Highly conserved epitope domain in major core protein p24 is
... MAbs directed against p24 proteins of HIV-1 and HIV2. Among them, eight MAbs reacted with a 30 amino acid peptide containing the sequence of the V 10 epitope. This indicates that the site could be one of the immunodominant epitopes of this core protein. Inhibition experiments using human sera by Car ...
... MAbs directed against p24 proteins of HIV-1 and HIV2. Among them, eight MAbs reacted with a 30 amino acid peptide containing the sequence of the V 10 epitope. This indicates that the site could be one of the immunodominant epitopes of this core protein. Inhibition experiments using human sera by Car ...
How flexible is α-actinin`s rod domain?
... Abstract: α−actinin, an actin binding protein, plays a Endo, and Ebashi (1967)]. On the other hand, in nonkey role in cell migration, cross-links actin filaments in muscle cells, α-actinin organizes the cortical cytoskelethe Z-disk, and is a major component of contractile mus- ton adjacent to membra ...
... Abstract: α−actinin, an actin binding protein, plays a Endo, and Ebashi (1967)]. On the other hand, in nonkey role in cell migration, cross-links actin filaments in muscle cells, α-actinin organizes the cortical cytoskelethe Z-disk, and is a major component of contractile mus- ton adjacent to membra ...
The orphan histidine protein kinase SgmT is a cdiGMP receptor and
... ensures specificity in TCS signalling and precludes deleterious cross-talk in vivo depends on the kinetic preference of cognate TCS protein pairs for each other (Skerker et al., 2005; Laub and Goulian, 2007). Typically, cognate TCS partners are encoded by adjacent genes and easily recognized (Stock ...
... ensures specificity in TCS signalling and precludes deleterious cross-talk in vivo depends on the kinetic preference of cognate TCS protein pairs for each other (Skerker et al., 2005; Laub and Goulian, 2007). Typically, cognate TCS partners are encoded by adjacent genes and easily recognized (Stock ...
Like-acetylglucosaminyltransferase (LARGE)
... blotting using (i) the monoclonal antibody IIH6, which recognizes the glycosylated form of α-dystroglycan and inhibits its ligand-binding activity, and (ii) an anti-Fc antibody, which binds the Fc moiety on the α-dystroglycan mutants independent of posttranslational modifications and thus provides an ...
... blotting using (i) the monoclonal antibody IIH6, which recognizes the glycosylated form of α-dystroglycan and inhibits its ligand-binding activity, and (ii) an anti-Fc antibody, which binds the Fc moiety on the α-dystroglycan mutants independent of posttranslational modifications and thus provides an ...
biomass composition
... B.1 Overall cellular composition of Lactococcus lactis The macromolecular composition of bacterial cells is dependent on the growth conditions (growth rate and limiting substrate). For example, as the growth rate increases the cellular content of RNA usually increases, while the protein and DNA cont ...
... B.1 Overall cellular composition of Lactococcus lactis The macromolecular composition of bacterial cells is dependent on the growth conditions (growth rate and limiting substrate). For example, as the growth rate increases the cellular content of RNA usually increases, while the protein and DNA cont ...
Label-free and redox proteomic analyses of the
... intracellular lipids in Rhodococcus strains were performed by TLC. For intracellular analysis, 4–5 mg of lyophilized cells were extracted with a mixture of chloroform and methanol (2 : 1, v/v) for 120 min at 4 uC. Fifteen to thirty microlitres of extracts (depending on culture conditions) were separ ...
... intracellular lipids in Rhodococcus strains were performed by TLC. For intracellular analysis, 4–5 mg of lyophilized cells were extracted with a mixture of chloroform and methanol (2 : 1, v/v) for 120 min at 4 uC. Fifteen to thirty microlitres of extracts (depending on culture conditions) were separ ...
Ch 5 Biomolc Strc & Fxn
... Amino Acid Polymers • Amino acids are linked by peptide bonds to make polypeptides • Polypeptide- polymer of amino acids, range in length from few to over a thousand monomers • Each has a unique linear amino acid sequence ...
... Amino Acid Polymers • Amino acids are linked by peptide bonds to make polypeptides • Polypeptide- polymer of amino acids, range in length from few to over a thousand monomers • Each has a unique linear amino acid sequence ...
The Age of the Common Ancestor of Eukaryotes and
... set, and the final estimate is the average over all possible combinations. It was shown that the asymptotic bias of the estimate cx can be significantly reduced if an appropriate weight function is chosen for combining the estimates of three-sequence sets (Gu 1996). The computer program, which was o ...
... set, and the final estimate is the average over all possible combinations. It was shown that the asymptotic bias of the estimate cx can be significantly reduced if an appropriate weight function is chosen for combining the estimates of three-sequence sets (Gu 1996). The computer program, which was o ...
Lecture 32: Protein (Part-I)
... Introduction: Proteins perform multiple functions in a cell and they are the factors to control several events.They are the building blocks and work as enzyme to participate in metabolic reactions of the organism. Peptide Bonds: Proteins are polymers of amino acids, joined by the covalent bonds, kno ...
... Introduction: Proteins perform multiple functions in a cell and they are the factors to control several events.They are the building blocks and work as enzyme to participate in metabolic reactions of the organism. Peptide Bonds: Proteins are polymers of amino acids, joined by the covalent bonds, kno ...
Autophagy_Marc
... - Annotation of big families is easier when done in teams or based on subject. Part can be left to curators with certain expertise. Example: PTHR24073 (Rab proteins family): over 2700 proteins Function in vesicular transport. ...
... - Annotation of big families is easier when done in teams or based on subject. Part can be left to curators with certain expertise. Example: PTHR24073 (Rab proteins family): over 2700 proteins Function in vesicular transport. ...
PDF only - at www.arxiv.org.
... analogy for the information conveyed by the quaternary encoding [2] of DNA. That is, each of the four possible nucleotide bases of DNA represents a maximum of log2(4) = 2 bits of information. However, this comparison extends far beyond a superficial similarity; the canonical genetic code, represente ...
... analogy for the information conveyed by the quaternary encoding [2] of DNA. That is, each of the four possible nucleotide bases of DNA represents a maximum of log2(4) = 2 bits of information. However, this comparison extends far beyond a superficial similarity; the canonical genetic code, represente ...
Selenium incorporation using recombinant techniques
... unlabelled protein that has already been secreted is removed. However, in 2007 Cronin and coworkers reported a systematic study of SeMet-labelling proteins in baculovirus expressionvector systems in order to determine an optimal protocol for obtaining consistent and reliable SeMet-labelled protein f ...
... unlabelled protein that has already been secreted is removed. However, in 2007 Cronin and coworkers reported a systematic study of SeMet-labelling proteins in baculovirus expressionvector systems in order to determine an optimal protocol for obtaining consistent and reliable SeMet-labelled protein f ...
GPCR–G fusion proteins
... Basic properties of GPCR–Ga fusion proteins Construction of fusion protein DNAs and structural properties of fusion proteins Fusion proteins are generated by linking the GPCR C-terminus, which is located intracellularly, to the Nterminus of Ga (Refs 1–6, 9–13, 18). This is achieved by fusing the ope ...
... Basic properties of GPCR–Ga fusion proteins Construction of fusion protein DNAs and structural properties of fusion proteins Fusion proteins are generated by linking the GPCR C-terminus, which is located intracellularly, to the Nterminus of Ga (Refs 1–6, 9–13, 18). This is achieved by fusing the ope ...
Test File
... the nucleus. 3. The human mitochondrial genome encodes only 22 tRNAs. This limited array of tRNAs can read the 64 possible triplet codons through extreme wobble in base pairing at the third codon position and the use of a(n) _______ genetic code. a. chloroplast-mitochondrial-specific b. nonuniversal ...
... the nucleus. 3. The human mitochondrial genome encodes only 22 tRNAs. This limited array of tRNAs can read the 64 possible triplet codons through extreme wobble in base pairing at the third codon position and the use of a(n) _______ genetic code. a. chloroplast-mitochondrial-specific b. nonuniversal ...
Quantitative iTRAQ Proteomics Revealed Possible Roles for
... Liu et al., 2009), and the MATE (multidrug and toxic compound extrusion) family of citrate efflux transporters in sorghum, barley, and Arabidopsis (Furukawa et al., 2007; Magalhaes et al., 2007; Liu et al., 2009). As much as 90% of the root Al is localized to negatively charged carboxyl residues in ...
... Liu et al., 2009), and the MATE (multidrug and toxic compound extrusion) family of citrate efflux transporters in sorghum, barley, and Arabidopsis (Furukawa et al., 2007; Magalhaes et al., 2007; Liu et al., 2009). As much as 90% of the root Al is localized to negatively charged carboxyl residues in ...
1Memstruc
... 15. Which of the following membrane protein structures… 1) single pass alpha helix 2) 5x multipass alpha helix …is most-likely to be found in a(n): A. aqueous ion-channel B) anchor protein Explain your answers. ...
... 15. Which of the following membrane protein structures… 1) single pass alpha helix 2) 5x multipass alpha helix …is most-likely to be found in a(n): A. aqueous ion-channel B) anchor protein Explain your answers. ...
Ribosome-tethered molecular chaperones
... prokaryotic and eukaryotic chaperones have evolved to associate specifically with ribosomes and bind to polypeptide chains that have just emerged from the tunnel. In addition, non-ribosome-bound chaperones act on longer nascent chains, either during the process of translation, or after they have bee ...
... prokaryotic and eukaryotic chaperones have evolved to associate specifically with ribosomes and bind to polypeptide chains that have just emerged from the tunnel. In addition, non-ribosome-bound chaperones act on longer nascent chains, either during the process of translation, or after they have bee ...
spin-system assignments
... assignments, followed by sequence-specific assignment using unique fragments of sequence, is known as sequential assignment (Wuthrich) • there are alternatives to this protocol: one is known as main-chain directed assignment (Englander). This technique does not focus on assigning all the spin system ...
... assignments, followed by sequence-specific assignment using unique fragments of sequence, is known as sequential assignment (Wuthrich) • there are alternatives to this protocol: one is known as main-chain directed assignment (Englander). This technique does not focus on assigning all the spin system ...
Sequence-based predictions of membrane-protein topology, homology and insertion
... major role in the origin of the field of bioinformatics, which deals with annotation, storage and analysis of such biological data. Accordingly, one of the first disciplines within bioinformatics, and still one of the largest, has been that of sequence analysis. Methods for automatic annotation of ...
... major role in the origin of the field of bioinformatics, which deals with annotation, storage and analysis of such biological data. Accordingly, one of the first disciplines within bioinformatics, and still one of the largest, has been that of sequence analysis. Methods for automatic annotation of ...
Novel Multiprotein Complexes Identified in the Hyperthermophilic
... 3, September 27, 姝1997–2007) was used to peak pick and extract peak lists from the tandem mass spectra into peak list (.dta) files. Mascot Daemon was used to run this program externally and to submit the searches to Mascot (Matrix Science Ltd.) for protein identification. The Mascot searches were co ...
... 3, September 27, 姝1997–2007) was used to peak pick and extract peak lists from the tandem mass spectra into peak list (.dta) files. Mascot Daemon was used to run this program externally and to submit the searches to Mascot (Matrix Science Ltd.) for protein identification. The Mascot searches were co ...
fa458c46b7c1dda
... Destruction of Defective mRNAs • Without a suppressor tRNA, a nonsense mutation will cause premature termination of translation and an incomplete polypeptide chain • Eukaryotic cells use nonsense-mediated decay to destroy mRNAs containing premature stop codons • In mammals, the exon junction complex ...
... Destruction of Defective mRNAs • Without a suppressor tRNA, a nonsense mutation will cause premature termination of translation and an incomplete polypeptide chain • Eukaryotic cells use nonsense-mediated decay to destroy mRNAs containing premature stop codons • In mammals, the exon junction complex ...
Chapter 17 End?of?Chapter Problems Key
... 35. Describe the three steps in the recycling of polymers. (Obj #33) The first step is collection of materials in curbside recycling bins or central collection areas. The next step is sorting. The recycling symbols found on objects made of polymers tell the recycling companies what type of polymer w ...
... 35. Describe the three steps in the recycling of polymers. (Obj #33) The first step is collection of materials in curbside recycling bins or central collection areas. The next step is sorting. The recycling symbols found on objects made of polymers tell the recycling companies what type of polymer w ...
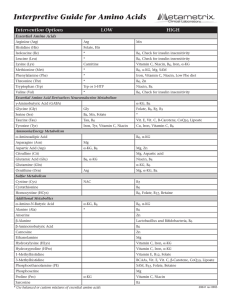
Interpretive Guide for Amino Acids
... High - indicative of connective and bone tissue breakdown. Collagen synthesis requires iron, α-KG and vitamin C. Supplementation of these plus chondroitin sulfate and manganese are extremely helpful. Hydroxyproline High - another indicator of bone resorption via collagen breakdown. Supplement as in ...
... High - indicative of connective and bone tissue breakdown. Collagen synthesis requires iron, α-KG and vitamin C. Supplementation of these plus chondroitin sulfate and manganese are extremely helpful. Hydroxyproline High - another indicator of bone resorption via collagen breakdown. Supplement as in ...
Protein

Proteins (/ˈproʊˌtiːnz/ or /ˈproʊti.ɨnz/) are large biomolecules, or macromolecules, consisting of one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within living organisms, including catalyzing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, responding to stimuli, and transporting molecules from one location to another. Proteins differ from one another primarily in their sequence of amino acids, which is dictated by the nucleotide sequence of their genes, and which usually results in protein folding into a specific three-dimensional structure that determines its activity.A linear chain of amino acid residues is called a polypeptide. A protein contains at least one long polypeptide. Short polypeptides, containing less than about 20-30 residues, are rarely considered to be proteins and are commonly called peptides, or sometimes oligopeptides. The individual amino acid residues are bonded together by peptide bonds and adjacent amino acid residues. The sequence of amino acid residues in a protein is defined by the sequence of a gene, which is encoded in the genetic code. In general, the genetic code specifies 20 standard amino acids; however, in certain organisms the genetic code can include selenocysteine and—in certain archaea—pyrrolysine. Shortly after or even during synthesis, the residues in a protein are often chemically modified by posttranslational modification, which alters the physical and chemical properties, folding, stability, activity, and ultimately, the function of the proteins. Sometimes proteins have non-peptide groups attached, which can be called prosthetic groups or cofactors. Proteins can also work together to achieve a particular function, and they often associate to form stable protein complexes.Once formed, proteins only exist for a certain period of time and are then degraded and recycled by the cell's machinery through the process of protein turnover. A protein's lifespan is measured in terms of its half-life and covers a wide range. They can exist for minutes or years with an average lifespan of 1–2 days in mammalian cells. Abnormal and or misfolded proteins are degraded more rapidly either due to being targeted for destruction or due to being unstable.Like other biological macromolecules such as polysaccharides and nucleic acids, proteins are essential parts of organisms and participate in virtually every process within cells. Many proteins are enzymes that catalyze biochemical reactions and are vital to metabolism. Proteins also have structural or mechanical functions, such as actin and myosin in muscle and the proteins in the cytoskeleton, which form a system of scaffolding that maintains cell shape. Other proteins are important in cell signaling, immune responses, cell adhesion, and the cell cycle. Proteins are also necessary in animals' diets, since animals cannot synthesize all the amino acids they need and must obtain essential amino acids from food. Through the process of digestion, animals break down ingested protein into free amino acids that are then used in metabolism.Proteins may be purified from other cellular components using a variety of techniques such as ultracentrifugation, precipitation, electrophoresis, and chromatography; the advent of genetic engineering has made possible a number of methods to facilitate purification. Methods commonly used to study protein structure and function include immunohistochemistry, site-directed mutagenesis, X-ray crystallography, nuclear magnetic resonance and mass spectrometry.