Lecture Notes
... • Three-dimensional arrangement of amino acids with the polypeptide chain in a corkscrew shape • Held by __________ between the H of –N-H group and the –O of C=O of the fourth amino acid along the chain • Looks like a coiled “telephone cord” ...
... • Three-dimensional arrangement of amino acids with the polypeptide chain in a corkscrew shape • Held by __________ between the H of –N-H group and the –O of C=O of the fourth amino acid along the chain • Looks like a coiled “telephone cord” ...
Translation - Fog.ccsf.edu
... Peptide bonds – between the carboxyl group at the end of growing chain and a free amino group of incoming amino acid Proteins are synthesized from its Nterminus to its C-terminus ...
... Peptide bonds – between the carboxyl group at the end of growing chain and a free amino group of incoming amino acid Proteins are synthesized from its Nterminus to its C-terminus ...
Wade Chapter Twenty-Four Outline: Amino Acids and Peptides
... o Add second N-protected amino acid via C-terminus ...
... o Add second N-protected amino acid via C-terminus ...
DYMATIZE
... derived from cross-flow microfiltration processing (cold-filtered) to preserve the many important whey protein fractions including lactoferrin and immunoglobins, which can be lost in other forms of processing. We have carefully formulated ISO•100 to deliver more of what you want, and less of what yo ...
... derived from cross-flow microfiltration processing (cold-filtered) to preserve the many important whey protein fractions including lactoferrin and immunoglobins, which can be lost in other forms of processing. We have carefully formulated ISO•100 to deliver more of what you want, and less of what yo ...
Zinc Finger Folding Activity
... beta sheet. The structure of the zinc finger is stabilized by a zinc atom that binds 2 cysteine and 2 histidine sidechains, and by hydrophobic amino acid sidechains that are buried on the inside of the folded motif. Zinc finger proteins function as regulators of gene expression. They bind to the neg ...
... beta sheet. The structure of the zinc finger is stabilized by a zinc atom that binds 2 cysteine and 2 histidine sidechains, and by hydrophobic amino acid sidechains that are buried on the inside of the folded motif. Zinc finger proteins function as regulators of gene expression. They bind to the neg ...
realburn
... The kinetics of protein denaturation is affected by so many different factors: density, solvent, bond strengths, interactions with surrounding molecules. ...
... The kinetics of protein denaturation is affected by so many different factors: density, solvent, bond strengths, interactions with surrounding molecules. ...
Unit 1.1 Building Blocks of Life The student knows the significance of
... I can explain the function of carbohydrates in a cell I can explain the function of proteins in a cell I can explain the function of lipids in a cell I can explain the function of nucleic acids in a cell Given a graphic of structures, I can determine what biomolecule is present biomolecule, carbohyd ...
... I can explain the function of carbohydrates in a cell I can explain the function of proteins in a cell I can explain the function of lipids in a cell I can explain the function of nucleic acids in a cell Given a graphic of structures, I can determine what biomolecule is present biomolecule, carbohyd ...
Chap. 4. "Proteins: Three-Dimensional Structure and Function
... function of a protein. O2 binds to an Fe2+ ion located in the center of the heme group. The heme group is located within an hydrophobic cleft in myoglobin and in each type of hemoglobin chain. Two histidines in the polypeptides interact with the heme iron. When O2 is bound to the heme, both proteins ...
... function of a protein. O2 binds to an Fe2+ ion located in the center of the heme group. The heme group is located within an hydrophobic cleft in myoglobin and in each type of hemoglobin chain. Two histidines in the polypeptides interact with the heme iron. When O2 is bound to the heme, both proteins ...
Purified Mouse Anti-p115 — 612260
... Maturation and post translational modification of proteins occurs after their biosynthesis at the endoplasmic reticulum and their transport through the Golgi apparatus. The process involves the transport of vesicles carrying the proteins through a vectorial process of vesicle budding and fusion from ...
... Maturation and post translational modification of proteins occurs after their biosynthesis at the endoplasmic reticulum and their transport through the Golgi apparatus. The process involves the transport of vesicles carrying the proteins through a vectorial process of vesicle budding and fusion from ...
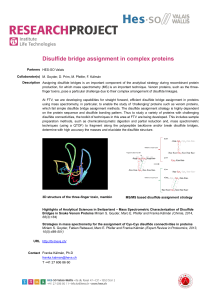
Disulfide bridge assignment in complex proteins - HES
... Description Assigning disulfide bridges is an important component of the analytical strategy during recombinant protein production, for which mass spectrometry (MS) is an important technique. Venom proteins, such as the threefinger toxins, pose a particular challenge due to their complex arrangement ...
... Description Assigning disulfide bridges is an important component of the analytical strategy during recombinant protein production, for which mass spectrometry (MS) is an important technique. Venom proteins, such as the threefinger toxins, pose a particular challenge due to their complex arrangement ...
No Slide Title
... fusions to investigate the topology of a “fictional” membrane protein we have named, BADH, which we discovered recently from an “unique” bacterium known as B. anseli. Our new protein, like the E. coli Tsr protein, seems to be involved in chemotaxis as a chemoreceptor and so we hypothesize that it ma ...
... fusions to investigate the topology of a “fictional” membrane protein we have named, BADH, which we discovered recently from an “unique” bacterium known as B. anseli. Our new protein, like the E. coli Tsr protein, seems to be involved in chemotaxis as a chemoreceptor and so we hypothesize that it ma ...
Chapter 3 - Cell Protein Production
... molecules with the matching anticodon are brought in • The amino acids carried by the tRNA are joined together so the protein is assembled with the amino acids in the correct sequence © 2010 McGraw-Hill Australia ...
... molecules with the matching anticodon are brought in • The amino acids carried by the tRNA are joined together so the protein is assembled with the amino acids in the correct sequence © 2010 McGraw-Hill Australia ...
Taylor_Sheridan_Biochemwebquest
... I think that the Shape of a protein molecule is complex because it has side chains and is made up of four diffrent elements, the structure of the molecule is also very complex to me. 3. 3. Which of the following occurs to form a protein? (circle the correct answer) A) forms a chain of amino acids B) ...
... I think that the Shape of a protein molecule is complex because it has side chains and is made up of four diffrent elements, the structure of the molecule is also very complex to me. 3. 3. Which of the following occurs to form a protein? (circle the correct answer) A) forms a chain of amino acids B) ...
PDF 52.16 KB
... In 2003, the Peltre –Thormann report commissioned by the World Anti-Doping Agency identified specific issues to address in order to improve the one-dimensional isoelectric focusing electrophoresis method currently being used for identifying drug doping with recombinant erythropoietin (rHuEPO). The n ...
... In 2003, the Peltre –Thormann report commissioned by the World Anti-Doping Agency identified specific issues to address in order to improve the one-dimensional isoelectric focusing electrophoresis method currently being used for identifying drug doping with recombinant erythropoietin (rHuEPO). The n ...
Assignment: Amino Acids, Peptides, and Proteins
... capable of hydrogen bonding, and easily interact with water. The OH present enables them to participate in hydrogen bonding. Asparagine and glutamine are Amide (NH2) derivative of the acidic amino acids. Amide functional group of the acidic amino acids make the amino acid is highly polar. Examples o ...
... capable of hydrogen bonding, and easily interact with water. The OH present enables them to participate in hydrogen bonding. Asparagine and glutamine are Amide (NH2) derivative of the acidic amino acids. Amide functional group of the acidic amino acids make the amino acid is highly polar. Examples o ...
Signal sequence
... • Large protein complexes spanning both membranes • Pathogenic bacteria use type III for protein secretion and injection • Agrobacterium tumefaciens (膿桿菌) use type IV to transport T-DNA into plant cells. ...
... • Large protein complexes spanning both membranes • Pathogenic bacteria use type III for protein secretion and injection • Agrobacterium tumefaciens (膿桿菌) use type IV to transport T-DNA into plant cells. ...
binding to negatively curved membranes
... Affinity for curvature = induces curvature ‘BAR domains as sensors or membrane curvature’ ...
... Affinity for curvature = induces curvature ‘BAR domains as sensors or membrane curvature’ ...
View PDF
... Editorial: RNA and Protein Mutations Lead to New Functional Chemosensory Protein It is just the way imposed by the genetic code in the deep inner core of tissue cells in all organisms. A series of defined triplets in the DNA encodes for a precise combination of amino acids at the protein level. ATGG ...
... Editorial: RNA and Protein Mutations Lead to New Functional Chemosensory Protein It is just the way imposed by the genetic code in the deep inner core of tissue cells in all organisms. A series of defined triplets in the DNA encodes for a precise combination of amino acids at the protein level. ATGG ...
Poster
... Many proteins are misfolded and dysfunctional when first formed. Chaperone proteins are used to refold, protect and disaggregate misshapen proteins. While chaperones are traditionally beneficial, it has been recently found they play a role in the formation of infectious protein aggregates. These inf ...
... Many proteins are misfolded and dysfunctional when first formed. Chaperone proteins are used to refold, protect and disaggregate misshapen proteins. While chaperones are traditionally beneficial, it has been recently found they play a role in the formation of infectious protein aggregates. These inf ...
Chapter 3 Cell Structure and Function 2013
... • Forms long fibers of chromatin that make up chromosomes • Human body cell has 46 chromosomes • Nucleus is large, membrane-bound structure • Consists of nucleoplasm and surrounded by double membrane nuclear envelope • Pores in the envelope control flow of materials in and out ...
... • Forms long fibers of chromatin that make up chromosomes • Human body cell has 46 chromosomes • Nucleus is large, membrane-bound structure • Consists of nucleoplasm and surrounded by double membrane nuclear envelope • Pores in the envelope control flow of materials in and out ...
Structure and Function of Macromolecules
... Proteins are very large molecules composed of combinations of about 20 different amino acids. The precise physical shape of a protein is very important for its function. A single cell may have 10,000 or more different proteins. This diversity of proteins is essential for the functioning of each cell ...
... Proteins are very large molecules composed of combinations of about 20 different amino acids. The precise physical shape of a protein is very important for its function. A single cell may have 10,000 or more different proteins. This diversity of proteins is essential for the functioning of each cell ...
Protein

Proteins (/ˈproʊˌtiːnz/ or /ˈproʊti.ɨnz/) are large biomolecules, or macromolecules, consisting of one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within living organisms, including catalyzing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, responding to stimuli, and transporting molecules from one location to another. Proteins differ from one another primarily in their sequence of amino acids, which is dictated by the nucleotide sequence of their genes, and which usually results in protein folding into a specific three-dimensional structure that determines its activity.A linear chain of amino acid residues is called a polypeptide. A protein contains at least one long polypeptide. Short polypeptides, containing less than about 20-30 residues, are rarely considered to be proteins and are commonly called peptides, or sometimes oligopeptides. The individual amino acid residues are bonded together by peptide bonds and adjacent amino acid residues. The sequence of amino acid residues in a protein is defined by the sequence of a gene, which is encoded in the genetic code. In general, the genetic code specifies 20 standard amino acids; however, in certain organisms the genetic code can include selenocysteine and—in certain archaea—pyrrolysine. Shortly after or even during synthesis, the residues in a protein are often chemically modified by posttranslational modification, which alters the physical and chemical properties, folding, stability, activity, and ultimately, the function of the proteins. Sometimes proteins have non-peptide groups attached, which can be called prosthetic groups or cofactors. Proteins can also work together to achieve a particular function, and they often associate to form stable protein complexes.Once formed, proteins only exist for a certain period of time and are then degraded and recycled by the cell's machinery through the process of protein turnover. A protein's lifespan is measured in terms of its half-life and covers a wide range. They can exist for minutes or years with an average lifespan of 1–2 days in mammalian cells. Abnormal and or misfolded proteins are degraded more rapidly either due to being targeted for destruction or due to being unstable.Like other biological macromolecules such as polysaccharides and nucleic acids, proteins are essential parts of organisms and participate in virtually every process within cells. Many proteins are enzymes that catalyze biochemical reactions and are vital to metabolism. Proteins also have structural or mechanical functions, such as actin and myosin in muscle and the proteins in the cytoskeleton, which form a system of scaffolding that maintains cell shape. Other proteins are important in cell signaling, immune responses, cell adhesion, and the cell cycle. Proteins are also necessary in animals' diets, since animals cannot synthesize all the amino acids they need and must obtain essential amino acids from food. Through the process of digestion, animals break down ingested protein into free amino acids that are then used in metabolism.Proteins may be purified from other cellular components using a variety of techniques such as ultracentrifugation, precipitation, electrophoresis, and chromatography; the advent of genetic engineering has made possible a number of methods to facilitate purification. Methods commonly used to study protein structure and function include immunohistochemistry, site-directed mutagenesis, X-ray crystallography, nuclear magnetic resonance and mass spectrometry.