Scientists clarify structural basis for biosynthesis of mysterious 21st
... understanding of protein synthesis and lay the groundwork for advances in protein design. ...
... understanding of protein synthesis and lay the groundwork for advances in protein design. ...
Primary structure: the sequence of amino acids in a polypeptide chain
... Regulation: certain proteins not only control the expression of genes, but also control when gene expression takes place Proteins are divided into two types: fibrous proteins Protection: blood clotting involves the protein fibrinogen; the body used proteins called antibodies to fight disease globula ...
... Regulation: certain proteins not only control the expression of genes, but also control when gene expression takes place Proteins are divided into two types: fibrous proteins Protection: blood clotting involves the protein fibrinogen; the body used proteins called antibodies to fight disease globula ...
Leukaemia Section t(8;17)(q24;q22) ???BCL3/MYC Atlas of Genetics and Cytogenetics
... Genes involved and proteins ...
... Genes involved and proteins ...
References
... region targeted by P65-6 and upstream of the region targeted by P65-3b. Thus it was clear that we had amplified and cloned a cDNA fragment that encodes a large portion of the amino-terminal region of the Cd CA. Two nested non-degenerate primers CdCT-2 (5'- GGTCGACGTCGATCCTCAAGGC-3') and CdCT- 1 (5' ...
... region targeted by P65-6 and upstream of the region targeted by P65-3b. Thus it was clear that we had amplified and cloned a cDNA fragment that encodes a large portion of the amino-terminal region of the Cd CA. Two nested non-degenerate primers CdCT-2 (5'- GGTCGACGTCGATCCTCAAGGC-3') and CdCT- 1 (5' ...
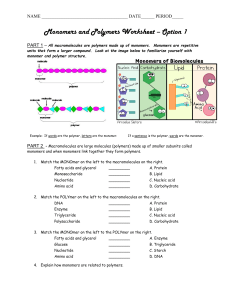
Macromolecule Worksheet
... PART 3 - Complete the chart below. Remember mono means one and poly means many. MACROMOLECULES ...
... PART 3 - Complete the chart below. Remember mono means one and poly means many. MACROMOLECULES ...
Protein Domain Boundary Prediction
... • Domains provide one of the most valuable information for the prediction of protein structure, function, evolution and design. • Since Anfinsen’s (1973) seminal work, many have proposed various structure prediction models from amino acid sequence only. • This study, - Provides an overview of the mo ...
... • Domains provide one of the most valuable information for the prediction of protein structure, function, evolution and design. • Since Anfinsen’s (1973) seminal work, many have proposed various structure prediction models from amino acid sequence only. • This study, - Provides an overview of the mo ...
Document
... • In order to practically synthesize peptides and proteins, time consuming purifications steps must be avoided until the very end of the synthesis. • Large excesses of reagents are used to drive reactions forward and accelerate the rate of reactions. • How are the excess reagents and by-products fr ...
... • In order to practically synthesize peptides and proteins, time consuming purifications steps must be avoided until the very end of the synthesis. • Large excesses of reagents are used to drive reactions forward and accelerate the rate of reactions. • How are the excess reagents and by-products fr ...
biochemistry, cell and molecular biology test
... a. sum of free energies of formation of many weak interactions among the hundreds of amino acids in a protein. b. entropy increase from the decrease in the number of ordered water molecules forming a solvent shell around a protein. c. sum of free energies of formation of many weak interactions betwe ...
... a. sum of free energies of formation of many weak interactions among the hundreds of amino acids in a protein. b. entropy increase from the decrease in the number of ordered water molecules forming a solvent shell around a protein. c. sum of free energies of formation of many weak interactions betwe ...
Protein - DNA interaction in chromatin
... biological oligomers and polymers, alongside nucleic acids, oligo- and polysaccharides, etc. Peptides have recently received prominence in molecular biology for several reasons. The first is that peptides allow the creation of peptide antibodies in animals without the need to purify the protein of i ...
... biological oligomers and polymers, alongside nucleic acids, oligo- and polysaccharides, etc. Peptides have recently received prominence in molecular biology for several reasons. The first is that peptides allow the creation of peptide antibodies in animals without the need to purify the protein of i ...
Is β-pleated sheet the molecular conformation which dictates
... experimental data, where individual prediction methods usually fail to produce meaningful results (Hamodrakas et al., 1982a; Hamodrakas and Kafatos, 1984; Hamodrakas, 1992). 2.2. Cuticular proteins The 27 proteins chosen for inclusion in this analysis are a subset of 36 unique insect cuticular prote ...
... experimental data, where individual prediction methods usually fail to produce meaningful results (Hamodrakas et al., 1982a; Hamodrakas and Kafatos, 1984; Hamodrakas, 1992). 2.2. Cuticular proteins The 27 proteins chosen for inclusion in this analysis are a subset of 36 unique insect cuticular prote ...
DNA Functions
... the ribosome, the proper amino acid is brought into the ribosome by tRNA. In the ribosome, the amino acid is transferred to the growing polypeptide chain [protein]. Each tRNA molecule carries only one kind of amino acid. In addition to an amino acid, each tRNA molecule has three upaired bases ...
... the ribosome, the proper amino acid is brought into the ribosome by tRNA. In the ribosome, the amino acid is transferred to the growing polypeptide chain [protein]. Each tRNA molecule carries only one kind of amino acid. In addition to an amino acid, each tRNA molecule has three upaired bases ...
An acidic region of the 89K murine cytomegalovirus immediate early
... proteins were stained with Coomassie blue (Fig. 4a) or were reacted with MAb 6/20/1 or antisera raised against peptides of pp89 (Miinch et al., 1991) (not shown). Extracts of bacterial cells expressing the fl-gal (Fig. 4b, lanes 1 to 8) or the TrpE proteins (Fig. 4b, lanes 9 to 16) contained only on ...
... proteins were stained with Coomassie blue (Fig. 4a) or were reacted with MAb 6/20/1 or antisera raised against peptides of pp89 (Miinch et al., 1991) (not shown). Extracts of bacterial cells expressing the fl-gal (Fig. 4b, lanes 1 to 8) or the TrpE proteins (Fig. 4b, lanes 9 to 16) contained only on ...
Folie 1 - FLI
... alignment using a modified Needleman–Wunsch algorithm. After the sequence or secondary structure alignment is complete, SuperPose then generates a difference distance (DD) matrix between aligned alpha carbon atoms. A difference distance matrix can be generated by first calculating the distances betw ...
... alignment using a modified Needleman–Wunsch algorithm. After the sequence or secondary structure alignment is complete, SuperPose then generates a difference distance (DD) matrix between aligned alpha carbon atoms. A difference distance matrix can be generated by first calculating the distances betw ...
birkbeck college - Principles of Protein Structure
... two amino acids that are classed as hydrophobic. [4 marks] b) Name and describe fully in chemical terms two types of interatomic interaction that hydrophobic amino acid side chains often make with neighbouring atoms or groups in a protein. [6 marks] ...
... two amino acids that are classed as hydrophobic. [4 marks] b) Name and describe fully in chemical terms two types of interatomic interaction that hydrophobic amino acid side chains often make with neighbouring atoms or groups in a protein. [6 marks] ...
Expressing Biologically Active Membrane Proteins in a Cell
... We first estimated the expression level of pSG73-75 in TX-TL by measuring the fluorescence of sfGFP which was fused at the C-terminal of β2AR or 1AR, using a plate reader at 485 nm (absorbance)/525 nm (emission). All the linear DNA constructs showed a GFP fluorescence signal, ind ...
... We first estimated the expression level of pSG73-75 in TX-TL by measuring the fluorescence of sfGFP which was fused at the C-terminal of β2AR or 1AR, using a plate reader at 485 nm (absorbance)/525 nm (emission). All the linear DNA constructs showed a GFP fluorescence signal, ind ...
What is natural immunity?
... 1. To determine the relationship (ie: distance) between two sequences (pair-wise alignment) 2. To search databanks for the presence of homologues 3. To look for sequence conservation in families of proteins 4. To use molecular approaches to phylogeny ...
... 1. To determine the relationship (ie: distance) between two sequences (pair-wise alignment) 2. To search databanks for the presence of homologues 3. To look for sequence conservation in families of proteins 4. To use molecular approaches to phylogeny ...
Computational Pharmacology - Carnegie Mellon School of
... = ab initio structure prediction (Blue Gene IBM ) B. When other information is used ("ab initio" methods that use pdb information) Common features: "fold recognition“, requires a method for evaluating the compatibility of a given sequence with a given folding pattern 1. 3D profiles 2. Rosetta: confo ...
... = ab initio structure prediction (Blue Gene IBM ) B. When other information is used ("ab initio" methods that use pdb information) Common features: "fold recognition“, requires a method for evaluating the compatibility of a given sequence with a given folding pattern 1. 3D profiles 2. Rosetta: confo ...
Understanding evolutionary dynamics of phosphorylation
... Movement in proteins requires energy. To this end, natural selection has selected phosphate as the principal energy currency in cells. On the other hand, depicting the state of transcription could come in the form of epigenetic markers, which are modifications on nucleotide residues. But, what are t ...
... Movement in proteins requires energy. To this end, natural selection has selected phosphate as the principal energy currency in cells. On the other hand, depicting the state of transcription could come in the form of epigenetic markers, which are modifications on nucleotide residues. But, what are t ...
Are Enzymes Necessary to your Health?
... Digesting food is one of the most energy-consuming tasks that the human body performs on a daily basis. When you eat foods that are enzyme deficient, the body uses a considerable amount of energy making enzymes for the digestion of that food. This can explain why we feel like we need a nap after eat ...
... Digesting food is one of the most energy-consuming tasks that the human body performs on a daily basis. When you eat foods that are enzyme deficient, the body uses a considerable amount of energy making enzymes for the digestion of that food. This can explain why we feel like we need a nap after eat ...
Lesson Plan
... 8/28 structure and functions of different types of biomolecules including carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids. ...
... 8/28 structure and functions of different types of biomolecules including carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids. ...
Gel Electrophoresis - Institute of Tropical Disease
... Separation of macro molecules depend upon two forces; charge and mass. During electrophoresis rate of movement of macromolecules through the electric field depends on the strength of the field, size and shape of the molecules, relative hydrophobicity of the sample and on the ionic strength and tempe ...
... Separation of macro molecules depend upon two forces; charge and mass. During electrophoresis rate of movement of macromolecules through the electric field depends on the strength of the field, size and shape of the molecules, relative hydrophobicity of the sample and on the ionic strength and tempe ...
Protein

Proteins (/ˈproʊˌtiːnz/ or /ˈproʊti.ɨnz/) are large biomolecules, or macromolecules, consisting of one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within living organisms, including catalyzing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, responding to stimuli, and transporting molecules from one location to another. Proteins differ from one another primarily in their sequence of amino acids, which is dictated by the nucleotide sequence of their genes, and which usually results in protein folding into a specific three-dimensional structure that determines its activity.A linear chain of amino acid residues is called a polypeptide. A protein contains at least one long polypeptide. Short polypeptides, containing less than about 20-30 residues, are rarely considered to be proteins and are commonly called peptides, or sometimes oligopeptides. The individual amino acid residues are bonded together by peptide bonds and adjacent amino acid residues. The sequence of amino acid residues in a protein is defined by the sequence of a gene, which is encoded in the genetic code. In general, the genetic code specifies 20 standard amino acids; however, in certain organisms the genetic code can include selenocysteine and—in certain archaea—pyrrolysine. Shortly after or even during synthesis, the residues in a protein are often chemically modified by posttranslational modification, which alters the physical and chemical properties, folding, stability, activity, and ultimately, the function of the proteins. Sometimes proteins have non-peptide groups attached, which can be called prosthetic groups or cofactors. Proteins can also work together to achieve a particular function, and they often associate to form stable protein complexes.Once formed, proteins only exist for a certain period of time and are then degraded and recycled by the cell's machinery through the process of protein turnover. A protein's lifespan is measured in terms of its half-life and covers a wide range. They can exist for minutes or years with an average lifespan of 1–2 days in mammalian cells. Abnormal and or misfolded proteins are degraded more rapidly either due to being targeted for destruction or due to being unstable.Like other biological macromolecules such as polysaccharides and nucleic acids, proteins are essential parts of organisms and participate in virtually every process within cells. Many proteins are enzymes that catalyze biochemical reactions and are vital to metabolism. Proteins also have structural or mechanical functions, such as actin and myosin in muscle and the proteins in the cytoskeleton, which form a system of scaffolding that maintains cell shape. Other proteins are important in cell signaling, immune responses, cell adhesion, and the cell cycle. Proteins are also necessary in animals' diets, since animals cannot synthesize all the amino acids they need and must obtain essential amino acids from food. Through the process of digestion, animals break down ingested protein into free amino acids that are then used in metabolism.Proteins may be purified from other cellular components using a variety of techniques such as ultracentrifugation, precipitation, electrophoresis, and chromatography; the advent of genetic engineering has made possible a number of methods to facilitate purification. Methods commonly used to study protein structure and function include immunohistochemistry, site-directed mutagenesis, X-ray crystallography, nuclear magnetic resonance and mass spectrometry.