Chapter 10 - Pegasus @ UCF
... theoretical basis for firm decision-making and LR costs and supply. In essence, we will assume that the firm’s goal is to maximize output subject to a cost constraint. We will see that this is the same as minimizing the cost of producing a given level of output. Keep in mind that all inputs are ...
... theoretical basis for firm decision-making and LR costs and supply. In essence, we will assume that the firm’s goal is to maximize output subject to a cost constraint. We will see that this is the same as minimizing the cost of producing a given level of output. Keep in mind that all inputs are ...
A Shopkeeper Economy - Federal Reserve Bank of Dallas
... firms face marginal labor costs, the existence of excess supply and in the labor market generates a role for demand in determining output. The model presented below is an analytically tractable way to capture the prevalence of excess capacity in the labor market and the consumer goods market, and t ...
... firms face marginal labor costs, the existence of excess supply and in the labor market generates a role for demand in determining output. The model presented below is an analytically tractable way to capture the prevalence of excess capacity in the labor market and the consumer goods market, and t ...
Contribution of Cultural Economics to the Analysis of the
... with the economic rights. Control of the artist’s reputation and of the integrity of their works is an incentive to create. Thus, copyright law satisfies both intrinsic and extrinsic motivation and reward with its combination of moral and economic rights. All told then, the case for copyright as an ...
... with the economic rights. Control of the artist’s reputation and of the integrity of their works is an incentive to create. Thus, copyright law satisfies both intrinsic and extrinsic motivation and reward with its combination of moral and economic rights. All told then, the case for copyright as an ...
The Oomph in economic philosophy: a bibliometric analysis of the
... RoE and RiE debate, economic philosophy broke itself free from a variety of an “unautonomous” issues, originating from subfields of economics, including economic psychology, development economics, “positive economics,” and other topics discussed by such economists as Lionel Robbins, Terence Hutchiso ...
... RoE and RiE debate, economic philosophy broke itself free from a variety of an “unautonomous” issues, originating from subfields of economics, including economic psychology, development economics, “positive economics,” and other topics discussed by such economists as Lionel Robbins, Terence Hutchiso ...
Chapter10 Externalities
... • Most economists would prefer the tax. The reason why economists would prefer the tax is that it reduces pollution more efficiently. The regulation requires each factory to reduce pollution by the same amount, but an equal reduction is not necessarily the least expensive way to clean up the water. ...
... • Most economists would prefer the tax. The reason why economists would prefer the tax is that it reduces pollution more efficiently. The regulation requires each factory to reduce pollution by the same amount, but an equal reduction is not necessarily the least expensive way to clean up the water. ...
From Anti-equilibrium to The Socialist System and Beyond Péter
... economy were developed. All these disciplines study the institutional aspects of economic action without giving up their aspiration for an analytical theory. This research perspective is embraced by János Kornai in his work. 3. In search of a new paradigm: Anti-equilibrium János Kornai has created t ...
... economy were developed. All these disciplines study the institutional aspects of economic action without giving up their aspiration for an analytical theory. This research perspective is embraced by János Kornai in his work. 3. In search of a new paradigm: Anti-equilibrium János Kornai has created t ...
The welfare state: a theoretical framework for justification and
... would be such that the group in question had best be the whole country, so that some centralized government power is called for. The modern approach to questions of this kind starts with an investigation of the properties of the market system. A central result of modern economic theory is that a sys ...
... would be such that the group in question had best be the whole country, so that some centralized government power is called for. The modern approach to questions of this kind starts with an investigation of the properties of the market system. A central result of modern economic theory is that a sys ...
Ecological Economics
... systems Renewable resources, such as wood or wind energy, are in continuous supply, although the rate at which they can be replenished will vary from resource to resource Non-renewable resources, such as iron ore or fossil fuels, are in limited supply within the earth’s crust, and thus once they are ...
... systems Renewable resources, such as wood or wind energy, are in continuous supply, although the rate at which they can be replenished will vary from resource to resource Non-renewable resources, such as iron ore or fossil fuels, are in limited supply within the earth’s crust, and thus once they are ...
Econ 2010 sec. 50 Final - University of Colorado Boulder
... A) The cost-minimizing way to achieve the required reduction is for the reduction to occur in the U.S. because production is more efficient in the U.S. than in China. B) Reducing carbon dioxide emission by 100 units in China (zero units in the U.S.) will cost the least in terms of the world's scare ...
... A) The cost-minimizing way to achieve the required reduction is for the reduction to occur in the U.S. because production is more efficient in the U.S. than in China. B) Reducing carbon dioxide emission by 100 units in China (zero units in the U.S.) will cost the least in terms of the world's scare ...
NBER WORKING PAPER SERIES TECHNOLOGICAL LINKAGES, MARKET SThUCTURE, AND OPTIMUM PRODUCTION POLICIES
... of firms enters the intermediates market. Whether the optimal lump-sum policy is a tax or subsidy is determined by comparing the rate at which additional varieties generate external economies to the rate at which imperfectly competitive input producers appropriate rents. ...
... of firms enters the intermediates market. Whether the optimal lump-sum policy is a tax or subsidy is determined by comparing the rate at which additional varieties generate external economies to the rate at which imperfectly competitive input producers appropriate rents. ...
Final: Version B Fall 2011 C) Production
... ski area: Dssb = 20 + .03Snowsb-.06Psb + .01Pvail, Where Dssb is the individual's demand, this year, for Steamboat ski days. Snowsb is Steamboat's total snow fall, last year, in inches. Psb is the cost of a steamboat ski day, measured in dollars. Pvail is the cost of a vail ski day, measured in doll ...
... ski area: Dssb = 20 + .03Snowsb-.06Psb + .01Pvail, Where Dssb is the individual's demand, this year, for Steamboat ski days. Snowsb is Steamboat's total snow fall, last year, in inches. Psb is the cost of a steamboat ski day, measured in dollars. Pvail is the cost of a vail ski day, measured in doll ...
Conflict and Cooperation: Institutional and Behavioral Economics
... rival/non-rival goods, decreasing and zero marginal cost, economies of scale, asset specificity, rent seeking and socio-emotional goods, with a constant focus on the goal of policy relevancy (p. 137): “If you do not know where the interdependencies are coming from, you can’t design institutions to d ...
... rival/non-rival goods, decreasing and zero marginal cost, economies of scale, asset specificity, rent seeking and socio-emotional goods, with a constant focus on the goal of policy relevancy (p. 137): “If you do not know where the interdependencies are coming from, you can’t design institutions to d ...
The Cambridge Contribution to the Revival of Classical
... impossible to measure it by looking only at the production process. Rather, we must look to market exchange to find how subjective aspects are being valued in market exchange. In this context, supply and demand start to be seen as the ultimate determinants of value and wealth. It is simply not possi ...
... impossible to measure it by looking only at the production process. Rather, we must look to market exchange to find how subjective aspects are being valued in market exchange. In this context, supply and demand start to be seen as the ultimate determinants of value and wealth. It is simply not possi ...
Interpreting Sustainability in Economic Terms
... reproducible capital is followed, then the economy can be made sustainable.5 Much as economists have long focused on potential rather than actual Pareto improvements, leaving the allocation of net gains among individuals (and, hence, the resolution of debates regarding distributional equity) to the ...
... reproducible capital is followed, then the economy can be made sustainable.5 Much as economists have long focused on potential rather than actual Pareto improvements, leaving the allocation of net gains among individuals (and, hence, the resolution of debates regarding distributional equity) to the ...
Lecture 1
... Social and economic institutions shape preferences All the tools needed for understanding this influence are – in principle – available ...
... Social and economic institutions shape preferences All the tools needed for understanding this influence are – in principle – available ...
chapter 1
... …are simplified versions of a more complex reality irrelevant details are stripped away …are used to show relationships between variables explain the economy’s behavior devise policies to improve economic performance ...
... …are simplified versions of a more complex reality irrelevant details are stripped away …are used to show relationships between variables explain the economy’s behavior devise policies to improve economic performance ...
Chapter 4:Demand
... A. Demand Elasticity Elasticity measures how sensitive consumers are to price changes. Demand is elastic when a change in price causes a large change in demand. Demand is inelastic when a change in price causes a small change in demand. Demand is unit elastic when a change in price causes a ...
... A. Demand Elasticity Elasticity measures how sensitive consumers are to price changes. Demand is elastic when a change in price causes a large change in demand. Demand is inelastic when a change in price causes a small change in demand. Demand is unit elastic when a change in price causes a ...
If a Pure Market Economy Is So Good, Why Doesn`t It Exist? The
... for pessimism are in Cowen (1992, 1994), which maintain that, without a government monopoly over the use of force, competing groups that can cooperate to resolve disputes also can collude to exercise coercion. Cowen and Sutter (1999) follows up with the more general claim that the very factors, such ...
... for pessimism are in Cowen (1992, 1994), which maintain that, without a government monopoly over the use of force, competing groups that can cooperate to resolve disputes also can collude to exercise coercion. Cowen and Sutter (1999) follows up with the more general claim that the very factors, such ...
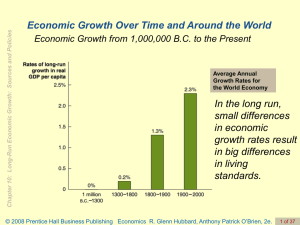
Economics R. Glenn Hubbard, Anthony Patrick O`Brien, 2e.
... What Determines How Fast Economies Grow? Economic growth model A model that explains growth rates in real GDP per capita over the long run. Labor productivity The quantity of goods and services that can be produced by one worker or by one hour of work. The more capital each worker has, the more prod ...
... What Determines How Fast Economies Grow? Economic growth model A model that explains growth rates in real GDP per capita over the long run. Labor productivity The quantity of goods and services that can be produced by one worker or by one hour of work. The more capital each worker has, the more prod ...
Knowledge in economics
... How knowledge is recognized in economic theory appears to be a hot topic in current research despite its methodological nature. It would seem that finally researchers have abandoned the simplistic notion that neoclassical economics requires some sort of perfect knowledge to be presumed on the part o ...
... How knowledge is recognized in economic theory appears to be a hot topic in current research despite its methodological nature. It would seem that finally researchers have abandoned the simplistic notion that neoclassical economics requires some sort of perfect knowledge to be presumed on the part o ...
Mankiw 6e PowerPoints
... …are simplified versions of a more complex reality irrelevant details are stripped away …are used to show relationships between variables explain the economy’s behavior devise policies to improve economic performance ...
... …are simplified versions of a more complex reality irrelevant details are stripped away …are used to show relationships between variables explain the economy’s behavior devise policies to improve economic performance ...
Mankiw 6e PowerPoints
... …are simplified versions of a more complex reality irrelevant details are stripped away …are used to show relationships between variables explain the economy’s behavior devise policies to improve economic performance ...
... …are simplified versions of a more complex reality irrelevant details are stripped away …are used to show relationships between variables explain the economy’s behavior devise policies to improve economic performance ...
General Equilibrium and the Efficiency of Perfect Competition
... composed of only one firm that produces a product for which there are no close substitutes and in which significant barriers exist to prevent new firms from entering the industry. ...
... composed of only one firm that produces a product for which there are no close substitutes and in which significant barriers exist to prevent new firms from entering the industry. ...
File - RAJ KUMAR
... They also define and protect the rights and obligations of property owned by individuals and institutions. • Key characteristics of market economies are [a] their ability to co-ordinate decentralized decisions without conscious control, [b] their determination of the distribution of income, and [c] ...
... They also define and protect the rights and obligations of property owned by individuals and institutions. • Key characteristics of market economies are [a] their ability to co-ordinate decentralized decisions without conscious control, [b] their determination of the distribution of income, and [c] ...
Some Basic Stuff on Empirical Work
... Some Basic Stuff on Empirical Work Example: Suppose we want to estimate the demand for doctors visits and we have prices and number of visits per person during a year. Suppose the demand for visits depends on price but also on the individuals’ level of exercise, for which there is no data and there ...
... Some Basic Stuff on Empirical Work Example: Suppose we want to estimate the demand for doctors visits and we have prices and number of visits per person during a year. Suppose the demand for visits depends on price but also on the individuals’ level of exercise, for which there is no data and there ...
Economics
Economics is the social science that seeks to describe the factors which determine the production, distribution and consumption of goods and services.The term economics comes from the Ancient Greek οἰκονομία from οἶκος (oikos, ""house"") and νόμος (nomos, ""custom"" or ""law""), hence ""rules of the house (hold for good management)"". 'Political economy' was the earlier name for the subject, but economists in the late 19th century suggested ""economics"" as a shorter term for ""economic science"" to establish itself as a separate discipline outside of political science and other social sciences.Economics focuses on the behavior and interactions of economic agents and how economies work. Consistent with this focus, primary textbooks often distinguish between microeconomics and macroeconomics. Microeconomics examines the behavior of basic elements in the economy, including individual agents and markets, their interactions, and the outcomes of interactions. Individual agents may include, for example, households, firms, buyers, and sellers. Macroeconomics analyzes the entire economy (meaning aggregated production, consumption, savings, and investment) and issues affecting it, including unemployment of resources (labor, capital, and land), inflation, economic growth, and the public policies that address these issues (monetary, fiscal, and other policies).Other broad distinctions within economics include those between positive economics, describing ""what is,"" and normative economics, advocating ""what ought to be""; between economic theory and applied economics; between rational and behavioral economics; and between mainstream economics (more ""orthodox"" and dealing with the ""rationality-individualism-equilibrium nexus"") and heterodox economics (more ""radical"" and dealing with the ""institutions-history-social structure nexus"").Besides the traditional concern in production, distribution, and consumption in an economy, economic analysis may be applied throughout society, as in business, finance, health care, and government. Economic analyses may also be applied to such diverse subjects as crime, education, the family, law, politics, religion, social institutions, war, science, and the environment. Education, for example, requires time, effort, and expenses, plus the foregone income and experience, yet these losses can be weighted against future benefits education may bring to the agent or the economy. At the turn of the 21st century, the expanding domain of economics in the social sciences has been described as economic imperialism.The ultimate goal of economics is to improve the living conditions of people in their everyday life.