Biology 12 - Biologically Important Molecules – Review Worksheet
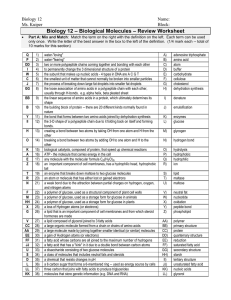
... water-"loving" water-"fearing" two or more polypeptide chains coming together and bonding with each other to permanently change the 3 dimensional structure of a protein the subunit that makes up nucleic acids - 4 types in DNA are A C G T the smallest unit of matter that cannot normally be broken int ...
... water-"loving" water-"fearing" two or more polypeptide chains coming together and bonding with each other to permanently change the 3 dimensional structure of a protein the subunit that makes up nucleic acids - 4 types in DNA are A C G T the smallest unit of matter that cannot normally be broken int ...
Company Introduction Product Home
... C Coom mppaannyy IInnttrroodduuccttiioonn The Taiwan Amino Acid Co. Ltd. collaborates with Japan and is a professional manufacturer that has made amino acids for over 30 years. Our products have wide applications in food, medicine, cosmetics, feeds and fertilizer-breakdown superior protein. The puri ...
... C Coom mppaannyy IInnttrroodduuccttiioonn The Taiwan Amino Acid Co. Ltd. collaborates with Japan and is a professional manufacturer that has made amino acids for over 30 years. Our products have wide applications in food, medicine, cosmetics, feeds and fertilizer-breakdown superior protein. The puri ...
Media - Inside Cancer
... a phosphate group. The source of the phosphate group is ATP. Kinases serve as relay molecules in the cell signaling pathway. Once activated, they activate other proteins, hence transmitting the message through the cell. 2. Since all cell signaling pathways end with a cellular response, explain why i ...
... a phosphate group. The source of the phosphate group is ATP. Kinases serve as relay molecules in the cell signaling pathway. Once activated, they activate other proteins, hence transmitting the message through the cell. 2. Since all cell signaling pathways end with a cellular response, explain why i ...
2.3: Carbon-Based Molecules
... • Energy-releasing enzymes power cell functions • Enzymes in nerve cells produce neurotransmitters to carry impulses from nerves to muscles • Muscle cells have enzymes that are triggered in response to the neurotransmitters ...
... • Energy-releasing enzymes power cell functions • Enzymes in nerve cells produce neurotransmitters to carry impulses from nerves to muscles • Muscle cells have enzymes that are triggered in response to the neurotransmitters ...
Chem*3560 Lecture 24: Membrane proteins
... Integral membrane proteins are physically embedded in the bilayer, and are only released by use of detergents that totally disrupt the bilayer organization. Detergents are micelle forming molecules, and the integral membrane protein is released, but in a form embedded in a detergent micelle. Integra ...
... Integral membrane proteins are physically embedded in the bilayer, and are only released by use of detergents that totally disrupt the bilayer organization. Detergents are micelle forming molecules, and the integral membrane protein is released, but in a form embedded in a detergent micelle. Integra ...
File
... 2.Which parts of amino acids are involved in peptide bonds? A. The carboxyl group on one amino acid and the side chain on the other B. The carboxyl group on both amino acids C. The amino group on one amino acid and the carboxyl group on the other D. The amino group on both amino acids ...
... 2.Which parts of amino acids are involved in peptide bonds? A. The carboxyl group on one amino acid and the side chain on the other B. The carboxyl group on both amino acids C. The amino group on one amino acid and the carboxyl group on the other D. The amino group on both amino acids ...
Biochemistry Notes Powerpoint presentation
... will affect the rate of reaction of the enzyme catalase. Independent variable: Temperature, pH, Amount of enzyme, amount of substrate. Dependent variable: the way you measure the rate of reaction. Can be: 1. The time it takes for the disk to rise in the beaker 2. The amount of time the disk continue ...
... will affect the rate of reaction of the enzyme catalase. Independent variable: Temperature, pH, Amount of enzyme, amount of substrate. Dependent variable: the way you measure the rate of reaction. Can be: 1. The time it takes for the disk to rise in the beaker 2. The amount of time the disk continue ...
Dejardin
... Protein Analysis - SDS-PAGE and Western Blot Nucleic Acid Analysis - Library Prep and Sequencing (ChIP-Seq) Allows for stringent capture and purification Not sensitive to ionic detergents Reduces non-specific binding of proteins ...
... Protein Analysis - SDS-PAGE and Western Blot Nucleic Acid Analysis - Library Prep and Sequencing (ChIP-Seq) Allows for stringent capture and purification Not sensitive to ionic detergents Reduces non-specific binding of proteins ...
here
... paralogs and their distribution in genomes provides clues on the way genomes evolved. Gen and genome duplication have emerged as the most important pathway to molecular innovation, including the evolution of developmental pathways. Xenologs: gene was obtained by organism through horizontal transfer. ...
... paralogs and their distribution in genomes provides clues on the way genomes evolved. Gen and genome duplication have emerged as the most important pathway to molecular innovation, including the evolution of developmental pathways. Xenologs: gene was obtained by organism through horizontal transfer. ...
Chapter 3: Organic Molecules
... Carbon is the central atom in all organic molecules. Can bond to one another, creating long chains or rings. Carbon likes to have ______ covalent bonds. When several carbon are present, they form the backbone to which other elements or molecules attach. ...
... Carbon is the central atom in all organic molecules. Can bond to one another, creating long chains or rings. Carbon likes to have ______ covalent bonds. When several carbon are present, they form the backbone to which other elements or molecules attach. ...
PPT
... • The matrix is searched against the appropriate genome database TRVI search allowing for gaps and substitutions: • A motif is developed by allowing for a flexible number of gaps wherever there are gaps in the alignment • Substitutions of amino acids with similar properties are allowed • The motif i ...
... • The matrix is searched against the appropriate genome database TRVI search allowing for gaps and substitutions: • A motif is developed by allowing for a flexible number of gaps wherever there are gaps in the alignment • Substitutions of amino acids with similar properties are allowed • The motif i ...
Protein: On the Scene
... Scientists have found 20 different amino acids in protein, and these 20 amino acids can combine in lots of ways - in fact, they have joined together to make thousands of different proteins! Some types of amino acids are made by you, right inside your body, without you ever thinking about it or doing ...
... Scientists have found 20 different amino acids in protein, and these 20 amino acids can combine in lots of ways - in fact, they have joined together to make thousands of different proteins! Some types of amino acids are made by you, right inside your body, without you ever thinking about it or doing ...
* Abundant! * Able to share 4 outer valence electrons! * Versatile
... • Organic compounds are critical to the structure and function of all living things. • There are 4 main categories (classes/groups) of organic compounds they are all polymers (very large structures); 1) Carbohydrates 2) Proteins 3) Nucleic Acids 4) Lipids • All of these (1-4) will be made out of dif ...
... • Organic compounds are critical to the structure and function of all living things. • There are 4 main categories (classes/groups) of organic compounds they are all polymers (very large structures); 1) Carbohydrates 2) Proteins 3) Nucleic Acids 4) Lipids • All of these (1-4) will be made out of dif ...
BBA IInd SEMESTER EXAMINATION 2008-09
... Answer any five of the following (limit your answer to 50 words). (4x5=20) Write about ketonic hydrolysis of acetoacetic ester. On basis of which two chemical properties Malonic ester is used as a synthetic reagent? Draw structure of Guanine. Define frie’s reaction. Define Witting reaction. Which na ...
... Answer any five of the following (limit your answer to 50 words). (4x5=20) Write about ketonic hydrolysis of acetoacetic ester. On basis of which two chemical properties Malonic ester is used as a synthetic reagent? Draw structure of Guanine. Define frie’s reaction. Define Witting reaction. Which na ...
Protein

Proteins (/ˈproʊˌtiːnz/ or /ˈproʊti.ɨnz/) are large biomolecules, or macromolecules, consisting of one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within living organisms, including catalyzing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, responding to stimuli, and transporting molecules from one location to another. Proteins differ from one another primarily in their sequence of amino acids, which is dictated by the nucleotide sequence of their genes, and which usually results in protein folding into a specific three-dimensional structure that determines its activity.A linear chain of amino acid residues is called a polypeptide. A protein contains at least one long polypeptide. Short polypeptides, containing less than about 20-30 residues, are rarely considered to be proteins and are commonly called peptides, or sometimes oligopeptides. The individual amino acid residues are bonded together by peptide bonds and adjacent amino acid residues. The sequence of amino acid residues in a protein is defined by the sequence of a gene, which is encoded in the genetic code. In general, the genetic code specifies 20 standard amino acids; however, in certain organisms the genetic code can include selenocysteine and—in certain archaea—pyrrolysine. Shortly after or even during synthesis, the residues in a protein are often chemically modified by posttranslational modification, which alters the physical and chemical properties, folding, stability, activity, and ultimately, the function of the proteins. Sometimes proteins have non-peptide groups attached, which can be called prosthetic groups or cofactors. Proteins can also work together to achieve a particular function, and they often associate to form stable protein complexes.Once formed, proteins only exist for a certain period of time and are then degraded and recycled by the cell's machinery through the process of protein turnover. A protein's lifespan is measured in terms of its half-life and covers a wide range. They can exist for minutes or years with an average lifespan of 1–2 days in mammalian cells. Abnormal and or misfolded proteins are degraded more rapidly either due to being targeted for destruction or due to being unstable.Like other biological macromolecules such as polysaccharides and nucleic acids, proteins are essential parts of organisms and participate in virtually every process within cells. Many proteins are enzymes that catalyze biochemical reactions and are vital to metabolism. Proteins also have structural or mechanical functions, such as actin and myosin in muscle and the proteins in the cytoskeleton, which form a system of scaffolding that maintains cell shape. Other proteins are important in cell signaling, immune responses, cell adhesion, and the cell cycle. Proteins are also necessary in animals' diets, since animals cannot synthesize all the amino acids they need and must obtain essential amino acids from food. Through the process of digestion, animals break down ingested protein into free amino acids that are then used in metabolism.Proteins may be purified from other cellular components using a variety of techniques such as ultracentrifugation, precipitation, electrophoresis, and chromatography; the advent of genetic engineering has made possible a number of methods to facilitate purification. Methods commonly used to study protein structure and function include immunohistochemistry, site-directed mutagenesis, X-ray crystallography, nuclear magnetic resonance and mass spectrometry.























