CH 2 OH
... Carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids are called macromolecules because of ...
... Carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids are called macromolecules because of ...
Remodeling of the natural product fumagillol
... Further optimization using La(OTf)3 and Zn(OTf)2 catalysts was next pursued. The transformations were robust and did not require inert atmosphere, nor special precautions for anhydrous solvent. Other nonpolar solvents provided similar regioselectivity, though toluene proved to be optimal, in which c ...
... Further optimization using La(OTf)3 and Zn(OTf)2 catalysts was next pursued. The transformations were robust and did not require inert atmosphere, nor special precautions for anhydrous solvent. Other nonpolar solvents provided similar regioselectivity, though toluene proved to be optimal, in which c ...
Application of IBX Method for the Synthesis of Ketones from
... changed into its chloride. Then the acid chloride reacts with an organometallic reagent or gives a FriedelCrafts type reaction in the presence of Lewis acids. These methods are very useful for most aliphatic acid halides and good yields can be obtained in this way. However, if this method is used fo ...
... changed into its chloride. Then the acid chloride reacts with an organometallic reagent or gives a FriedelCrafts type reaction in the presence of Lewis acids. These methods are very useful for most aliphatic acid halides and good yields can be obtained in this way. However, if this method is used fo ...
102 Lecture Ch17
... • Because esters can’t H-bond with themselves, they have lower boiling points than carboxylic acids and alcohols • However, they are fairly polar, and have higher boiling points than ethers or hydrocarbons (similar to aldehydes and ketones) • Esters with less than 5 carbons are somewhat soluble in w ...
... • Because esters can’t H-bond with themselves, they have lower boiling points than carboxylic acids and alcohols • However, they are fairly polar, and have higher boiling points than ethers or hydrocarbons (similar to aldehydes and ketones) • Esters with less than 5 carbons are somewhat soluble in w ...
3 | biological macromolecules
... Benefits of Carbohydrates Are carbohydrates good for you? People who wish to lose weight are often told that carbohydrates are bad for them and should be avoided. Some diets completely forbid carbohydrate consumption, claiming that a low-carbohydrate diet helps people to lose weight faster. However, ...
... Benefits of Carbohydrates Are carbohydrates good for you? People who wish to lose weight are often told that carbohydrates are bad for them and should be avoided. Some diets completely forbid carbohydrate consumption, claiming that a low-carbohydrate diet helps people to lose weight faster. However, ...
The Basics: In Vitro Translation
... folding studies, and incorporation of modified or unnatural amino acids for functional studies. The use of in vitro translation systems can have advantages over in vivo gene expression when the over-expressed product is toxic to the host cell, when the product is insoluble or forms inclusion bodies, ...
... folding studies, and incorporation of modified or unnatural amino acids for functional studies. The use of in vitro translation systems can have advantages over in vivo gene expression when the over-expressed product is toxic to the host cell, when the product is insoluble or forms inclusion bodies, ...
Ch.17Outline_001
... Parent chain is the longest that includes -COOH Change “e” at the end of alkane name to “oic acid” Monocarboxylic acids (alkanoic acid) Dicarboxylic acids (alkanedioic acid) Aromatic carboxylic acids (benzoic acid) Common - names are related to the common source of the acid ...
... Parent chain is the longest that includes -COOH Change “e” at the end of alkane name to “oic acid” Monocarboxylic acids (alkanoic acid) Dicarboxylic acids (alkanedioic acid) Aromatic carboxylic acids (benzoic acid) Common - names are related to the common source of the acid ...
Friedel-Crafts Alkylations (Exp.II)
... Proton NMR Chemical Shifts () For 1H NMR, the scale generally extends from 0-12 ppm (TMS standard) • Simple hydrocarbon protons absorb in the region 0.5-1.5 • Protons on a carbon adjacent to a carbonyl are shifted to 2 (acetone!) ...
... Proton NMR Chemical Shifts () For 1H NMR, the scale generally extends from 0-12 ppm (TMS standard) • Simple hydrocarbon protons absorb in the region 0.5-1.5 • Protons on a carbon adjacent to a carbonyl are shifted to 2 (acetone!) ...
pdf
... that in total catalyze five enzymatic steps, converting chorismic acid to tryptophan. However, there is not a 1:1 correspondence between a cistron and an enzyme. For example, trpB and trpA encode, respectively, the β and α subunits of tryptophan synthase, which catalyzes the replacement of glycerol- ...
... that in total catalyze five enzymatic steps, converting chorismic acid to tryptophan. However, there is not a 1:1 correspondence between a cistron and an enzyme. For example, trpB and trpA encode, respectively, the β and α subunits of tryptophan synthase, which catalyzes the replacement of glycerol- ...
Module 3 Regulation of Gene Expression in Prokaryotes
... but the ribosome is stalled at the trp codons in leader peptide due to absence of trp-tRNA. Region 2/3 stemloop forms, preventing formation of the 3/4 transcription termination stem-loop. This allows expression of the trp operon structural genes. ...
... but the ribosome is stalled at the trp codons in leader peptide due to absence of trp-tRNA. Region 2/3 stemloop forms, preventing formation of the 3/4 transcription termination stem-loop. This allows expression of the trp operon structural genes. ...
Demonstrate skill in organic chemistry techniques.
... Use the mechanism, thermodynamics, and kinetics of a reaction to predict which of several possible products is the major product. Identify reactive intermediates and explain their properties. ...
... Use the mechanism, thermodynamics, and kinetics of a reaction to predict which of several possible products is the major product. Identify reactive intermediates and explain their properties. ...
Computational Docking Experiments to Find a Ligand that Will Bind
... kcal/mol and is positioned significantly different than the original ligand (Fig. 4D). However, the Carboxylic Acid #8 (derivative) has a significantly higher affinity value (-6.7 kcal/mol) than the allopurinol and is positioned just slightly different from the original ligand. This suggests that Ca ...
... kcal/mol and is positioned significantly different than the original ligand (Fig. 4D). However, the Carboxylic Acid #8 (derivative) has a significantly higher affinity value (-6.7 kcal/mol) than the allopurinol and is positioned just slightly different from the original ligand. This suggests that Ca ...
Reactions of 2, 6-cycloheptadienone and 2, 7
... aldehyde and acetonedicarboxylic acid, Robinson' also noted '(that tropinone might result.. .by the addition of methylamine to a cycloheptadienone. . . . I ' Yearly 10 years ago, Hor&k2reported the characterization by paper chromatography of tropinone prepared from a large excess of methylamine and ...
... aldehyde and acetonedicarboxylic acid, Robinson' also noted '(that tropinone might result.. .by the addition of methylamine to a cycloheptadienone. . . . I ' Yearly 10 years ago, Hor&k2reported the characterization by paper chromatography of tropinone prepared from a large excess of methylamine and ...
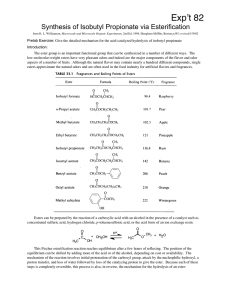
Synthesis of Isobutyl Propionate via Esterification
... we can, by Le Chatelier's principle, increase the concentration of either the alcohol or acid, as noted above. If either one is doubled, the theoretical yield increases to 85%. When one is tripled, it goes to 90%. But note that in the example cited the boiling point of the relatively nonpolar ester ...
... we can, by Le Chatelier's principle, increase the concentration of either the alcohol or acid, as noted above. If either one is doubled, the theoretical yield increases to 85%. When one is tripled, it goes to 90%. But note that in the example cited the boiling point of the relatively nonpolar ester ...
... cameras are allowed in the class room. The violators might loose points from the total points. (6) No eating food inside the class (7) Must bring scientific calculators and books. (8) The students must be seated separately enough during the quiz or exam period. Class Environment: Talking is complete ...
Unit 3 Outcome 1
... strategies. Provide examples for each strategy that can be used to encourage behavioural change and reduce PA barriers Question 9 In the paragraph below, options to complete each sentence are given within the brackets. Circle the correct option in each case. The advantage of measuring physical activ ...
... strategies. Provide examples for each strategy that can be used to encourage behavioural change and reduce PA barriers Question 9 In the paragraph below, options to complete each sentence are given within the brackets. Circle the correct option in each case. The advantage of measuring physical activ ...
Chapter 17 Protein Synthesis
... called the template strand, provides a template for ordering the sequence of complementary nucleotides in an RNA transcript • The template strand is always the same strand for a given gene • During translation, the mRNA base triplets, called codons, are read in the 5 to 3 direction ...
... called the template strand, provides a template for ordering the sequence of complementary nucleotides in an RNA transcript • The template strand is always the same strand for a given gene • During translation, the mRNA base triplets, called codons, are read in the 5 to 3 direction ...
Proteins, the Essence of Life
... point the mRNA is an immature mRNA molecule and must be processed. In eukaryotic genes, there are nucleotides that are not used or expressed. One might view these DNA nucleotides as “junk DNA”. They are called introns because they are intervening sequences. RNA polymerase can not tell the difference ...
... point the mRNA is an immature mRNA molecule and must be processed. In eukaryotic genes, there are nucleotides that are not used or expressed. One might view these DNA nucleotides as “junk DNA”. They are called introns because they are intervening sequences. RNA polymerase can not tell the difference ...
Chemistry 212 — Fall Semester 1996 Examination #2
... Formic acid, HCOOH, also known as _____methanoic acid__________ in the IUPAC nomenclature, is the simplest carboxylic acid. Considering HCOOH, let us review a few properties of carboxylic acids. (a) Boiling Points. The molecular mass of HCOOH is 46 and very close to the molecular mass of 44 of propa ...
... Formic acid, HCOOH, also known as _____methanoic acid__________ in the IUPAC nomenclature, is the simplest carboxylic acid. Considering HCOOH, let us review a few properties of carboxylic acids. (a) Boiling Points. The molecular mass of HCOOH is 46 and very close to the molecular mass of 44 of propa ...
Organic Chemistry III Laboratory
... H-NMR can distinguish between the cis and trans diastereomers produced in these reduction reactions. The hydrogen on the carbon bearing the hydroxyl group will have a different chemical shift depending upon whether it is in an axial or equatorial position. Coupling constants can be used to determine ...
... H-NMR can distinguish between the cis and trans diastereomers produced in these reduction reactions. The hydrogen on the carbon bearing the hydroxyl group will have a different chemical shift depending upon whether it is in an axial or equatorial position. Coupling constants can be used to determine ...
Bottromycin

Bottromycin is a macrocyclic peptide with antibiotic activity. It was first discovered in 1957 as a natural product isolated from Streptomyces bottropensis. It has been shown to inhibit methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) and vancomycin-resistant Enterococci (VRE) among other Gram-positive bacteria and mycoplasma. Bottromycin is structurally distinct from both vancomycin, a glycopeptide antibiotic, and methicillin, a beta-lactam antibiotic.Bottromycin binds to the A site of the ribosome and blocks the binding of aminoacyl-tRNA, therefore inhibiting bacterial protein synthesis. Although bottromycin exhibits antibacterial activity in vitro, it has not yet been developed as a clinical antibiotic, potentially due to its poor stability in blood plasma. To increase its stability in vivo, some bottromycin derivatives have been explored.The structure of bottromycin contains a macrocyclic amidine as well as a thiazole ring. The absolute stereochemistry at several chiral centers has been determined as of 2009. In 2012, a three-dimensional solution structure of bottromycin was published. The solution structure revealed that several methyl groups are on the same face of the structure.Bottromycin falls within the ribosomally synthesized and post-translationally modified peptide class of natural product.