Genetics and Genetic Engineering
... change the function of cells by inserting their DNA into the DNA of the cell ...
... change the function of cells by inserting their DNA into the DNA of the cell ...
E coli
... • Bacterial chromosome is a large (4 Mb in E coli) circular molecule • Bacterial cells may also contain small circular chromosomes called plasmids (4kb - 100kb; 1 - 1000 copies) that code for optional functions such as antibiotic resistance • Will look at circular DNA in this lecture • The bacterial ...
... • Bacterial chromosome is a large (4 Mb in E coli) circular molecule • Bacterial cells may also contain small circular chromosomes called plasmids (4kb - 100kb; 1 - 1000 copies) that code for optional functions such as antibiotic resistance • Will look at circular DNA in this lecture • The bacterial ...
Learning Guide:
... o Describe how gene regulation is like conducting an orchestra. Bacteria often respond to environmental change by regulating transcription o Explain why bacteria express only the genes whose products are needed by the cell. o List the three parts of an operon and explain the role of each one. o Di ...
... o Describe how gene regulation is like conducting an orchestra. Bacteria often respond to environmental change by regulating transcription o Explain why bacteria express only the genes whose products are needed by the cell. o List the three parts of an operon and explain the role of each one. o Di ...
Gene Expression
... and effectively remove it before it can be translated into protein • Exon shuffling – one gene encodes for different proteins – depends on which exons translation machinery “keeps” • Protein folding – one protein can be folded differently to have different functions – depends on enzymes and chaperon ...
... and effectively remove it before it can be translated into protein • Exon shuffling – one gene encodes for different proteins – depends on which exons translation machinery “keeps” • Protein folding – one protein can be folded differently to have different functions – depends on enzymes and chaperon ...
DNA/Strawberry Lab Write the question and answers on your own
... will filter out of your solution and you will actually see DNA. Write a brief description of what you think the DNA will look like. _____________________________________________________________________________ ANSWER THESE QUESTIONS AFTER YOU FINISH THE LAB: 1. What was the purpose of mashing the st ...
... will filter out of your solution and you will actually see DNA. Write a brief description of what you think the DNA will look like. _____________________________________________________________________________ ANSWER THESE QUESTIONS AFTER YOU FINISH THE LAB: 1. What was the purpose of mashing the st ...
Reverse genetics - From protein or RNA to gene Up until
... regulating different cellular functions, but share sequences based on the activity of one component as a histidine protein kinase, and of the other component as a substrate. Degenerate PCR primers designed to match the consensus sequences of conserved motifs have been used to isolate genes encoding ...
... regulating different cellular functions, but share sequences based on the activity of one component as a histidine protein kinase, and of the other component as a substrate. Degenerate PCR primers designed to match the consensus sequences of conserved motifs have been used to isolate genes encoding ...
Lecture 3: More Transmission Genetics
... (indicates a dominant disease) and males and females are both about equally affected (indicates autosomal inheritance) ...
... (indicates a dominant disease) and males and females are both about equally affected (indicates autosomal inheritance) ...
Problem Set
... baldness in humans. After reading several reviews on DNA microarray technology, you decide that performing microarray studies on skin biopsies from wookie starwarius would be your method of choice for this work. However, these studies pose certain technical and theoretical problems: 1) Being a new s ...
... baldness in humans. After reading several reviews on DNA microarray technology, you decide that performing microarray studies on skin biopsies from wookie starwarius would be your method of choice for this work. However, these studies pose certain technical and theoretical problems: 1) Being a new s ...
9 Genomics and Beyond
... (2) The DNA fragments must overlap other fragments, so the restriction enzyme is not allowed to cut at every possible restriction site. (3) Computers assemble the fragments into contigs by determining which DNA pieces have bands that are common. (4) Unique regions of DNA can also be used to identify ...
... (2) The DNA fragments must overlap other fragments, so the restriction enzyme is not allowed to cut at every possible restriction site. (3) Computers assemble the fragments into contigs by determining which DNA pieces have bands that are common. (4) Unique regions of DNA can also be used to identify ...
DNA Control Mechanisms
... D. Heterochromatin - This refers to DNA that remains condensed even during interphase. – It is NOT active. 1. This CANNOT do transcription so it is inactivated. (“hetero” means “different”) E. Euchromatin - This refers to DNA that IS loose during interphase. – It IS active. 1. It CAN do transcriptio ...
... D. Heterochromatin - This refers to DNA that remains condensed even during interphase. – It is NOT active. 1. This CANNOT do transcription so it is inactivated. (“hetero” means “different”) E. Euchromatin - This refers to DNA that IS loose during interphase. – It IS active. 1. It CAN do transcriptio ...
Ab_initio_predition_tools - Compgenomics2010
... • Viterbi algorithm then calculates the functional sequence X* such that P(X*|S) is the largest among all possible values of X. • Ribosome binding site model was also added to augment accuracy in the prediction of translational start sites. ...
... • Viterbi algorithm then calculates the functional sequence X* such that P(X*|S) is the largest among all possible values of X. • Ribosome binding site model was also added to augment accuracy in the prediction of translational start sites. ...
DNA Sequencing
... Chemical degradation of purified fragments (chemical degradation) The single stranded DNA fragment to be sequenced is end-labeled by treatment with alkaline phosphatase to remove the 5’phosphate It is then followed by reaction with P-labeled ATP in the presence of polynucleotide kinase, which att ...
... Chemical degradation of purified fragments (chemical degradation) The single stranded DNA fragment to be sequenced is end-labeled by treatment with alkaline phosphatase to remove the 5’phosphate It is then followed by reaction with P-labeled ATP in the presence of polynucleotide kinase, which att ...
Microbial Genetics
... • Gene product refers to the actual structures, enzymes or regulators. • Most gene products will be a polypeptide, which fold-up into functions proteins. • The instructions are manifest as a unique sequence of nucleotide base pairs within a larger DNA molecule. • A universal genetic code is followed ...
... • Gene product refers to the actual structures, enzymes or regulators. • Most gene products will be a polypeptide, which fold-up into functions proteins. • The instructions are manifest as a unique sequence of nucleotide base pairs within a larger DNA molecule. • A universal genetic code is followed ...
Nucleic Acids and DNA Replication
... • A always to T (with 2 hydrogen bonds) • C always to G (with 3 hydrogen bonds) • Chargraff’s Rule: for any given species the % of Ts will by equivalent of the % of As while the % of Cs will be equivalent to the % of Gs ...
... • A always to T (with 2 hydrogen bonds) • C always to G (with 3 hydrogen bonds) • Chargraff’s Rule: for any given species the % of Ts will by equivalent of the % of As while the % of Cs will be equivalent to the % of Gs ...
Chromatin Structure and Function
... B. Histone H1 is involved in 30 nm fiber formation. Binds to DNA and surface of nucleosome and helps condense chromatin. ...
... B. Histone H1 is involved in 30 nm fiber formation. Binds to DNA and surface of nucleosome and helps condense chromatin. ...
Genome Annotation - Virginia Commonwealth University
... Match genomic DNA to genes that have been previously cloned and sequenced looking for sequence similarity using BLAST programs Predict genes using computer programs to scan genomic DNA using known elements Many strategies use a combination of both methods ...
... Match genomic DNA to genes that have been previously cloned and sequenced looking for sequence similarity using BLAST programs Predict genes using computer programs to scan genomic DNA using known elements Many strategies use a combination of both methods ...
B3a Worksheet 3: DNA - School
... Genetic engineering – cut and paste! Here is a description of how bacteria can be genetically engineered to produce human insulin. Insulin is needed for the treatment of diabetics. Many bacterial cells contain rings of DNA, which are called plasmids. These plasmids can be used in genetic engineering ...
... Genetic engineering – cut and paste! Here is a description of how bacteria can be genetically engineered to produce human insulin. Insulin is needed for the treatment of diabetics. Many bacterial cells contain rings of DNA, which are called plasmids. These plasmids can be used in genetic engineering ...
Document
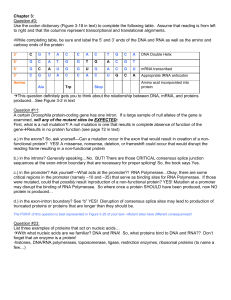
... A certain Drosophila protein-coding gene has one intron. If a large sample of null alleles of the gene is examined, will any of the mutant sites be EXPECTED: First, what is a null mutation?! A null mutation is one that results in complete absence of function of the geneResults in no protein functio ...
... A certain Drosophila protein-coding gene has one intron. If a large sample of null alleles of the gene is examined, will any of the mutant sites be EXPECTED: First, what is a null mutation?! A null mutation is one that results in complete absence of function of the geneResults in no protein functio ...
Human Genome Project
... generate a probe. – Extract mRNA – Reverse transcribe it (RNA complementary DNA ...
... generate a probe. – Extract mRNA – Reverse transcribe it (RNA complementary DNA ...
Slide 1
... Cell wall contains openings that let food go in and waste goes out through its pores. ...
... Cell wall contains openings that let food go in and waste goes out through its pores. ...
Bio 262- Genetics Study Guide
... (T). In nature, base pairs form only between A and T and between G and C; thus the base sequence of each single strand can be deduced from that of its partner. DNA fingerprinting: a unique pattern of dna fragments as revealed by southern hybridization or by the polymerase chain reaction. DNA replica ...
... (T). In nature, base pairs form only between A and T and between G and C; thus the base sequence of each single strand can be deduced from that of its partner. DNA fingerprinting: a unique pattern of dna fragments as revealed by southern hybridization or by the polymerase chain reaction. DNA replica ...
Gene Set Enrichment Analysis
... point where most different from zero Most significantly down-regulated genes ...
... point where most different from zero Most significantly down-regulated genes ...