9.5 Genomics and Bioinformatics
... • Genomics is the study of genomes. – can include the sequencing of the genome – comparisons of genomes within and across species ...
... • Genomics is the study of genomes. – can include the sequencing of the genome – comparisons of genomes within and across species ...
9.5 Genomics and Bioinformatics KEY CONCEPT Entire genomes are sequenced, studied, and compared.
... and entire genomes. • Genomics is the study of genomes. – can include the sequencing of the genome – comparisons of genomes within and across species ...
... and entire genomes. • Genomics is the study of genomes. – can include the sequencing of the genome – comparisons of genomes within and across species ...
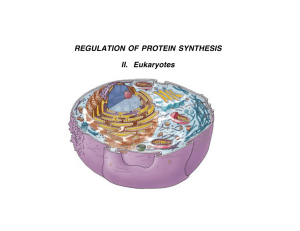
Honors Biology Unit 6 Ch. 10 “DNA, RNA & Protein synthesis”
... b. I can describe how DNA nucleotides are connected together to make DNA molecules. c. I can describe the structure of an RNA nucleotide and function of RNA. Vocabulary: double helix, nucleotide, deoxyribose, phosphate group, nitrogen base, thymine, cytosine, guanine, adenine, purine, pyrimidine 3. ...
... b. I can describe how DNA nucleotides are connected together to make DNA molecules. c. I can describe the structure of an RNA nucleotide and function of RNA. Vocabulary: double helix, nucleotide, deoxyribose, phosphate group, nitrogen base, thymine, cytosine, guanine, adenine, purine, pyrimidine 3. ...
Fact Sheet 3 | GENE MUTATIONS Genes contain the instructions for
... The way that a protein is made depends on the DNA messages in the gene. The three letter codons code for specific amino acids. It is these amino acids which build up to form the proteins. Codons do not always code for an amino acid. Some have other specialised messages for the cell such as stop or s ...
... The way that a protein is made depends on the DNA messages in the gene. The three letter codons code for specific amino acids. It is these amino acids which build up to form the proteins. Codons do not always code for an amino acid. Some have other specialised messages for the cell such as stop or s ...
Characteristics of Living Things (Essay
... Importance of each process Stages. What happens? When? Spermatogenesis & Oogenesis 2. DNA in different forms DNA basic structure. Remember nucleotides? Drawings? What is a gene? Centromere? Homologous Chromosomes 3. Mutations & Cancer & Aging Mutations: Good? Bad? Indifferent? Mutati ...
... Importance of each process Stages. What happens? When? Spermatogenesis & Oogenesis 2. DNA in different forms DNA basic structure. Remember nucleotides? Drawings? What is a gene? Centromere? Homologous Chromosomes 3. Mutations & Cancer & Aging Mutations: Good? Bad? Indifferent? Mutati ...
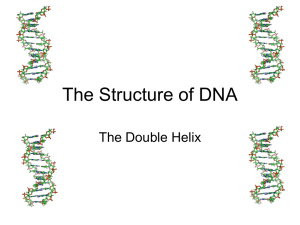
DNA Structure powerpoint
... • Why is DNA wrapped so tightly? • How are DNA, proteins, and traits related? ...
... • Why is DNA wrapped so tightly? • How are DNA, proteins, and traits related? ...
Protein synthesis
... 12. The second step is called _______________________________ and links _____________________________________ together to form a chain, which folds into a 3D structure to form a ______________________. Be sure to click through Transcription and Translation, too, not just the overview. What three reg ...
... 12. The second step is called _______________________________ and links _____________________________________ together to form a chain, which folds into a 3D structure to form a ______________________. Be sure to click through Transcription and Translation, too, not just the overview. What three reg ...
• •
... The mRNA codons GAA and GAG code for the amino acid Glutamic Acid (Glu). The mRNA codons GCU, GCC, GCA, and GCG all code for the amino acid Alanine (Ala). The mRNA codons GGU, GGC, GGA, and GGG all code for the amino acid Glycine (Gly). ...
... The mRNA codons GAA and GAG code for the amino acid Glutamic Acid (Glu). The mRNA codons GCU, GCC, GCA, and GCG all code for the amino acid Alanine (Ala). The mRNA codons GGU, GGC, GGA, and GGG all code for the amino acid Glycine (Gly). ...
Unit VII: Genetics
... ________ reads next _____ and brings in next tRNA with matching anticodon Since _____ is attached to ________ – two amino acids are located next to each other This proximity allows the ________________ Makes a _____________ Repeats until mRNA says stop ...
... ________ reads next _____ and brings in next tRNA with matching anticodon Since _____ is attached to ________ – two amino acids are located next to each other This proximity allows the ________________ Makes a _____________ Repeats until mRNA says stop ...
geneticengineering fall 2012 genetics unit
... WHAT IS GENETIC ENGINEERING IS USED FOR? Scientists uses genetic engineering to knock out certain genes from an organism in order to observe the effects and mutations caused by those genes. With the mapping of the human genome and the genomes of other important animals and plants, scientists ha ...
... WHAT IS GENETIC ENGINEERING IS USED FOR? Scientists uses genetic engineering to knock out certain genes from an organism in order to observe the effects and mutations caused by those genes. With the mapping of the human genome and the genomes of other important animals and plants, scientists ha ...
BIO 304 Genetics
... 8. scaffold______ A central core of non-histone proteins in the eukaryote chromosome from which loops of DNA project. 9. snRNA_______ This class of RNA is involved in pre-mRNA splicing in eukaryotes. 10. primer______ A short nucleic acid fragment that is extended at its 3’ end in DNA synthesis. 11. ...
... 8. scaffold______ A central core of non-histone proteins in the eukaryote chromosome from which loops of DNA project. 9. snRNA_______ This class of RNA is involved in pre-mRNA splicing in eukaryotes. 10. primer______ A short nucleic acid fragment that is extended at its 3’ end in DNA synthesis. 11. ...
Gene Cloning 2
... – Every time this cell reproduces, the recombinant plasmid is replicated as well and passed on to its descendents. – Under suitable conditions, the bacterial clone will make the protein encoded by the foreign gene. ...
... – Every time this cell reproduces, the recombinant plasmid is replicated as well and passed on to its descendents. – Under suitable conditions, the bacterial clone will make the protein encoded by the foreign gene. ...
Unit 2 DNA Outline - Westgate Mennonite Collegiate
... of DNA very quickly in a test tube without the use of a vector or a host cell. DNA Analysis DNA fingerprinting, STR profiling, and other applications of PCR can be used to determine the differing sequences of DNA nucleotides that exist between individuals. These techniques have many uses, including ...
... of DNA very quickly in a test tube without the use of a vector or a host cell. DNA Analysis DNA fingerprinting, STR profiling, and other applications of PCR can be used to determine the differing sequences of DNA nucleotides that exist between individuals. These techniques have many uses, including ...
Glossary Algae: Unicellular or simple multicellular photosynthetic
... molecule and associated proteins. Codon bias: Refers to the fact that not all codons are used equally frequently in the genes of a particular organism. Cytochrome: Any of several iron-containing protein pigments that serve as electron carriers in transport chains of photosynthesis and cellular respi ...
... molecule and associated proteins. Codon bias: Refers to the fact that not all codons are used equally frequently in the genes of a particular organism. Cytochrome: Any of several iron-containing protein pigments that serve as electron carriers in transport chains of photosynthesis and cellular respi ...
Szerkezetvizsgálati módszerek a biofizikában_2016_opt_mikr_1
... The basic plasmid vector configuration useful in fluorescent protein gene transfer experiments has several requisite components. The plasmid must contain prokaryotic nucleotide sequences coding for a bacterial replication origin for DNA and an antibiotic resistance gene. These elements, often termed ...
... The basic plasmid vector configuration useful in fluorescent protein gene transfer experiments has several requisite components. The plasmid must contain prokaryotic nucleotide sequences coding for a bacterial replication origin for DNA and an antibiotic resistance gene. These elements, often termed ...
flyer
... After data-processing, a shortlist of suspect mutations is referenced to selected DNA variation databases. These databases contain all published mutations and their clinical features. Expert laboratory geneticists then identify the disease-causing mutation(s). You will receive the results in a clear ...
... After data-processing, a shortlist of suspect mutations is referenced to selected DNA variation databases. These databases contain all published mutations and their clinical features. Expert laboratory geneticists then identify the disease-causing mutation(s). You will receive the results in a clear ...
(Genetics).
... For a number of years, scientists at Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory have been attempting to map every known human gene. By mapping, scientists mean that they are trying to find out on which of the 46 chromosomes each gene is located and exactly where on the chromosome the gene is located. By locating ...
... For a number of years, scientists at Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory have been attempting to map every known human gene. By mapping, scientists mean that they are trying to find out on which of the 46 chromosomes each gene is located and exactly where on the chromosome the gene is located. By locating ...
A diet rich in `nucleotides` would include foods
... accredited to Bill Gates, the creator of Microsoft, "DNA is like a computer program but far, far more advanced than any software ever created." Software is a set of instructions for a new program in a computer, likewise, DNA, contains a set of instructions for the assembly of parts, namely proteins, ...
... accredited to Bill Gates, the creator of Microsoft, "DNA is like a computer program but far, far more advanced than any software ever created." Software is a set of instructions for a new program in a computer, likewise, DNA, contains a set of instructions for the assembly of parts, namely proteins, ...
DNAandProteinSynthesis
... When the cell is ready to divide! • could be for growth, or to repair injury ...
... When the cell is ready to divide! • could be for growth, or to repair injury ...