protein. Egg - Egg Nutrition Center
... 1. Layman D and Rodriguez N. Egg protein as a source of power, strength and energy. Nutr Today.2009;44:43-48. 2. Campbell B et al. International society of sports nutrition position stand: protein and exercise. J Int Soc Sport Nutr. 2007;4:8. 3. US Department of Agriculture, Agriculture Research Ser ...
... 1. Layman D and Rodriguez N. Egg protein as a source of power, strength and energy. Nutr Today.2009;44:43-48. 2. Campbell B et al. International society of sports nutrition position stand: protein and exercise. J Int Soc Sport Nutr. 2007;4:8. 3. US Department of Agriculture, Agriculture Research Ser ...
Plant Molecular Biology
... act as signaling GTPase, dynamin-related proteins are larger (60–110 kDa) and function in part by wrapping around pinching off membranes, though there is evidence that they also have a signaling role. However, besides binding to GTP, they share little homology with other large GTP-binding proteins s ...
... act as signaling GTPase, dynamin-related proteins are larger (60–110 kDa) and function in part by wrapping around pinching off membranes, though there is evidence that they also have a signaling role. However, besides binding to GTP, they share little homology with other large GTP-binding proteins s ...
reading - Science with Ms. Wang
... Carbohydrates usually contain carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen atoms in a ratio of 1:2:1. This means that for each carbon atom a carbohydrate molecule contains, it also contains twice as many hydrogen atoms and the same number of oxygen atoms. Carbohydrates are important because they contain a great dea ...
... Carbohydrates usually contain carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen atoms in a ratio of 1:2:1. This means that for each carbon atom a carbohydrate molecule contains, it also contains twice as many hydrogen atoms and the same number of oxygen atoms. Carbohydrates are important because they contain a great dea ...
3 - Dr. Jerry Cronin
... and extracellular matrix (ECM) Elements of the cytoskeleton (cell’s internal supports) and the extracellular matrix (fibers and other substances outside the cell) may be anchored to membrane proteins, which help maintain cell shape and fix the location of certain membrane proteins. Others play a rol ...
... and extracellular matrix (ECM) Elements of the cytoskeleton (cell’s internal supports) and the extracellular matrix (fibers and other substances outside the cell) may be anchored to membrane proteins, which help maintain cell shape and fix the location of certain membrane proteins. Others play a rol ...
A comprehensive investigation of ribosomal genes in complete
... the course of archaeal evolution. This first documented case of reductive evolution at the domain scale provides a new framework for discussing the shape of the universal tree of life and the selective forces directing the evolution of prokaryotes. ...
... the course of archaeal evolution. This first documented case of reductive evolution at the domain scale provides a new framework for discussing the shape of the universal tree of life and the selective forces directing the evolution of prokaryotes. ...
Bone building: perfect protein
... an important role. It oversees both types of cells—without it, bones have osteoporosis in some parts (too little bone, thus very weak), and are too dense in other patches.2 Osteocalcin and hydroxyapatite ...
... an important role. It oversees both types of cells—without it, bones have osteoporosis in some parts (too little bone, thus very weak), and are too dense in other patches.2 Osteocalcin and hydroxyapatite ...
Protein Purification and Analysis Ion exchange
... Collection of samples and measurements of Void volume (Vo) and elution volume (Ve) Ve/Vo - used in gel filtration chrom ...
... Collection of samples and measurements of Void volume (Vo) and elution volume (Ve) Ve/Vo - used in gel filtration chrom ...
Protein Synthesis
... Overview of Protein Synthesis •During transcription, one DNA strand, (template strand), provides a template for making an RNA molecule. ...
... Overview of Protein Synthesis •During transcription, one DNA strand, (template strand), provides a template for making an RNA molecule. ...
17-Gene to Protein
... • Introns: noncoding sequences that are removed • Exons: coding sequences that are spliced together • Small nuclear ribonucleoproteins (snRNPs): identify and help bring about the splicing process • Spliceosome: catalyzes splicing reactions ...
... • Introns: noncoding sequences that are removed • Exons: coding sequences that are spliced together • Small nuclear ribonucleoproteins (snRNPs): identify and help bring about the splicing process • Spliceosome: catalyzes splicing reactions ...
NIDA-svisit-20071219-PARE - Yale Bioinformatics -
... Gene expression major place for regulation (easy to measure) ...
... Gene expression major place for regulation (easy to measure) ...
study-guide-solutions-biochemistry
... some oxygen oxygen smaller than macromolecules most are macromolecules generally non-polar, so do not dissolve in include many polar functional groups, so do water dissolve in water not polymers polymers of monomeric units 8. The four main biological functions of lipids are energy storage, building ...
... some oxygen oxygen smaller than macromolecules most are macromolecules generally non-polar, so do not dissolve in include many polar functional groups, so do water dissolve in water not polymers polymers of monomeric units 8. The four main biological functions of lipids are energy storage, building ...
Chemistry SL HL Assessment Statements 2009 Revised
... The aim of this option is to give students an understanding of the chemistry of important molecules found in the human body, and the need for a balanced and healthy diet. Although the role that these molecules play in the body should be appreciated, the emphasis is placed on their chemistry, and stu ...
... The aim of this option is to give students an understanding of the chemistry of important molecules found in the human body, and the need for a balanced and healthy diet. Although the role that these molecules play in the body should be appreciated, the emphasis is placed on their chemistry, and stu ...
Proteins - e
... Proteomics is far more challenging than genomics, because of the complexity of interactions that can take place between proteins. Moreover, the pattern and function of proteins present in a cell depend on the type of cell it is, and this pattern can alter in the diseased state. Nevertheless, the rac ...
... Proteomics is far more challenging than genomics, because of the complexity of interactions that can take place between proteins. Moreover, the pattern and function of proteins present in a cell depend on the type of cell it is, and this pattern can alter in the diseased state. Nevertheless, the rac ...
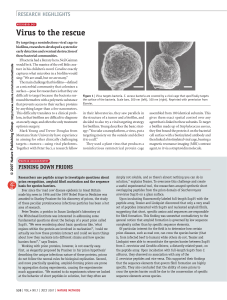
Nutritional Timing
... use the glycemic index chart in order to choose the appropriate food before, during and after competition. ...
... use the glycemic index chart in order to choose the appropriate food before, during and after competition. ...
Understanding DNA
... A. mRNA enters the ribosome B. 3 mRNA nucleotides (codons) pair up with 3 tRNA nucleotides (anticodons) C. amino acids are added until the “stop” message is reached ...
... A. mRNA enters the ribosome B. 3 mRNA nucleotides (codons) pair up with 3 tRNA nucleotides (anticodons) C. amino acids are added until the “stop” message is reached ...
Digestion & absorption of carbs & proteins
... glucose, amino acids, fats distribution precursors, available fuels metabolism macromolecules, energy, end products ...
... glucose, amino acids, fats distribution precursors, available fuels metabolism macromolecules, energy, end products ...
No Slide Title
... • Typically, ca. 500 - 1500 Å2 of surface buried upon complex formation by two globular proteins • Epitopes on protein surface thus may have a “hybrid” character, compatible with both a solvent-exposed (‘free”) state and a buried, solvent-inaccessible (“bound”) state • Energetics of binding primaril ...
... • Typically, ca. 500 - 1500 Å2 of surface buried upon complex formation by two globular proteins • Epitopes on protein surface thus may have a “hybrid” character, compatible with both a solvent-exposed (‘free”) state and a buried, solvent-inaccessible (“bound”) state • Energetics of binding primaril ...
Photo Album
... Figure 2.6 Examples of microtubule motor proteins in the mammalian nervous system. The first microtubule motor identified in nervous tissue was a kinesin 1, but studies in mammalian genomes identified 3 kinesin 1 genes, including a neuron-specific form (kinesin 1A). Motor domains are well conserved ...
... Figure 2.6 Examples of microtubule motor proteins in the mammalian nervous system. The first microtubule motor identified in nervous tissue was a kinesin 1, but studies in mammalian genomes identified 3 kinesin 1 genes, including a neuron-specific form (kinesin 1A). Motor domains are well conserved ...
gene expression - cloudfront.net
... strand of mRNA is synthesized according to the nitrogenous base code of DNA. Transcription can be summarized by the following steps: 1. The enzyme, RNA polymerase, binds to an area of one of the DNA molecules in the double helix. During transcription, only one DNA strand serves as a template (a guid ...
... strand of mRNA is synthesized according to the nitrogenous base code of DNA. Transcription can be summarized by the following steps: 1. The enzyme, RNA polymerase, binds to an area of one of the DNA molecules in the double helix. During transcription, only one DNA strand serves as a template (a guid ...
Similarity
... The previous alignment was global. However, many proteins do not display global patterns of similarity. Instead, they possess local regions of similarity. Proteins can be thought of as assemblies of modular domains. It is thought that this may, in some cases, be due to an evolutionary process known ...
... The previous alignment was global. However, many proteins do not display global patterns of similarity. Instead, they possess local regions of similarity. Proteins can be thought of as assemblies of modular domains. It is thought that this may, in some cases, be due to an evolutionary process known ...
Translation
... cytoplasm, ribosomes attach to them. 2. Each tRNA molecule attaches to only one type of amino acid. The tRNA brings the amino acid to the ribosome. ...
... cytoplasm, ribosomes attach to them. 2. Each tRNA molecule attaches to only one type of amino acid. The tRNA brings the amino acid to the ribosome. ...
Protein

Proteins (/ˈproʊˌtiːnz/ or /ˈproʊti.ɨnz/) are large biomolecules, or macromolecules, consisting of one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within living organisms, including catalyzing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, responding to stimuli, and transporting molecules from one location to another. Proteins differ from one another primarily in their sequence of amino acids, which is dictated by the nucleotide sequence of their genes, and which usually results in protein folding into a specific three-dimensional structure that determines its activity.A linear chain of amino acid residues is called a polypeptide. A protein contains at least one long polypeptide. Short polypeptides, containing less than about 20-30 residues, are rarely considered to be proteins and are commonly called peptides, or sometimes oligopeptides. The individual amino acid residues are bonded together by peptide bonds and adjacent amino acid residues. The sequence of amino acid residues in a protein is defined by the sequence of a gene, which is encoded in the genetic code. In general, the genetic code specifies 20 standard amino acids; however, in certain organisms the genetic code can include selenocysteine and—in certain archaea—pyrrolysine. Shortly after or even during synthesis, the residues in a protein are often chemically modified by posttranslational modification, which alters the physical and chemical properties, folding, stability, activity, and ultimately, the function of the proteins. Sometimes proteins have non-peptide groups attached, which can be called prosthetic groups or cofactors. Proteins can also work together to achieve a particular function, and they often associate to form stable protein complexes.Once formed, proteins only exist for a certain period of time and are then degraded and recycled by the cell's machinery through the process of protein turnover. A protein's lifespan is measured in terms of its half-life and covers a wide range. They can exist for minutes or years with an average lifespan of 1–2 days in mammalian cells. Abnormal and or misfolded proteins are degraded more rapidly either due to being targeted for destruction or due to being unstable.Like other biological macromolecules such as polysaccharides and nucleic acids, proteins are essential parts of organisms and participate in virtually every process within cells. Many proteins are enzymes that catalyze biochemical reactions and are vital to metabolism. Proteins also have structural or mechanical functions, such as actin and myosin in muscle and the proteins in the cytoskeleton, which form a system of scaffolding that maintains cell shape. Other proteins are important in cell signaling, immune responses, cell adhesion, and the cell cycle. Proteins are also necessary in animals' diets, since animals cannot synthesize all the amino acids they need and must obtain essential amino acids from food. Through the process of digestion, animals break down ingested protein into free amino acids that are then used in metabolism.Proteins may be purified from other cellular components using a variety of techniques such as ultracentrifugation, precipitation, electrophoresis, and chromatography; the advent of genetic engineering has made possible a number of methods to facilitate purification. Methods commonly used to study protein structure and function include immunohistochemistry, site-directed mutagenesis, X-ray crystallography, nuclear magnetic resonance and mass spectrometry.