Cellular Localization Data - SGD-Wiki
... Hidden Markov models (HMM) have been successfully applied to the tasks of transmembrane protein topology prediction and signal peptide prediction. Philius, is inspired by a previously published HMM, Ph ...
... Hidden Markov models (HMM) have been successfully applied to the tasks of transmembrane protein topology prediction and signal peptide prediction. Philius, is inspired by a previously published HMM, Ph ...
Cell Membranes
... A. The cell membrane was composed of lipids and proteins. B. The cell membrane was composed of a phospholipid bilayer between two layers of globular proteins. C. The cell membrane was composed of a phospholipid bilayer with globular proteins actually inserted into the bilayer. D. The cell membrane w ...
... A. The cell membrane was composed of lipids and proteins. B. The cell membrane was composed of a phospholipid bilayer between two layers of globular proteins. C. The cell membrane was composed of a phospholipid bilayer with globular proteins actually inserted into the bilayer. D. The cell membrane w ...
Chemical Foundations of Life The origin of life and organic
... Amino acids are small molecules that contain a carboxyl group, an amino group, a central carbon, and a functional group (side chain). There are 20 amino acids and they are all differentiated by the functional groups they have. A peptide bond is a covalent bond that joins two amino acid groups togeth ...
... Amino acids are small molecules that contain a carboxyl group, an amino group, a central carbon, and a functional group (side chain). There are 20 amino acids and they are all differentiated by the functional groups they have. A peptide bond is a covalent bond that joins two amino acid groups togeth ...
Introduction to Bioinformatics Protein Structure and
... called the active site. The folding happens to place the 195th amino acid in the chain, serine, near a hole that has the shape of the amino acid phenylalanine. When a phenylalanine within a protein you eat finds its way into the phenylalanine-shaped hole of chymotrypsin, the amide bond adjacent to p ...
... called the active site. The folding happens to place the 195th amino acid in the chain, serine, near a hole that has the shape of the amino acid phenylalanine. When a phenylalanine within a protein you eat finds its way into the phenylalanine-shaped hole of chymotrypsin, the amide bond adjacent to p ...
Reading Guide
... 27. Aromatic amino acids are both keto- and glucogenic because they are broken down into ___________________ and either ______________ or _______________. 28. Why is excess nitrogen from metabolic processes not simply excreted as ammonia? 29. What is glutamate’s particular role in nitrogen eliminat ...
... 27. Aromatic amino acids are both keto- and glucogenic because they are broken down into ___________________ and either ______________ or _______________. 28. Why is excess nitrogen from metabolic processes not simply excreted as ammonia? 29. What is glutamate’s particular role in nitrogen eliminat ...
Protein Supplements
... disease or if overused or abused. Always consult physician before using! Workout supplements will automatically build muscle? Workout supplements will not aid in muscle growth unless paired with regular exercise/workouts. ...
... disease or if overused or abused. Always consult physician before using! Workout supplements will automatically build muscle? Workout supplements will not aid in muscle growth unless paired with regular exercise/workouts. ...
FOOD-CHEMISTRY-CARBOHYDRATES-BY
... oligosaccharide chains of these glycoproteins. Such diseases, and gene knockout studies in mice, have been used to define pathways of modification of oligosaccharide chains of glycoproteins and glycolipids. * Carbohydrate chains of plasma membrane glycoproteins and glycolipids usually face the outsi ...
... oligosaccharide chains of these glycoproteins. Such diseases, and gene knockout studies in mice, have been used to define pathways of modification of oligosaccharide chains of glycoproteins and glycolipids. * Carbohydrate chains of plasma membrane glycoproteins and glycolipids usually face the outsi ...
Basic virology
... are composed of viral nucleic acid and proteins but cannot replicate without a "helper" virus, which provides the missing function. usually have a mutation or a deletion of part of their ...
... are composed of viral nucleic acid and proteins but cannot replicate without a "helper" virus, which provides the missing function. usually have a mutation or a deletion of part of their ...
gmo adv
... Then, answer the following questions: 1. What methods are used to predict whether a protein may be an allergen? What are the advantages and disadvantages of each of these models? 2. Describe in detail the conditions used to test the digestibility of proteins and how digestion was evaluated. What cri ...
... Then, answer the following questions: 1. What methods are used to predict whether a protein may be an allergen? What are the advantages and disadvantages of each of these models? 2. Describe in detail the conditions used to test the digestibility of proteins and how digestion was evaluated. What cri ...
Prediction of protein function using a deep convolutional
... The building blocks of proteins are amino acids which are linked together by peptide bonds into a chain. The polypeptide folds into a specific conformation depending on the interactions between its amino acid side chains which have different chemistries. Many conformations of this chain are possible ...
... The building blocks of proteins are amino acids which are linked together by peptide bonds into a chain. The polypeptide folds into a specific conformation depending on the interactions between its amino acid side chains which have different chemistries. Many conformations of this chain are possible ...
Define biology
... What is the difference between monomers and polymers? Give examples of each. Describe the structure, function, monomers and basic variations of carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids. Peptide bonds, polypeptides Nucleotides Amino acids Solvent, solute, solution, Identify the structural d ...
... What is the difference between monomers and polymers? Give examples of each. Describe the structure, function, monomers and basic variations of carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids. Peptide bonds, polypeptides Nucleotides Amino acids Solvent, solute, solution, Identify the structural d ...
Plant proteomics workshop_final072114
... The majority of mitochondrial proteins encoded by the nucleus and synthesized as precursors in the cytosol before being targeted to mitochondria. Low abundance proteins identification is a challenge but they play a very important role. Mitotracker. ...
... The majority of mitochondrial proteins encoded by the nucleus and synthesized as precursors in the cytosol before being targeted to mitochondria. Low abundance proteins identification is a challenge but they play a very important role. Mitotracker. ...
Biophysics 101 Genomics and Computational Biology
... 1) Assign function to proteins with only cellular or phenotypic function 2) Assign functional differences within a sequence family 3) Interpret disease associated single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs). Selection criteria 35% identity clusters: Large Families with a predefined limit on sequence leng ...
... 1) Assign function to proteins with only cellular or phenotypic function 2) Assign functional differences within a sequence family 3) Interpret disease associated single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs). Selection criteria 35% identity clusters: Large Families with a predefined limit on sequence leng ...
Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum (RER)
... The endoplasmic reticulum is a network of folded membranes that form channels. ...
... The endoplasmic reticulum is a network of folded membranes that form channels. ...
05- macromolecules
... of biological organization is reached when small organic molecules are joined together – Atom ---> molecule --- compound ...
... of biological organization is reached when small organic molecules are joined together – Atom ---> molecule --- compound ...
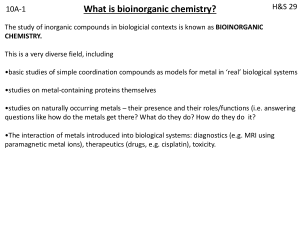
bioinorganic 1
... Neither the Fe protein nor the FeMo protein bind N2 separately. Together they do bind N2 but subsequent reduction occurs too rapidly to allow detection of intermediates. Nitrogenase is strongly inhibited by (a) CO and (b) O2. There is consensus opinion that N2 initially binds somewhere at the FeMo c ...
... Neither the Fe protein nor the FeMo protein bind N2 separately. Together they do bind N2 but subsequent reduction occurs too rapidly to allow detection of intermediates. Nitrogenase is strongly inhibited by (a) CO and (b) O2. There is consensus opinion that N2 initially binds somewhere at the FeMo c ...
Protein synthesis
... Many antibiotics inhibit the protein synthesis at some specific steps: Streptomycin: It is a highly basic ...
... Many antibiotics inhibit the protein synthesis at some specific steps: Streptomycin: It is a highly basic ...
FindTarget: software for subtractive genome analysis
... identifying genus- or species-specific genes, or groups of genes that are responsible for a unique phenotype. By this method, one searches for genes present in one group of bacteria and absent in another group. A software package has been developed, named FindTarget, that has a user-friendly web int ...
... identifying genus- or species-specific genes, or groups of genes that are responsible for a unique phenotype. By this method, one searches for genes present in one group of bacteria and absent in another group. A software package has been developed, named FindTarget, that has a user-friendly web int ...
PROTEIN SEQUENCING First Sequence
... – Pre- or post-column derivatization is used to increase sensitivity ...
... – Pre- or post-column derivatization is used to increase sensitivity ...
Protein Purification
... 1. Coomassie Stain: • Denatures protein and binds to hydrophobic core • Excess can be washed away • Detection limit is 0.1 μg ...
... 1. Coomassie Stain: • Denatures protein and binds to hydrophobic core • Excess can be washed away • Detection limit is 0.1 μg ...
Unit 1 PPT 3 (2biii-iv Binding and conformation)
... specific to particular sequences of doublestranded DNA and when bound to can either stimulate or inhibit initiation of transcription. • lac Operon • Transcription animation ...
... specific to particular sequences of doublestranded DNA and when bound to can either stimulate or inhibit initiation of transcription. • lac Operon • Transcription animation ...
capitolo 1 - Structural Biology
... Another factor to consider is the frequency with which a given amino acid is represented within the proteins. Not all amino acids are represented in the same way: there are amino acids that are not very frequent while others have a much higher frequency, as shown in Table I. An amino acid having a l ...
... Another factor to consider is the frequency with which a given amino acid is represented within the proteins. Not all amino acids are represented in the same way: there are amino acids that are not very frequent while others have a much higher frequency, as shown in Table I. An amino acid having a l ...
Protein

Proteins (/ˈproʊˌtiːnz/ or /ˈproʊti.ɨnz/) are large biomolecules, or macromolecules, consisting of one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within living organisms, including catalyzing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, responding to stimuli, and transporting molecules from one location to another. Proteins differ from one another primarily in their sequence of amino acids, which is dictated by the nucleotide sequence of their genes, and which usually results in protein folding into a specific three-dimensional structure that determines its activity.A linear chain of amino acid residues is called a polypeptide. A protein contains at least one long polypeptide. Short polypeptides, containing less than about 20-30 residues, are rarely considered to be proteins and are commonly called peptides, or sometimes oligopeptides. The individual amino acid residues are bonded together by peptide bonds and adjacent amino acid residues. The sequence of amino acid residues in a protein is defined by the sequence of a gene, which is encoded in the genetic code. In general, the genetic code specifies 20 standard amino acids; however, in certain organisms the genetic code can include selenocysteine and—in certain archaea—pyrrolysine. Shortly after or even during synthesis, the residues in a protein are often chemically modified by posttranslational modification, which alters the physical and chemical properties, folding, stability, activity, and ultimately, the function of the proteins. Sometimes proteins have non-peptide groups attached, which can be called prosthetic groups or cofactors. Proteins can also work together to achieve a particular function, and they often associate to form stable protein complexes.Once formed, proteins only exist for a certain period of time and are then degraded and recycled by the cell's machinery through the process of protein turnover. A protein's lifespan is measured in terms of its half-life and covers a wide range. They can exist for minutes or years with an average lifespan of 1–2 days in mammalian cells. Abnormal and or misfolded proteins are degraded more rapidly either due to being targeted for destruction or due to being unstable.Like other biological macromolecules such as polysaccharides and nucleic acids, proteins are essential parts of organisms and participate in virtually every process within cells. Many proteins are enzymes that catalyze biochemical reactions and are vital to metabolism. Proteins also have structural or mechanical functions, such as actin and myosin in muscle and the proteins in the cytoskeleton, which form a system of scaffolding that maintains cell shape. Other proteins are important in cell signaling, immune responses, cell adhesion, and the cell cycle. Proteins are also necessary in animals' diets, since animals cannot synthesize all the amino acids they need and must obtain essential amino acids from food. Through the process of digestion, animals break down ingested protein into free amino acids that are then used in metabolism.Proteins may be purified from other cellular components using a variety of techniques such as ultracentrifugation, precipitation, electrophoresis, and chromatography; the advent of genetic engineering has made possible a number of methods to facilitate purification. Methods commonly used to study protein structure and function include immunohistochemistry, site-directed mutagenesis, X-ray crystallography, nuclear magnetic resonance and mass spectrometry.