane include all of the following except a. channel proteins b. receptor proteins c. genetic proteins d. marker proteins e. both receptor and channel proteins All of the following are examples of passive transport except a. diffusion b. osmosis c. A ...
... Major kinds of proteins embedded in the plasma membrane include all of the following except a. channel proteins b. receptor proteins c. genetic proteins d. marker proteins e. both receptor and channel proteins All of the following are examples of passive transport except a. diffusion b. osmosis c. A ...
File
... Proteins: Proteins have a great variety of functions in the body---as structural materials, as energy sources, as certain hormones, as receptors on cell membranes, as antibodies, and as enzymes to catalyze metabolic reactions. Proteins contain what 4 elements? Building blocks of proteins are the ami ...
... Proteins: Proteins have a great variety of functions in the body---as structural materials, as energy sources, as certain hormones, as receptors on cell membranes, as antibodies, and as enzymes to catalyze metabolic reactions. Proteins contain what 4 elements? Building blocks of proteins are the ami ...
Chapter 2 Study Outline
... Fatty acids with hydrogen at every position along the carbon chain are saturated; those with one or more double bonds are called ______________ fats. ____________ contain glycerol, two fatty acids, and a phosphate group, and are important in cell structures. _______________ are complex ring structur ...
... Fatty acids with hydrogen at every position along the carbon chain are saturated; those with one or more double bonds are called ______________ fats. ____________ contain glycerol, two fatty acids, and a phosphate group, and are important in cell structures. _______________ are complex ring structur ...
protein-protein interactions
... between multiple proteins that form complexes. Do not reveal the precise chemical nature of the interactions but simply report that such interactions take place. The major high-throughput technology: systematic affinity purification followed by mass spectrometry ...
... between multiple proteins that form complexes. Do not reveal the precise chemical nature of the interactions but simply report that such interactions take place. The major high-throughput technology: systematic affinity purification followed by mass spectrometry ...
Nutrition - GCO 2 - Proteins.notebook
... cell. It has the instructions for how amino acids will be linked to form the proteins in your body. ...
... cell. It has the instructions for how amino acids will be linked to form the proteins in your body. ...
Solid Tumour Section Kidney: t(X;17)(p11.2;q23) in renal cell carcinoma
... Kidney: t(X;17)(p11.2;q23) in renal cell carcinoma Pedram Argani, Marc Ladanyi Department of Pathology, room S-801, MSKCC, 1275 York Avenue, New York, NY 10021, USA (PA); Department of Surgical Pathology, The Johns Hopkins Hospital, Weinberg Building, Room 2242, 401 North ...
... Kidney: t(X;17)(p11.2;q23) in renal cell carcinoma Pedram Argani, Marc Ladanyi Department of Pathology, room S-801, MSKCC, 1275 York Avenue, New York, NY 10021, USA (PA); Department of Surgical Pathology, The Johns Hopkins Hospital, Weinberg Building, Room 2242, 401 North ...
Ch03Pt2
... So, trp in a protein molecular weight is 204 – 18 = 186 daltons. a. The relationship of weight by weight is the same a molecular weight by molecular weight. This can be expressed where n is the number of trp/protein is assumed to be 1 (this calculates the minimum MW): ...
... So, trp in a protein molecular weight is 204 – 18 = 186 daltons. a. The relationship of weight by weight is the same a molecular weight by molecular weight. This can be expressed where n is the number of trp/protein is assumed to be 1 (this calculates the minimum MW): ...
Macromolecule Expert Sheets
... 10. How are “hydrogenated oils” changed chemically? (Not in the book! We will discuss this in class.) They have had hydrogen atoms atoms force on to make them more solid (breaking some of the double bonds between carbons), 11. What is a steroid? It is a lipid molecule in which the carbon skeleton fo ...
... 10. How are “hydrogenated oils” changed chemically? (Not in the book! We will discuss this in class.) They have had hydrogen atoms atoms force on to make them more solid (breaking some of the double bonds between carbons), 11. What is a steroid? It is a lipid molecule in which the carbon skeleton fo ...
Protein Structure
... state depends strongly on its local environment. This feature is often exploited and histidine is used as a molecular switch. ...
... state depends strongly on its local environment. This feature is often exploited and histidine is used as a molecular switch. ...
Biochemistry
... have been linked and a water lost The bond holding the sugars together is a glycosidic bond Isomers—same chemical formula with different structures ...
... have been linked and a water lost The bond holding the sugars together is a glycosidic bond Isomers—same chemical formula with different structures ...
Biochemistry Powerpoint
... maintain body (20%) Nucleic Acids- needed to build genetic code (found in all foods) ...
... maintain body (20%) Nucleic Acids- needed to build genetic code (found in all foods) ...
Biochemistry PPT - Madison County Schools
... Where fats have a third fatty acid linked to glycerol, phospholipids have a negatively charged phosphate group. This makes the “head” of the phospholipid hydrophilic; the hydrocarbon “tails” are hydrophobic. Phospholipids are the major components of cell membranes. In a cell membrane, the hydrophobi ...
... Where fats have a third fatty acid linked to glycerol, phospholipids have a negatively charged phosphate group. This makes the “head” of the phospholipid hydrophilic; the hydrocarbon “tails” are hydrophobic. Phospholipids are the major components of cell membranes. In a cell membrane, the hydrophobi ...
Creative Cuisine Notes: Proteins, Water, Carbohydrates, Fats
... • Important energy source. • Belong to a group called lipids. • Cholesterol is a fatlike substance found in every cell of the body. ...
... • Important energy source. • Belong to a group called lipids. • Cholesterol is a fatlike substance found in every cell of the body. ...
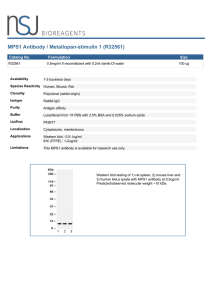
MPS1 Antibody / Metallopan-stimulin 1 (R32561)
... ribosomal proteins. It contains a C4-type zinc finger domain that can bind to zinc. The encoded protein has been shown to be able to bind to nucleic acid. It is located in the cytoplasm as a ribosomal component, but it has also been detected in the nucleus. Studies in rat indicate that ribosomal pro ...
... ribosomal proteins. It contains a C4-type zinc finger domain that can bind to zinc. The encoded protein has been shown to be able to bind to nucleic acid. It is located in the cytoplasm as a ribosomal component, but it has also been detected in the nucleus. Studies in rat indicate that ribosomal pro ...
Ch.5
... (acidic proteins have pI < 7) If pH < pI, the protein is positively charged (basic proteins have pI > 7) ...
... (acidic proteins have pI < 7) If pH < pI, the protein is positively charged (basic proteins have pI > 7) ...
Basic organic chemistry of important macromolecules (Lecture 11-12)
... As a cell prepares to divide, the two strands of the double helix separate, and each serves as a template for the precise ordering of nucleotides into new complementary strands. Ribonucleic acid (RNA) Ribonucleic acid has three distinct roles in protein synthesis: -messenger RNA (mRNA) carries the i ...
... As a cell prepares to divide, the two strands of the double helix separate, and each serves as a template for the precise ordering of nucleotides into new complementary strands. Ribonucleic acid (RNA) Ribonucleic acid has three distinct roles in protein synthesis: -messenger RNA (mRNA) carries the i ...
presentation
... classes across these criteria. We are proving some hypothesis that can all improve several types of prediction algorithms. ...
... classes across these criteria. We are proving some hypothesis that can all improve several types of prediction algorithms. ...
CHE-3H84 14-15 exam FINAL
... mg of a highly purified recombinant engineered IgG antibody light chain (rIgG-L). rIgG-L has a molecular weight of 25 kDa, a pI of 8.0 and has neither cofactors nor disulfide bridges. An inducible vector, pIgG-L, is available for overexpression of rIgGL in the cytoplasm of Escherichia coli. Note tha ...
... mg of a highly purified recombinant engineered IgG antibody light chain (rIgG-L). rIgG-L has a molecular weight of 25 kDa, a pI of 8.0 and has neither cofactors nor disulfide bridges. An inducible vector, pIgG-L, is available for overexpression of rIgGL in the cytoplasm of Escherichia coli. Note tha ...
H 2 O - cloudfront.net
... – “S” – storage: This type of proteins are found in seeds and eggs. Provides a source of amino acids for developing plants and animals. – “S” – signal: This type of proteins are responsible for cell communication. Includes insulin & other hormones – “C” – contractile: found mostly in muscle; Respons ...
... – “S” – storage: This type of proteins are found in seeds and eggs. Provides a source of amino acids for developing plants and animals. – “S” – signal: This type of proteins are responsible for cell communication. Includes insulin & other hormones – “C” – contractile: found mostly in muscle; Respons ...
Table of Contents - Arizona Science Center
... When we eat animal or vegetable protein, our body breaks down the protein back into amino acids. Once digested, the amino acids are then put back together to create new and different proteins the body needs to function. You can think of the amino acids as beads on a bracelet. You could take the brac ...
... When we eat animal or vegetable protein, our body breaks down the protein back into amino acids. Once digested, the amino acids are then put back together to create new and different proteins the body needs to function. You can think of the amino acids as beads on a bracelet. You could take the brac ...
Protein

Proteins (/ˈproʊˌtiːnz/ or /ˈproʊti.ɨnz/) are large biomolecules, or macromolecules, consisting of one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within living organisms, including catalyzing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, responding to stimuli, and transporting molecules from one location to another. Proteins differ from one another primarily in their sequence of amino acids, which is dictated by the nucleotide sequence of their genes, and which usually results in protein folding into a specific three-dimensional structure that determines its activity.A linear chain of amino acid residues is called a polypeptide. A protein contains at least one long polypeptide. Short polypeptides, containing less than about 20-30 residues, are rarely considered to be proteins and are commonly called peptides, or sometimes oligopeptides. The individual amino acid residues are bonded together by peptide bonds and adjacent amino acid residues. The sequence of amino acid residues in a protein is defined by the sequence of a gene, which is encoded in the genetic code. In general, the genetic code specifies 20 standard amino acids; however, in certain organisms the genetic code can include selenocysteine and—in certain archaea—pyrrolysine. Shortly after or even during synthesis, the residues in a protein are often chemically modified by posttranslational modification, which alters the physical and chemical properties, folding, stability, activity, and ultimately, the function of the proteins. Sometimes proteins have non-peptide groups attached, which can be called prosthetic groups or cofactors. Proteins can also work together to achieve a particular function, and they often associate to form stable protein complexes.Once formed, proteins only exist for a certain period of time and are then degraded and recycled by the cell's machinery through the process of protein turnover. A protein's lifespan is measured in terms of its half-life and covers a wide range. They can exist for minutes or years with an average lifespan of 1–2 days in mammalian cells. Abnormal and or misfolded proteins are degraded more rapidly either due to being targeted for destruction or due to being unstable.Like other biological macromolecules such as polysaccharides and nucleic acids, proteins are essential parts of organisms and participate in virtually every process within cells. Many proteins are enzymes that catalyze biochemical reactions and are vital to metabolism. Proteins also have structural or mechanical functions, such as actin and myosin in muscle and the proteins in the cytoskeleton, which form a system of scaffolding that maintains cell shape. Other proteins are important in cell signaling, immune responses, cell adhesion, and the cell cycle. Proteins are also necessary in animals' diets, since animals cannot synthesize all the amino acids they need and must obtain essential amino acids from food. Through the process of digestion, animals break down ingested protein into free amino acids that are then used in metabolism.Proteins may be purified from other cellular components using a variety of techniques such as ultracentrifugation, precipitation, electrophoresis, and chromatography; the advent of genetic engineering has made possible a number of methods to facilitate purification. Methods commonly used to study protein structure and function include immunohistochemistry, site-directed mutagenesis, X-ray crystallography, nuclear magnetic resonance and mass spectrometry.