Study Guide Unit 4 - Mrs. Wolodkowicz`s Biological Realm
... autosome, & sex linkage. the components of DNA the nitrogen bases & their complementary base pairs in DNA & RNA functions of tRNA & mRNA the laws of segregation & independent assortment the terms: dominant, recessive, genotype, phenotype, homozygous, heterozygous, heredity, genetics, pureb ...
... autosome, & sex linkage. the components of DNA the nitrogen bases & their complementary base pairs in DNA & RNA functions of tRNA & mRNA the laws of segregation & independent assortment the terms: dominant, recessive, genotype, phenotype, homozygous, heterozygous, heredity, genetics, pureb ...
Frontiers of Genetics
... species, into a single DNA molecule • Bacteria have small circular pieces of DNA called plasmids separate from their larger single chromosome • Plasmids can replicate and pass between bacterial cells allowing gene sharing – associated with antibacterial resistance ...
... species, into a single DNA molecule • Bacteria have small circular pieces of DNA called plasmids separate from their larger single chromosome • Plasmids can replicate and pass between bacterial cells allowing gene sharing – associated with antibacterial resistance ...
Diversity of Saccharomyces cerevisiae
... Differences in organelle genomes or composition Presence of extrachromosomal circular and linear nucleic acids Inherited transcriptional states Inherited protein conformational states ...
... Differences in organelle genomes or composition Presence of extrachromosomal circular and linear nucleic acids Inherited transcriptional states Inherited protein conformational states ...
Plant Transformation
... kanamycin-resistant transformants (Fig A) • difficult to identify (tag) a promoter that is active only during a certain developmental stage or that is induced by a specific ...
... kanamycin-resistant transformants (Fig A) • difficult to identify (tag) a promoter that is active only during a certain developmental stage or that is induced by a specific ...
gene control regions?
... Introns Evolution: Early vs Late? Getting Bigger or Getting Smaller? Both genes have identical Patterns of introns (66) -Illustrate… -Common ancestor -If not early, at least they’ve been around for a while… Human HD = 180,000 bps F. Rubripes HD = 24,000 bps -Difference due to intron size Difference ...
... Introns Evolution: Early vs Late? Getting Bigger or Getting Smaller? Both genes have identical Patterns of introns (66) -Illustrate… -Common ancestor -If not early, at least they’ve been around for a while… Human HD = 180,000 bps F. Rubripes HD = 24,000 bps -Difference due to intron size Difference ...
Gen.1303 Genome: The total genetic content contained in a haploid
... A threadlike linear strand of DNA and associated proteins in the nucleus of eukaryotic cells that carries the genes and functions in the transmission of hereditary information. A circular strand of DNA in bacteria that contains the hereditary information necessary for cell life. Gene: A hereditary u ...
... A threadlike linear strand of DNA and associated proteins in the nucleus of eukaryotic cells that carries the genes and functions in the transmission of hereditary information. A circular strand of DNA in bacteria that contains the hereditary information necessary for cell life. Gene: A hereditary u ...
Binary Switches in Gene Expression: The Histone Code
... human genome exists within every cell, only a small percentage of genes are activated in any given cell type. These different gene expression profiles are formulated during early development in a multicellular organism, when cell division, cell differentiation, tissue and organ formation rapidly occ ...
... human genome exists within every cell, only a small percentage of genes are activated in any given cell type. These different gene expression profiles are formulated during early development in a multicellular organism, when cell division, cell differentiation, tissue and organ formation rapidly occ ...
Genetic engineering - Association of the British Pharmaceutical
... genetic engineering Since genetic engineering (also known as recombinant DNA technology or genetic modification) was first developed in the 1970s, scientists have discovered more and more ways in which the technology can be used in human medicine. Now techniques, including the gene editing tool know ...
... genetic engineering Since genetic engineering (also known as recombinant DNA technology or genetic modification) was first developed in the 1970s, scientists have discovered more and more ways in which the technology can be used in human medicine. Now techniques, including the gene editing tool know ...
Document
... - Shotgun cloning: one first clones a large number of DNA fragments, knowing that one or more contains the DNA of interest. - Gene library: a collection of clones containing all the DNA fragments from one source Creating a genomic DNA library ...
... - Shotgun cloning: one first clones a large number of DNA fragments, knowing that one or more contains the DNA of interest. - Gene library: a collection of clones containing all the DNA fragments from one source Creating a genomic DNA library ...
Genetic Engineering
... source of genetic variability • Occur spontaneously • Use of radiation, chemicals • Hard to get desired mutants ...
... source of genetic variability • Occur spontaneously • Use of radiation, chemicals • Hard to get desired mutants ...
Name - Schuette Science
... 1. What is the name of the first process to take place during the synthesis of protein? 2. What is manufactured as a result of this process? ...
... 1. What is the name of the first process to take place during the synthesis of protein? 2. What is manufactured as a result of this process? ...
Statistical tests in Gene Set Analysis
... Gene set analysis is widely used to facilitate biological interpretations in the analyses of differential expression from high throughput profiling data. Wilcoxon Rank-Sum (WRS) test is one of the commonly used methods in gene set enrichment analysis because it is easy to implement and it eliminates ...
... Gene set analysis is widely used to facilitate biological interpretations in the analyses of differential expression from high throughput profiling data. Wilcoxon Rank-Sum (WRS) test is one of the commonly used methods in gene set enrichment analysis because it is easy to implement and it eliminates ...
Biology 325: Genetics
... Prokaryotic Gene Regulation: To enable bacteria to respond to their environments, transcription initiation is turned on and off mainly by trans-acting proteins; gene expression is also regulated after initiation by cis- or transacting RNAs, or trans-acting proteins. Eukaryotic Gene Regulation: Multi ...
... Prokaryotic Gene Regulation: To enable bacteria to respond to their environments, transcription initiation is turned on and off mainly by trans-acting proteins; gene expression is also regulated after initiation by cis- or transacting RNAs, or trans-acting proteins. Eukaryotic Gene Regulation: Multi ...
High throughput gene sequencing to identify new genes that cause
... myopathies. The life-threatening congenital myopathies are present in all populations, affecting children as well as adults. Considerable progress in human genetics within the past 25 years led to the identification of the molecular basis for 50% of these pathologies. However, the causative mutation ...
... myopathies. The life-threatening congenital myopathies are present in all populations, affecting children as well as adults. Considerable progress in human genetics within the past 25 years led to the identification of the molecular basis for 50% of these pathologies. However, the causative mutation ...
Leaving Cert Biology Notes - Genetics Definitions
... A nucleus having two sets / of chromosomes (NOT having pairs) ...
... A nucleus having two sets / of chromosomes (NOT having pairs) ...
DNA Sequencing
... 6. As part of a routine medical procedure, your doctor discovers that you have a rare, beneficial variant of a protein that protects you from heart disease. Should your doctor be able to patent the protein? 7. Should you be entitled to any money from the ...
... 6. As part of a routine medical procedure, your doctor discovers that you have a rare, beneficial variant of a protein that protects you from heart disease. Should your doctor be able to patent the protein? 7. Should you be entitled to any money from the ...
CHAPTER OUTLINE
... engineering is when we clone genes and then use them to alter the genome (complete genetic makeup of an organism) of viruses and cells. The Cloning of a Gene Gene cloning is the production of many identical copies of a single gene. Transgenic organisms are those with foreign DNA or genes inserted in ...
... engineering is when we clone genes and then use them to alter the genome (complete genetic makeup of an organism) of viruses and cells. The Cloning of a Gene Gene cloning is the production of many identical copies of a single gene. Transgenic organisms are those with foreign DNA or genes inserted in ...
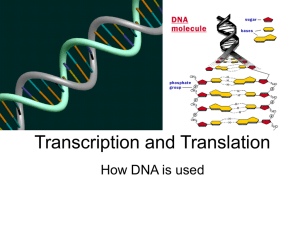
Transcription and Translation
... • DNA unwinds, and separates to expose 1 side of the code. • mRNA is built by connecting nucleotides 1 at a time that are complimentary to the code. • RNA replaces (T)hymine with (U)racil so it can leave the nucleus. ...
... • DNA unwinds, and separates to expose 1 side of the code. • mRNA is built by connecting nucleotides 1 at a time that are complimentary to the code. • RNA replaces (T)hymine with (U)racil so it can leave the nucleus. ...
Unit 4 Part2 wksht3
... 2. What do we call the new DNA that has the gene added to it? _________________________________ ...
... 2. What do we call the new DNA that has the gene added to it? _________________________________ ...
The Future of Genetics Research - Blyth-Biology11
... • Over 50% of genome is repeating sequences • Very little genetic variation within our species – 99.9% of all humans is exactly the same ...
... • Over 50% of genome is repeating sequences • Very little genetic variation within our species – 99.9% of all humans is exactly the same ...