CHM 3200 - Miami Dade College
... Course Description: This one-semester course briefly examines the structure, synthesis, nomenclature and reactivity of selected mono- and poly-functional organic compounds. Theories that relate the structure of organic molecules to their chemical reactivity will be presented as a unifying principle. ...
... Course Description: This one-semester course briefly examines the structure, synthesis, nomenclature and reactivity of selected mono- and poly-functional organic compounds. Theories that relate the structure of organic molecules to their chemical reactivity will be presented as a unifying principle. ...
Pdf
... have noteworthy impact on network predictions of secondary structure. As a straightforward implementation of this general idea, we have designed the following highly simplified network. The input representation for each amino acid is a 5-bit binary number ordered to reflect one of the following scal ...
... have noteworthy impact on network predictions of secondary structure. As a straightforward implementation of this general idea, we have designed the following highly simplified network. The input representation for each amino acid is a 5-bit binary number ordered to reflect one of the following scal ...
Classification of Halogen Derivatives
... On the basis of the nature of the carbon to which halogen atom is attached, halogen derivatives are classified as 1°, 2°, 3°, allylic, benzylic, vinylic and aryl derivatives, e.g., ...
... On the basis of the nature of the carbon to which halogen atom is attached, halogen derivatives are classified as 1°, 2°, 3°, allylic, benzylic, vinylic and aryl derivatives, e.g., ...
Carboxylic Acids Theory Sheet
... Carboxylic acids are compounds with the formula of that illustrated in Figure 1 and the general formula R-COOH where R is part of a larger organic molecule e.g.CH3, C2H5, C6H5. To name carboxylic acids you must look at the alkyl chain, take its prefix and add “oic acid” to it. CH3CH2COOH is PROPANOI ...
... Carboxylic acids are compounds with the formula of that illustrated in Figure 1 and the general formula R-COOH where R is part of a larger organic molecule e.g.CH3, C2H5, C6H5. To name carboxylic acids you must look at the alkyl chain, take its prefix and add “oic acid” to it. CH3CH2COOH is PROPANOI ...
Single Amino Acids as Additives Modulating CaCO3 Mineralization
... sulphur group. Proline has a unique structure among the twenty amino acids because of its secondary α-amino group. The cyclic structure of proline shows nonpolar behavior. Serine is a polar amino acid due to the hydroxyl group in the side chain. Valine is an essential amino acid. Together with leuci ...
... sulphur group. Proline has a unique structure among the twenty amino acids because of its secondary α-amino group. The cyclic structure of proline shows nonpolar behavior. Serine is a polar amino acid due to the hydroxyl group in the side chain. Valine is an essential amino acid. Together with leuci ...
electron microscopic autoradiographic study of rna synthesis in
... published data [2, 31 that the dense crescent of the yeast nucleus may be functioning as a nucleolus. The loose and sponge-like structure of the dense crescent may be related to the high rate of synthesis of ribosomal RNA in exponentially growing yeast. The nucleus of the yeast cell is very actively ...
... published data [2, 31 that the dense crescent of the yeast nucleus may be functioning as a nucleolus. The loose and sponge-like structure of the dense crescent may be related to the high rate of synthesis of ribosomal RNA in exponentially growing yeast. The nucleus of the yeast cell is very actively ...
A. Acid Halides
... HCl is usually formed as a by-product. A weak base like pyridine (C5H5N) is added to the reaction mixture to remove the strong acid (HCl), forming an ammonium salt. ...
... HCl is usually formed as a by-product. A weak base like pyridine (C5H5N) is added to the reaction mixture to remove the strong acid (HCl), forming an ammonium salt. ...
Specialty Chemicals and Food Additives
... pathway and sophisticated rDNA techniques that are available should facilitate strain construction in the enterobacteria. As for constructing a tryptophan-producing Corynebacterium, basic understanding of the synthetic pathway and development of a vector system remain to be achieved. Manipulating an ...
... pathway and sophisticated rDNA techniques that are available should facilitate strain construction in the enterobacteria. As for constructing a tryptophan-producing Corynebacterium, basic understanding of the synthetic pathway and development of a vector system remain to be achieved. Manipulating an ...
Ribosome engineering to promote new crystal forms
... protein. Structural understanding of this process was greatly advanced by the determination of the complete structures of the 50S ribosomal subunit from Haloarcula marismortui (Ban et al., 2000) and the 30S ribosomal subunit from Thermus thermophilus (Wimberly et al., 2000). Subsequently, these stru ...
... protein. Structural understanding of this process was greatly advanced by the determination of the complete structures of the 50S ribosomal subunit from Haloarcula marismortui (Ban et al., 2000) and the 30S ribosomal subunit from Thermus thermophilus (Wimberly et al., 2000). Subsequently, these stru ...
mRNA
... • The flow of information from gene to protein is based on a triplet code: a series of nonoverlapping, three-nucleotide words • These triplets are the smallest units of uniform length that can code for all the amino acids • Example: AGT at a particular position on a DNA strand results in the placeme ...
... • The flow of information from gene to protein is based on a triplet code: a series of nonoverlapping, three-nucleotide words • These triplets are the smallest units of uniform length that can code for all the amino acids • Example: AGT at a particular position on a DNA strand results in the placeme ...
What is Bee Venom?
... There Gram (+) bacteria; Staphylococcus aureus, Bacillus subtilis and Listeria monocytogenes and two Gram (-); Escherichia coli and Salmonella enteritidis were used ...
... There Gram (+) bacteria; Staphylococcus aureus, Bacillus subtilis and Listeria monocytogenes and two Gram (-); Escherichia coli and Salmonella enteritidis were used ...
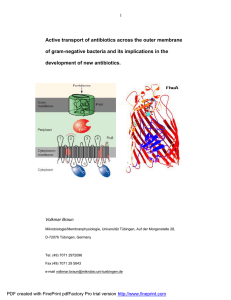
Active transport of antibiotics across the outer membrane of gram
... the cytoplasmic membrane. After transport into the cytoplasm, iron is released from albomycin, and the thioribosyl pyrimidine group has to be cleaved from the carrier to be inhibitory; in E. coli, this is mainly achieved by peptidase N. Mutants devoid of peptidase N activity are resistant to albomyc ...
... the cytoplasmic membrane. After transport into the cytoplasm, iron is released from albomycin, and the thioribosyl pyrimidine group has to be cleaved from the carrier to be inhibitory; in E. coli, this is mainly achieved by peptidase N. Mutants devoid of peptidase N activity are resistant to albomyc ...
FTIR Spectoscopy of Ca++ DOPED Alq3 OLED Phospor
... cm-1 by averaging 500 scans at a maximum resolution of 20 C-N Amines. The presence of C-O is revealed by the peak at cm-1 as shown in Fig 2. In case of the polycrystalline 1115.69.The peaks between the range 1000 -400 reveals the samples, scattering due to crystalline is responsible for the bending ...
... cm-1 by averaging 500 scans at a maximum resolution of 20 C-N Amines. The presence of C-O is revealed by the peak at cm-1 as shown in Fig 2. In case of the polycrystalline 1115.69.The peaks between the range 1000 -400 reveals the samples, scattering due to crystalline is responsible for the bending ...
INTRODUCTION - Open Access Repository of Indian Theses
... existing ones is an important subject of recent research in Organic Chemistry. These are aimed mainly for selectivity, and mild reaction conditions for the synthesis and conversion of bioactive natural products. Several classical synthetic methodologies involve expensive reagents and catalysts, whic ...
... existing ones is an important subject of recent research in Organic Chemistry. These are aimed mainly for selectivity, and mild reaction conditions for the synthesis and conversion of bioactive natural products. Several classical synthetic methodologies involve expensive reagents and catalysts, whic ...
An Overview of Carbonyl Compound Chemistry
... base as the catalyst. In most cases for esters or derivatives less reactive than esters, for example, hydrolysis of esters, amides, and nitriles, either acids or bases would be added to accelerate the rates of reactions. Also be aware that under these conditions proton transfer(s) can easily occur o ...
... base as the catalyst. In most cases for esters or derivatives less reactive than esters, for example, hydrolysis of esters, amides, and nitriles, either acids or bases would be added to accelerate the rates of reactions. Also be aware that under these conditions proton transfer(s) can easily occur o ...
Lesson Plan: Synthesis of Isopentyl Acetate
... Esters are a class of compounds found widely in nature. Low molecular weight esters tend to have characteristic flavors and pleasant odors that are most often associated with essential oils, even though essential oils are a complex mixture. ...
... Esters are a class of compounds found widely in nature. Low molecular weight esters tend to have characteristic flavors and pleasant odors that are most often associated with essential oils, even though essential oils are a complex mixture. ...
DIGESTIVE PROTEASES OF TWO SPtrCIES OF WASPS OF THE
... acids.The trypsin in the worker and male wasps was demonstrated. inhibited by 0.4 mM TLCK (Figs. 1(a),1(d)),indicating similarity between the V germanicatrypsin and Mitlptut proteaseuctiuity oJ'Y. maculifrons The trypsin-like activities of V. maculifrons were bovine trypsin. The range of inhibition ...
... acids.The trypsin in the worker and male wasps was demonstrated. inhibited by 0.4 mM TLCK (Figs. 1(a),1(d)),indicating similarity between the V germanicatrypsin and Mitlptut proteaseuctiuity oJ'Y. maculifrons The trypsin-like activities of V. maculifrons were bovine trypsin. The range of inhibition ...
Tech Info - Davis Instruments
... have to NMR as an analytical tool. While the technical aspects of executing the aldol reaction are not difficult, the analysis of products is challenging since this is frequently a student's first time using NMR instrumentation, interpreting NMR spectra and evaluating the outcome of their synthetic ...
... have to NMR as an analytical tool. While the technical aspects of executing the aldol reaction are not difficult, the analysis of products is challenging since this is frequently a student's first time using NMR instrumentation, interpreting NMR spectra and evaluating the outcome of their synthetic ...
Abstracts - Thieme Verlag
... Hydroformylation of alkenes is a mild and clean method for the functionalization of hydrocarbons and has grown to be among the most important homogeneously catalyzed reactions in industry. It is a 100% atom-economic reaction to prepare aldehydes that are important synthons for organic synthesis, and ...
... Hydroformylation of alkenes is a mild and clean method for the functionalization of hydrocarbons and has grown to be among the most important homogeneously catalyzed reactions in industry. It is a 100% atom-economic reaction to prepare aldehydes that are important synthons for organic synthesis, and ...
Case study from Almac
... •14C present in the skeleton of all drug molecules. • 14C is Detectable at very low concentrations (scintillation counting) • Long half life means no need for correction for radioactive decay. •3H is also used but is more subject to exchange. ...
... •14C present in the skeleton of all drug molecules. • 14C is Detectable at very low concentrations (scintillation counting) • Long half life means no need for correction for radioactive decay. •3H is also used but is more subject to exchange. ...
Bottromycin

Bottromycin is a macrocyclic peptide with antibiotic activity. It was first discovered in 1957 as a natural product isolated from Streptomyces bottropensis. It has been shown to inhibit methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) and vancomycin-resistant Enterococci (VRE) among other Gram-positive bacteria and mycoplasma. Bottromycin is structurally distinct from both vancomycin, a glycopeptide antibiotic, and methicillin, a beta-lactam antibiotic.Bottromycin binds to the A site of the ribosome and blocks the binding of aminoacyl-tRNA, therefore inhibiting bacterial protein synthesis. Although bottromycin exhibits antibacterial activity in vitro, it has not yet been developed as a clinical antibiotic, potentially due to its poor stability in blood plasma. To increase its stability in vivo, some bottromycin derivatives have been explored.The structure of bottromycin contains a macrocyclic amidine as well as a thiazole ring. The absolute stereochemistry at several chiral centers has been determined as of 2009. In 2012, a three-dimensional solution structure of bottromycin was published. The solution structure revealed that several methyl groups are on the same face of the structure.Bottromycin falls within the ribosomally synthesized and post-translationally modified peptide class of natural product.