Changes In Protein Sequences Of the HIV-1 gp120
... • The V3 region of the gp 120 env protein is a variable loop with a high mutation rate. • V3 is what binds to the CD4 receptor sites on cell. • The amino acid sequence determines how the V3 region will function. – And therefore, how the CD4 will interact ...
... • The V3 region of the gp 120 env protein is a variable loop with a high mutation rate. • V3 is what binds to the CD4 receptor sites on cell. • The amino acid sequence determines how the V3 region will function. – And therefore, how the CD4 will interact ...
BCM 6200 - Purification des proteines membranaires
... Lipidic cubic phase (LCP) is one of many liquid crystalline phases that form spontaneously upon mixing lipids with water at proper conditions. The protein is mixed with Monoolein and other lipid additives in tightly coupled syringes. Drops are laid down on a glass slide and precipitation solutions a ...
... Lipidic cubic phase (LCP) is one of many liquid crystalline phases that form spontaneously upon mixing lipids with water at proper conditions. The protein is mixed with Monoolein and other lipid additives in tightly coupled syringes. Drops are laid down on a glass slide and precipitation solutions a ...
Protein /amino acids deficiency causes
... Approximately 40% of rumen bacterials have proteolityc activity ...
... Approximately 40% of rumen bacterials have proteolityc activity ...
1 INTRODUCTION TO PROTEIN STRUCTURE AND MODELING I
... zig-zag sheet. In both cases, the secondary structure is stabilized by several hydrogen bonds; while these are much weaker than covalent bonds, several of them in one region can provide significant stability. The Alpha Helix and Beta Sheet Construction Kits allow you to model these two secondary str ...
... zig-zag sheet. In both cases, the secondary structure is stabilized by several hydrogen bonds; while these are much weaker than covalent bonds, several of them in one region can provide significant stability. The Alpha Helix and Beta Sheet Construction Kits allow you to model these two secondary str ...
Chapter 6: An Introduction to Proteins
... much more of the dissolved oxygen will bind to myoglobin than to hemoglobin. hemoglobin subunits will dissociate. hemoglobin will reach nearly 100% saturation with oxygen while myoglobin will remain essentially as deoxymyoglobin. ...
... much more of the dissolved oxygen will bind to myoglobin than to hemoglobin. hemoglobin subunits will dissociate. hemoglobin will reach nearly 100% saturation with oxygen while myoglobin will remain essentially as deoxymyoglobin. ...
Macromolecules - Haiku Learning
... Our bodies are amazing machines capable of breaking down and building up complex molecules required for life. Since these molecules are microscopic, it is easier to understand how they are built using models. In this part of the activity, your team will be modeling dehydration and hydrolysis reactio ...
... Our bodies are amazing machines capable of breaking down and building up complex molecules required for life. Since these molecules are microscopic, it is easier to understand how they are built using models. In this part of the activity, your team will be modeling dehydration and hydrolysis reactio ...
Protein Synthesis - Overview
... protein travels through the ER to the Golgi. The Golgi modifies the structure and packages it into a vesicle. Vesicle moves to the membrane and is released by exocytosis. ...
... protein travels through the ER to the Golgi. The Golgi modifies the structure and packages it into a vesicle. Vesicle moves to the membrane and is released by exocytosis. ...
ch 6 review key 3 26
... Answer: FALSE 2) Plant proteins may be less digestible, especially when eaten raw. Answer: TRUE 3) Hemoglobin acts as a transport protein that carries nitrogen to cells from the lungs. Answer: FALSE 4) Whole-wheat bread contains complete proteins. Answer: FALSE 5) Proteins within the body help to ma ...
... Answer: FALSE 2) Plant proteins may be less digestible, especially when eaten raw. Answer: TRUE 3) Hemoglobin acts as a transport protein that carries nitrogen to cells from the lungs. Answer: FALSE 4) Whole-wheat bread contains complete proteins. Answer: FALSE 5) Proteins within the body help to ma ...
testing for organic macromolecules
... fatty acid "tails" are long chains of carbon and hydrogen that contribute to the non-polar behavior of fats - they don't mix with (polar) water. The fatty acid chains can be saturated, with all carbons saturated with hydrogen atoms forming a straight chain without double bonds. Unsaturated fatty ac ...
... fatty acid "tails" are long chains of carbon and hydrogen that contribute to the non-polar behavior of fats - they don't mix with (polar) water. The fatty acid chains can be saturated, with all carbons saturated with hydrogen atoms forming a straight chain without double bonds. Unsaturated fatty ac ...
ch 6 review key 4 2
... Answer: FALSE 2) Plant proteins may be less digestible, especially when eaten raw. Answer: TRUE 3) Hemoglobin acts as a transport protein that carries nitrogen to cells from the lungs. Answer: FALSE 4) Whole-wheat bread contains complete proteins.Answer: FALSE 5) Proteins within the body help to mai ...
... Answer: FALSE 2) Plant proteins may be less digestible, especially when eaten raw. Answer: TRUE 3) Hemoglobin acts as a transport protein that carries nitrogen to cells from the lungs. Answer: FALSE 4) Whole-wheat bread contains complete proteins.Answer: FALSE 5) Proteins within the body help to mai ...
PowerPoint プレゼンテーション
... layer of human and animal skin) carrying out a variety of biological functions: enzymatic catalysis, transportation, immune response, hormones, storage, control of genetic transcription made up of 20 different kinds of amino acids linked together in a long string ...
... layer of human and animal skin) carrying out a variety of biological functions: enzymatic catalysis, transportation, immune response, hormones, storage, control of genetic transcription made up of 20 different kinds of amino acids linked together in a long string ...
Protein
... be eaten together to count as a complete protein source? NO. In the past, it was thought that these complementary proteins needed to be eaten at the same meal for your body to use them together. Now studies show that your body can combine complementary proteins that are eaten within the ...
... be eaten together to count as a complete protein source? NO. In the past, it was thought that these complementary proteins needed to be eaten at the same meal for your body to use them together. Now studies show that your body can combine complementary proteins that are eaten within the ...
F8676 - Datasheet - Sigma
... precursor protein with two alternative (21 amino acid or 24 amino acid residues) putative signal peptides, a 76 amino acid residue globular chemokine domain, a 238 amino acid residue stalk region (rich in Gly, Pro, Ser, and Thr and containing degenerate mucin-like repeats), a 19 amino acid residue t ...
... precursor protein with two alternative (21 amino acid or 24 amino acid residues) putative signal peptides, a 76 amino acid residue globular chemokine domain, a 238 amino acid residue stalk region (rich in Gly, Pro, Ser, and Thr and containing degenerate mucin-like repeats), a 19 amino acid residue t ...
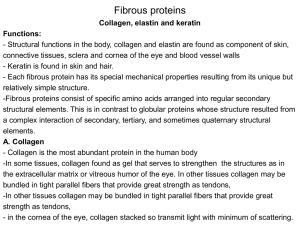
A. Collagen
... - Structural functions in the body, collagen and elastin are found as component of skin, connective tissues, sclera and cornea of the eye and blood vessel walls - Keratin is found in skin and hair. - Each fibrous protein has its special mechanical properties resulting from its unique but relatively ...
... - Structural functions in the body, collagen and elastin are found as component of skin, connective tissues, sclera and cornea of the eye and blood vessel walls - Keratin is found in skin and hair. - Each fibrous protein has its special mechanical properties resulting from its unique but relatively ...
Biomolecules - Mercer Island School District
... get the energy they need. •Complex carbs need to be ___________________to be absorbed and used. The slow breakdown allow organisms to ___________________ use energy since it is stored in a large structure. (like the Bank) •Plants use ___________________ for their cell wall which provides structure a ...
... get the energy they need. •Complex carbs need to be ___________________to be absorbed and used. The slow breakdown allow organisms to ___________________ use energy since it is stored in a large structure. (like the Bank) •Plants use ___________________ for their cell wall which provides structure a ...
BMT 242 Immunology
... Protein structure of immunoglobulins • Early amino acid sequence experiments were unsuccessful—too much variation • Multiple myeloma serum is 95% same antibody • Bence-jones protein found in urine of myeloma patients is excess light chain • 110 amino acids highly variable, rest are quite constant • ...
... Protein structure of immunoglobulins • Early amino acid sequence experiments were unsuccessful—too much variation • Multiple myeloma serum is 95% same antibody • Bence-jones protein found in urine of myeloma patients is excess light chain • 110 amino acids highly variable, rest are quite constant • ...
STUDY GUIDE
... carbohydrates, peptide bond, amino acids, glycerol, disaccharide, fatty acids, proteins, unsaturated, organic compounds, oxygen, polymerization, carbon, lipids, saturated) Living organisms are composed of a special category of molecules called ______________________. Molecules must have both _______ ...
... carbohydrates, peptide bond, amino acids, glycerol, disaccharide, fatty acids, proteins, unsaturated, organic compounds, oxygen, polymerization, carbon, lipids, saturated) Living organisms are composed of a special category of molecules called ______________________. Molecules must have both _______ ...
ORGANELLE-SPECIFIC PROTEIN QUALITY CONTROL SYSTEMS
... conjunction with post-translational modifications, e.g., signal peptide cleavage, disulfide bond formation, and N-linked glycosylation. In this respect, the ER plays a crucial role in the PQC, regulating the transport of proteins from the ER to the Golgi apparatus, as only proteins that have attaine ...
... conjunction with post-translational modifications, e.g., signal peptide cleavage, disulfide bond formation, and N-linked glycosylation. In this respect, the ER plays a crucial role in the PQC, regulating the transport of proteins from the ER to the Golgi apparatus, as only proteins that have attaine ...
COMPARATIVE MODELING AND MOLECULAR
... The Aspartyl-tRNA synthetase (AspRS) belonging to the ligase family of enzymes has an important role not only in the protein fidelity by specifically recognizing its cognate amino acid but also in the aminoacylation of tRNAAsp. Several crystal structures of AspRS have been determined. None of these ...
... The Aspartyl-tRNA synthetase (AspRS) belonging to the ligase family of enzymes has an important role not only in the protein fidelity by specifically recognizing its cognate amino acid but also in the aminoacylation of tRNAAsp. Several crystal structures of AspRS have been determined. None of these ...
CHAPTER 3 THE CHEMISTRY OF ORGANIC MOLECULES
... are also made of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen, though not in the same fixed ratio. Fats and oils, also called triglycerides, allow long-term energy storage and are formed from the dehydration reaction between one glycerol and three fatty acids. Both glycerol and fatty acids have polar groups, but fa ...
... are also made of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen, though not in the same fixed ratio. Fats and oils, also called triglycerides, allow long-term energy storage and are formed from the dehydration reaction between one glycerol and three fatty acids. Both glycerol and fatty acids have polar groups, but fa ...
Protein

Proteins (/ˈproʊˌtiːnz/ or /ˈproʊti.ɨnz/) are large biomolecules, or macromolecules, consisting of one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within living organisms, including catalyzing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, responding to stimuli, and transporting molecules from one location to another. Proteins differ from one another primarily in their sequence of amino acids, which is dictated by the nucleotide sequence of their genes, and which usually results in protein folding into a specific three-dimensional structure that determines its activity.A linear chain of amino acid residues is called a polypeptide. A protein contains at least one long polypeptide. Short polypeptides, containing less than about 20-30 residues, are rarely considered to be proteins and are commonly called peptides, or sometimes oligopeptides. The individual amino acid residues are bonded together by peptide bonds and adjacent amino acid residues. The sequence of amino acid residues in a protein is defined by the sequence of a gene, which is encoded in the genetic code. In general, the genetic code specifies 20 standard amino acids; however, in certain organisms the genetic code can include selenocysteine and—in certain archaea—pyrrolysine. Shortly after or even during synthesis, the residues in a protein are often chemically modified by posttranslational modification, which alters the physical and chemical properties, folding, stability, activity, and ultimately, the function of the proteins. Sometimes proteins have non-peptide groups attached, which can be called prosthetic groups or cofactors. Proteins can also work together to achieve a particular function, and they often associate to form stable protein complexes.Once formed, proteins only exist for a certain period of time and are then degraded and recycled by the cell's machinery through the process of protein turnover. A protein's lifespan is measured in terms of its half-life and covers a wide range. They can exist for minutes or years with an average lifespan of 1–2 days in mammalian cells. Abnormal and or misfolded proteins are degraded more rapidly either due to being targeted for destruction or due to being unstable.Like other biological macromolecules such as polysaccharides and nucleic acids, proteins are essential parts of organisms and participate in virtually every process within cells. Many proteins are enzymes that catalyze biochemical reactions and are vital to metabolism. Proteins also have structural or mechanical functions, such as actin and myosin in muscle and the proteins in the cytoskeleton, which form a system of scaffolding that maintains cell shape. Other proteins are important in cell signaling, immune responses, cell adhesion, and the cell cycle. Proteins are also necessary in animals' diets, since animals cannot synthesize all the amino acids they need and must obtain essential amino acids from food. Through the process of digestion, animals break down ingested protein into free amino acids that are then used in metabolism.Proteins may be purified from other cellular components using a variety of techniques such as ultracentrifugation, precipitation, electrophoresis, and chromatography; the advent of genetic engineering has made possible a number of methods to facilitate purification. Methods commonly used to study protein structure and function include immunohistochemistry, site-directed mutagenesis, X-ray crystallography, nuclear magnetic resonance and mass spectrometry.