Gene Section TRIAP1 (TP53 regulated inhibitor of apoptosis 1)
... shock protein 70 (HSP70), preventing the induction of apoptosis. When cells are submitted to low levels of genotoxic stress, it is an important player in P53mediated cell survivor pathway (Park and Nakamura, 2005; Felix et al., 2009). P53CSV can inhibit apoptosis through interaction with APAF1 and H ...
... shock protein 70 (HSP70), preventing the induction of apoptosis. When cells are submitted to low levels of genotoxic stress, it is an important player in P53mediated cell survivor pathway (Park and Nakamura, 2005; Felix et al., 2009). P53CSV can inhibit apoptosis through interaction with APAF1 and H ...
Now - Missouri State University
... called histones that can wind up a stretch of DNA so that the cell cannot make transcripts from it. All of the molecules that hang onto DNA, collectively known as epigenetic marks, are essential for cells to take their final form in the body. As an embryo matures, epigenetic marks in different cells ...
... called histones that can wind up a stretch of DNA so that the cell cannot make transcripts from it. All of the molecules that hang onto DNA, collectively known as epigenetic marks, are essential for cells to take their final form in the body. As an embryo matures, epigenetic marks in different cells ...
Name: ____________ Protein Synthesis Children`s Book Due
... Protein synthesis is one of the most important processes in an organism. As you’ve learned, it creates proteins needed for an organism to function. It is also a multi-step process that some students find difficult to remember. You, however, are going to have no problem mastering it! To simplify the ...
... Protein synthesis is one of the most important processes in an organism. As you’ve learned, it creates proteins needed for an organism to function. It is also a multi-step process that some students find difficult to remember. You, however, are going to have no problem mastering it! To simplify the ...
Studying Genomes
... One approach to locating genes is to use a DNA probe. This is a short section of DNA that has been labelled, for example with radioactive phosphorous or a fluorescent marker. The DNA is of a known sequence corresponding to the gene being looked for, for example the cystic fibrosis ...
... One approach to locating genes is to use a DNA probe. This is a short section of DNA that has been labelled, for example with radioactive phosphorous or a fluorescent marker. The DNA is of a known sequence corresponding to the gene being looked for, for example the cystic fibrosis ...
Biotechnology and Genetic Engineering
... 1. Produce genetically modify plants and animals by inserting desirable genes from one organism into the DNA of another organism. ...
... 1. Produce genetically modify plants and animals by inserting desirable genes from one organism into the DNA of another organism. ...
DNA Microarray - Montana State University
... Simon, R., Radmacher, M.D., Dobbin, K., & McShane, L.M. Pitfalls in the Use of DNA Microarray Data for Diagnostic and Prognostic Classification. Journal of the National Cancer Institute. 95. ...
... Simon, R., Radmacher, M.D., Dobbin, K., & McShane, L.M. Pitfalls in the Use of DNA Microarray Data for Diagnostic and Prognostic Classification. Journal of the National Cancer Institute. 95. ...
Ch. 13 - Genetic Engineering
... the cell, the external DNA gets incorporated into the bacterium’s own DNA. Recombinant DNA has been made. The cell has been transformed. It will make a new protein(s). ...
... the cell, the external DNA gets incorporated into the bacterium’s own DNA. Recombinant DNA has been made. The cell has been transformed. It will make a new protein(s). ...
organization of chromatin and the fate of a cell
... cells, muscle cells, brain cells, etc.) have exactly the same DNA, these cells function very differently. How is this achieved is not well understood. We now know that the fate of a cell is not just decided by the sequence of the DNA but also by the “state” of its chromatin. Chromatin is a 3-dimensi ...
... cells, muscle cells, brain cells, etc.) have exactly the same DNA, these cells function very differently. How is this achieved is not well understood. We now know that the fate of a cell is not just decided by the sequence of the DNA but also by the “state” of its chromatin. Chromatin is a 3-dimensi ...
RISE AND FALL OF GENE FAMILIES Dynamics of Their Expansion
... The comprehensive study of the interactions and functional dynamics of whole sets of genes and their products. (NIAAA, NIH) A "scaled-up" version of genetics research in which scientists can look at all of the genes in a living creature at the same time. (NIGMS, NIH) ...
... The comprehensive study of the interactions and functional dynamics of whole sets of genes and their products. (NIAAA, NIH) A "scaled-up" version of genetics research in which scientists can look at all of the genes in a living creature at the same time. (NIGMS, NIH) ...
BIOL212Experience1keyAPR2012
... 53.) What is a protein? (1 point) long chain molecules (polypeptides) of amino acids, includes enzymes 54.) What is a nucleic acid? (2 points) The components (other than sugar backbone) of DNA & RNA (for the four above, key has minimum answers.) 55.) How does the concept of descent with modification ...
... 53.) What is a protein? (1 point) long chain molecules (polypeptides) of amino acids, includes enzymes 54.) What is a nucleic acid? (2 points) The components (other than sugar backbone) of DNA & RNA (for the four above, key has minimum answers.) 55.) How does the concept of descent with modification ...
File - RBV Honors Biology 2016-2017
... How many chromosomes does a somatic (body cells) human chromosome cell have? How many chromosomes does a human gamete (sperm or egg) have? What is the difference between diploid and haploid? What are homologous chromosomes? What are sister chromatids? Describe what happens during crossing over. What ...
... How many chromosomes does a somatic (body cells) human chromosome cell have? How many chromosomes does a human gamete (sperm or egg) have? What is the difference between diploid and haploid? What are homologous chromosomes? What are sister chromatids? Describe what happens during crossing over. What ...
SGN tutorial - Sol Genomics Network
... information available, including general information about this group of plants (for example, click on “What are Solanaceae?”), a newsletter for scientists interested in this project, upcoming meetings, but also very specific higher-level scientific information that is only relevant (or even underst ...
... information available, including general information about this group of plants (for example, click on “What are Solanaceae?”), a newsletter for scientists interested in this project, upcoming meetings, but also very specific higher-level scientific information that is only relevant (or even underst ...
DNA plasmid minipreps - How it works: Solution I: 50 mM glucose
... - The positively charged potassium ions are used in ethanol precipitation to shield the negative charge on the phosphate backbone of the DNA. As a result, non-ionic, hydrophobic interactions take place which provoke aggregation of the DNA. - Potassium acetate is more effective than sodium acetate, b ...
... - The positively charged potassium ions are used in ethanol precipitation to shield the negative charge on the phosphate backbone of the DNA. As a result, non-ionic, hydrophobic interactions take place which provoke aggregation of the DNA. - Potassium acetate is more effective than sodium acetate, b ...
Slide 1
... Basic studies to reveal conditions and mechanisms involved in induction of akinetes formation, dormancy and desiccation: Nutrient Depletion (P), Light, Temp, O2 (hypoxia) Specialized envelopes Storage of metabolites [carbohydrates, cyanophycin (N)] – enzymes involved, e.g cyanophycine synthase Toler ...
... Basic studies to reveal conditions and mechanisms involved in induction of akinetes formation, dormancy and desiccation: Nutrient Depletion (P), Light, Temp, O2 (hypoxia) Specialized envelopes Storage of metabolites [carbohydrates, cyanophycin (N)] – enzymes involved, e.g cyanophycine synthase Toler ...
Slide 1 - Loyola Blakefield
... • Biotechnology is the manipulation of organisms or their components to provide useful products or perform practical tasks ...
... • Biotechnology is the manipulation of organisms or their components to provide useful products or perform practical tasks ...
THE CHROMOSOMAL BASIS OF INHERITANCE
... 1. A white-eyed female fruit-fly is mated with a red• Barr body eyed male. What genotypes and phenotypes do you predict for the offspring? • SRY gene • Linked genes ...
... 1. A white-eyed female fruit-fly is mated with a red• Barr body eyed male. What genotypes and phenotypes do you predict for the offspring? • SRY gene • Linked genes ...
recombinant dna technology
... THE SAME STICKY ENDS CARRIED BY THE FRAGMENTS • MIXING THE FRAGMENTS WITH THE CUT PLASMIDS ALLOWS BASE-PAIRING AT THE STICKY ENDS. • APPLICATION OF DNA LIGASE STABILIZES THE ATTACHMENT. • THE RECOMBINANT PLASMID IS THEN INTRODUCED INTO A BACTERIUM BY TRANSFORMATION ...
... THE SAME STICKY ENDS CARRIED BY THE FRAGMENTS • MIXING THE FRAGMENTS WITH THE CUT PLASMIDS ALLOWS BASE-PAIRING AT THE STICKY ENDS. • APPLICATION OF DNA LIGASE STABILIZES THE ATTACHMENT. • THE RECOMBINANT PLASMID IS THEN INTRODUCED INTO A BACTERIUM BY TRANSFORMATION ...
File - MRS. WILSON Science
... nucleus. Certain enzymes start to unzip the double helix at places called origins of replication. The double helix unzips in both directions along the strand. Eukaryotic chromosomes are very long, so they have many origins of replication to help speed the process. Other proteins hold the two strands ...
... nucleus. Certain enzymes start to unzip the double helix at places called origins of replication. The double helix unzips in both directions along the strand. Eukaryotic chromosomes are very long, so they have many origins of replication to help speed the process. Other proteins hold the two strands ...
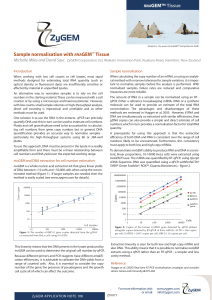
Sample normalisation with RNAGEM™ Tissue
... Ploidy and cell growth-phase need to be accounted for in calculating cell numbers from gene copy number, but in general, DNA quantification provides an accurate way to normalise samples particularly for high-throughput systems using 96 or 384-well plates. To use this approach, DNA must be present in ...
... Ploidy and cell growth-phase need to be accounted for in calculating cell numbers from gene copy number, but in general, DNA quantification provides an accurate way to normalise samples particularly for high-throughput systems using 96 or 384-well plates. To use this approach, DNA must be present in ...
DNA
... • The codons code for 20 amino acids • Just like the alphabet has 26 letters to make all the words we know, the 20 amino acids make all the different proteins found in living organisms •This makes it possible to have 64 different combinations for amino acids • The codons are the template for protein ...
... • The codons code for 20 amino acids • Just like the alphabet has 26 letters to make all the words we know, the 20 amino acids make all the different proteins found in living organisms •This makes it possible to have 64 different combinations for amino acids • The codons are the template for protein ...
CH 23 Part 2 Modern Genetics
... The polymerase chain reaction (PCR) copies a sequence of DNA. (a) A strand of DNA is mixed in solution with DNA precursors (nucleotides), a primer that targets a specific piece of DNA, and an enzyme (polymerase) that helps to assemble DNA. The mix is heated to 200°F to separate DNA strands. ...
... The polymerase chain reaction (PCR) copies a sequence of DNA. (a) A strand of DNA is mixed in solution with DNA precursors (nucleotides), a primer that targets a specific piece of DNA, and an enzyme (polymerase) that helps to assemble DNA. The mix is heated to 200°F to separate DNA strands. ...