1.7AMIDES
... bonds are polar. As a result the physical properties of amides are similar to carboxylic acids. 1) Primary amides have two N-H bonds so they have even stronger hydrogen bonds than carboxylic acid. Secondary amides also have one N-H bond and experience hydrogen bonding. Tertiary amides do not experie ...
... bonds are polar. As a result the physical properties of amides are similar to carboxylic acids. 1) Primary amides have two N-H bonds so they have even stronger hydrogen bonds than carboxylic acid. Secondary amides also have one N-H bond and experience hydrogen bonding. Tertiary amides do not experie ...
Biology Slide 1 of 39 End Show
... A codon consists of three consecutive nucleotides on mRNA that specify a particular amino acid. ...
... A codon consists of three consecutive nucleotides on mRNA that specify a particular amino acid. ...
function
... 4-7. Structure from Sequence : Profile-Based Threading and “Rosetta” Profile-based threading tries to predict the structure of a sequence even if no sequence homologs are known -Computer program forces the sequence to adopt every known protein fold in turn, and in each case a scoring function is ca ...
... 4-7. Structure from Sequence : Profile-Based Threading and “Rosetta” Profile-based threading tries to predict the structure of a sequence even if no sequence homologs are known -Computer program forces the sequence to adopt every known protein fold in turn, and in each case a scoring function is ca ...
CHEM 212B, Organic Chemistry - City College of San Francisco
... polarity, dipole moments, boiling point trends, solubility, and reactivity of different functional groups. c. Predict the product of organic reactions of conjugated alkenes, aromatics, carbonyl compounds, amines, carbohydrates, lipids, and amino acids. D. Write detailed mechanisms for pericyclic rea ...
... polarity, dipole moments, boiling point trends, solubility, and reactivity of different functional groups. c. Predict the product of organic reactions of conjugated alkenes, aromatics, carbonyl compounds, amines, carbohydrates, lipids, and amino acids. D. Write detailed mechanisms for pericyclic rea ...
Pandemic Flu - Egan Supply Co.
... large proportion of the human population. – The World Health Organization (WHO) warns that there is a substantial risk of an Pandemic Flu within the next few years. – Pandemic Flu is an infectious disease of birds and mammals caused by an RNA virus of the family Orthomyxovidridae (the influenza viru ...
... large proportion of the human population. – The World Health Organization (WHO) warns that there is a substantial risk of an Pandemic Flu within the next few years. – Pandemic Flu is an infectious disease of birds and mammals caused by an RNA virus of the family Orthomyxovidridae (the influenza viru ...
nomenclature continued… - Turner Fenton Secondary School
... 1. Find longest alkyl chain containing Nitrogen. 2. Replace alkane with amine. Include position of carbon attached to nitrogen. 3. If there are 2 or more alkyl groups attached to the nitrogen then use N as a prefix. Note: a nitrogen can have a maximum of three alkyl groups attached therefore the nam ...
... 1. Find longest alkyl chain containing Nitrogen. 2. Replace alkane with amine. Include position of carbon attached to nitrogen. 3. If there are 2 or more alkyl groups attached to the nitrogen then use N as a prefix. Note: a nitrogen can have a maximum of three alkyl groups attached therefore the nam ...
Visualizing Macromolecules
... ____________________________ . Clearly the number of possible combinations is almost infinite when larger numbers of amino acids are combined to form a polypeptide. 3. What is PRIMARY STRUCTURE? ______________________________________________________________________________ __________________________ ...
... ____________________________ . Clearly the number of possible combinations is almost infinite when larger numbers of amino acids are combined to form a polypeptide. 3. What is PRIMARY STRUCTURE? ______________________________________________________________________________ __________________________ ...
Protein Structure III
... Only 10s of thousands of protein structures are known Yet 100s of thousands of proteins are identified ...
... Only 10s of thousands of protein structures are known Yet 100s of thousands of proteins are identified ...
Tr-dT, 2-cyanoethanol
... pyridine with the main types of the reactive phosphorylating intermediates formed by treatment of pdT-Act pdTpdT-Ac, Tr-dTpdT-Ac, Tr-dTpdTpdT-Ac with 2,4,6-triisopropylbenzenesulfonyl chloride (TPS): 1) B type derivatives with phosphomono ester ( M E ) group converted to a phosphoryl pyridinium resi ...
... pyridine with the main types of the reactive phosphorylating intermediates formed by treatment of pdT-Act pdTpdT-Ac, Tr-dTpdT-Ac, Tr-dTpdTpdT-Ac with 2,4,6-triisopropylbenzenesulfonyl chloride (TPS): 1) B type derivatives with phosphomono ester ( M E ) group converted to a phosphoryl pyridinium resi ...
MRSA Fact Sheet - Student Health Center
... bacteria lives on the skin or in the nasal passages of a healthy person but does not cause an infection. About 1% of the US population is colonized with MRSA. Non‐resistant Staph bacteria as well as MRSA can cause an infection when they enter the skin through a cut or a sore. The infection can ...
... bacteria lives on the skin or in the nasal passages of a healthy person but does not cause an infection. About 1% of the US population is colonized with MRSA. Non‐resistant Staph bacteria as well as MRSA can cause an infection when they enter the skin through a cut or a sore. The infection can ...
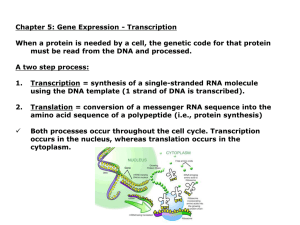
05_GENE_EXPRESSION
... Fairly stable Found in ribosomes Made as subunits in the nucleolus rRNA provides the platform from protein synthesis ...
... Fairly stable Found in ribosomes Made as subunits in the nucleolus rRNA provides the platform from protein synthesis ...
Ester - SCH4U-SRB
... Esters are responsible for the “fruity” odours and flavours of many naturally occurring products. Chemists can reproduce these odours or flavours in the lab by mixing the right alcohol and carboxylic acid together; thus, producing “artificial” or “synthetic” versions of these naturally occurring com ...
... Esters are responsible for the “fruity” odours and flavours of many naturally occurring products. Chemists can reproduce these odours or flavours in the lab by mixing the right alcohol and carboxylic acid together; thus, producing “artificial” or “synthetic” versions of these naturally occurring com ...
Synthesis of the hexoses
... route has a decisive advantage. Combined with the benzenethiolate opening reaction, trans-2,Bepoxy alcohols give erythro-2,3-diols and cis-2,3-epoxy alcohols give three-2,3-diols. ...
... route has a decisive advantage. Combined with the benzenethiolate opening reaction, trans-2,Bepoxy alcohols give erythro-2,3-diols and cis-2,3-epoxy alcohols give three-2,3-diols. ...
Paper chromatography and electrophoresis
... Chromatography separates small molecules in a mixture on the basis of size As the solvent moves up the paper, molecules move at different rates When the spots are colourless (most amino acids), a locating agent is needed to visualise their positions on the chromatography paper ...
... Chromatography separates small molecules in a mixture on the basis of size As the solvent moves up the paper, molecules move at different rates When the spots are colourless (most amino acids), a locating agent is needed to visualise their positions on the chromatography paper ...
Friedel-Crafts Alkylations (Exp.II)
... 4. is soluble in dilute HCl solution? 5. is soluble only in conc H2SO4? 6. is not soluble in any of the above solvents? ...
... 4. is soluble in dilute HCl solution? 5. is soluble only in conc H2SO4? 6. is not soluble in any of the above solvents? ...
PHL 224 Biochemistry II
... 2. Solubility: Most of the amino acids are usually soluble in water and insoluble in organic solvents. 3. Melting points: Amino acids generally melt at higher temperatures, often above 200°C. 4. Taste: Amino acids may be sweet (Gly, Ala, Val), tasteless (Leu) or bitter (Arg, lle). Monosodium glutama ...
... 2. Solubility: Most of the amino acids are usually soluble in water and insoluble in organic solvents. 3. Melting points: Amino acids generally melt at higher temperatures, often above 200°C. 4. Taste: Amino acids may be sweet (Gly, Ala, Val), tasteless (Leu) or bitter (Arg, lle). Monosodium glutama ...
Multistep Small-Molecule Synthesis Programmed by
... methods used to purify reaction products are not suitable for synthesis on the molecular biology (picograms to micrograms) scale. To address the first of these challenges, we implemented three distinct strategies for linking chemical reagents with their decoding DNA oligonucleotides, inspired by pre ...
... methods used to purify reaction products are not suitable for synthesis on the molecular biology (picograms to micrograms) scale. To address the first of these challenges, we implemented three distinct strategies for linking chemical reagents with their decoding DNA oligonucleotides, inspired by pre ...
Chemical Synthesis of Oligonucleotides
... Scale refers to the amount of starting material which is composed solely of the 3’-most nucleotide of a sequence attached to a solid support used to make the oligonucleotide. Yield refers to the amount of final product recovered after all the synthesis, processing, and purification steps associated ...
... Scale refers to the amount of starting material which is composed solely of the 3’-most nucleotide of a sequence attached to a solid support used to make the oligonucleotide. Yield refers to the amount of final product recovered after all the synthesis, processing, and purification steps associated ...
Protein Synthesis I
... 2. When that codon is read, enzyme stops translation and essentially cuts off the protein so no new amino acid is added to the growing polypeptide chain d. The looseness of these codes is remarkable, but there is a reason we will discuss e. This is classic redundancy i. You would call this degenerat ...
... 2. When that codon is read, enzyme stops translation and essentially cuts off the protein so no new amino acid is added to the growing polypeptide chain d. The looseness of these codes is remarkable, but there is a reason we will discuss e. This is classic redundancy i. You would call this degenerat ...
Bottromycin

Bottromycin is a macrocyclic peptide with antibiotic activity. It was first discovered in 1957 as a natural product isolated from Streptomyces bottropensis. It has been shown to inhibit methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) and vancomycin-resistant Enterococci (VRE) among other Gram-positive bacteria and mycoplasma. Bottromycin is structurally distinct from both vancomycin, a glycopeptide antibiotic, and methicillin, a beta-lactam antibiotic.Bottromycin binds to the A site of the ribosome and blocks the binding of aminoacyl-tRNA, therefore inhibiting bacterial protein synthesis. Although bottromycin exhibits antibacterial activity in vitro, it has not yet been developed as a clinical antibiotic, potentially due to its poor stability in blood plasma. To increase its stability in vivo, some bottromycin derivatives have been explored.The structure of bottromycin contains a macrocyclic amidine as well as a thiazole ring. The absolute stereochemistry at several chiral centers has been determined as of 2009. In 2012, a three-dimensional solution structure of bottromycin was published. The solution structure revealed that several methyl groups are on the same face of the structure.Bottromycin falls within the ribosomally synthesized and post-translationally modified peptide class of natural product.