Statements
... this is indeed, great news, our preferred outcome would have gone even further and found that any form of a gene is not patentable because it is the information content that is naturally occurring regardless of whether its genomic or cDNA. It is ACMG's long-standing position that genes and their mut ...
... this is indeed, great news, our preferred outcome would have gone even further and found that any form of a gene is not patentable because it is the information content that is naturally occurring regardless of whether its genomic or cDNA. It is ACMG's long-standing position that genes and their mut ...
Unit 10: Cell Biology, Molecular Biology, DNA NGSS Priority
... ELA/Literacy RST.11-12.1 Cite specific textual evidence to support analysis of science and technical texts, attending to important distinctions the author makes and to any gaps or inconsistencies in the account. WHST.9-12.9 Draw evidence from informational texts to support analysis, reflection, and ...
... ELA/Literacy RST.11-12.1 Cite specific textual evidence to support analysis of science and technical texts, attending to important distinctions the author makes and to any gaps or inconsistencies in the account. WHST.9-12.9 Draw evidence from informational texts to support analysis, reflection, and ...
Polyploid Genomics
... ◦ Gradual conversion from polyploidy to diploidy through genetic changes that differentiate duplicated loci ...
... ◦ Gradual conversion from polyploidy to diploidy through genetic changes that differentiate duplicated loci ...
Document
... they extrapolate back to 10 minutes. For thiL+, they extrapolate back to 20 minutes. Therefore, the distance between the two genes is approximately 10 minutes. S4. Genetic transfer via transformation can also be used to map genes along the bacterial chromosome. In this approach, fragments of chromos ...
... they extrapolate back to 10 minutes. For thiL+, they extrapolate back to 20 minutes. Therefore, the distance between the two genes is approximately 10 minutes. S4. Genetic transfer via transformation can also be used to map genes along the bacterial chromosome. In this approach, fragments of chromos ...
BIO 420 – Mammalian Physiology
... A. Dihybrid crosses involving at least one non-classical ratio will result in F2 progeny with altered ratios as well. B. Example – Inheritance of albinism and blood type in the same individual VI. Gene Interaction A. Definition – phenotype may be affected by more than one gene B. Epistasis – masking ...
... A. Dihybrid crosses involving at least one non-classical ratio will result in F2 progeny with altered ratios as well. B. Example – Inheritance of albinism and blood type in the same individual VI. Gene Interaction A. Definition – phenotype may be affected by more than one gene B. Epistasis – masking ...
Honors Biology Biotechnology Unit Homework/Pre
... What are the two forms of DNA found in bacteria? How many plasmids can be in a bacterial cell? Explain the 3 characteristics of plasmids that make them ideal vectors for genetic engineering What 2 antibiotics will some of our plasmids have resistance to? and how exactly do they create this resistanc ...
... What are the two forms of DNA found in bacteria? How many plasmids can be in a bacterial cell? Explain the 3 characteristics of plasmids that make them ideal vectors for genetic engineering What 2 antibiotics will some of our plasmids have resistance to? and how exactly do they create this resistanc ...
5 In vivo gene cloning
... • Firstly, we must identify the bacteria containing the plasmids – we do this by growing the bacteria on a medium containing an antibiotic. • We know to which antibiotics the bacteria should be resistant. No plasmid = no resistance! ...
... • Firstly, we must identify the bacteria containing the plasmids – we do this by growing the bacteria on a medium containing an antibiotic. • We know to which antibiotics the bacteria should be resistant. No plasmid = no resistance! ...
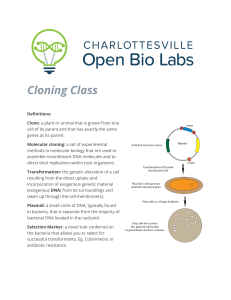
Cloning Class - Open Bio Labs
... The plate has an antibiotic on it that will kill everything without resistance to that specific antibiotic. The idea is that the bacteria cells do not have an innate resistance to the antibiotic so they would be killed upon contact. The plasmid DNA will usually contain a gene that will confer antibi ...
... The plate has an antibiotic on it that will kill everything without resistance to that specific antibiotic. The idea is that the bacteria cells do not have an innate resistance to the antibiotic so they would be killed upon contact. The plasmid DNA will usually contain a gene that will confer antibi ...
Cell Biology
... There will also be an optimum pH, and either above or below this, will cause the enzyme to denature. ...
... There will also be an optimum pH, and either above or below this, will cause the enzyme to denature. ...
Genetic Notes
... by the disease, but pass it on to their sons. These women are known as carriers. • X-chromosomes are larger so they carry more genes. The ability to see color is on the x-chromosome. ...
... by the disease, but pass it on to their sons. These women are known as carriers. • X-chromosomes are larger so they carry more genes. The ability to see color is on the x-chromosome. ...
Some abandoned Chinese patent applications
... highly GC-rich regions possible. However, such high concentration of glycerin may interfere with the activity of the DNA polymerase. It seems the invention is not practical and the application was abandoned. Amplification of This application discloses a method of DNA and improving the ramping and st ...
... highly GC-rich regions possible. However, such high concentration of glycerin may interfere with the activity of the DNA polymerase. It seems the invention is not practical and the application was abandoned. Amplification of This application discloses a method of DNA and improving the ramping and st ...
Physiology of Cells
... • Remaining portions (exons) are spliced back together • mRNA travels to the nucleus via nuclear pores ...
... • Remaining portions (exons) are spliced back together • mRNA travels to the nucleus via nuclear pores ...
Document
... Departures from strand symmetry or Chargaff asymmetries can be expressed by differences: (A-T)/(A+T) and (C-G)/(C+G) for each strand Strand symmetry originates from identical mutation/substitution processes affecting each strand ...
... Departures from strand symmetry or Chargaff asymmetries can be expressed by differences: (A-T)/(A+T) and (C-G)/(C+G) for each strand Strand symmetry originates from identical mutation/substitution processes affecting each strand ...
1) Semiconservative DNA replication means that A) each daughter
... DNA Replication/Transcription/Translation Quiz 1) Semiconservative DNA replication means that A) each daughter DNA molecule is composed of one original strand and one new strand. B) nucleotides are constantly being recycled as cells make DNA. C) the cell can proofread its newly synthesized DNA only ...
... DNA Replication/Transcription/Translation Quiz 1) Semiconservative DNA replication means that A) each daughter DNA molecule is composed of one original strand and one new strand. B) nucleotides are constantly being recycled as cells make DNA. C) the cell can proofread its newly synthesized DNA only ...
Gene Regulation - Cloudfront.net
... The operon can be switched off by a protein repressor The repressor prevents gene transcription by binding to the operator and blocking ...
... The operon can be switched off by a protein repressor The repressor prevents gene transcription by binding to the operator and blocking ...
Biotech quiz review
... What is the correct order? ____ Insert recombinant DNA into bacteria cells ____ Isolate desired product from bacteria cells ____ Cut plasmid and desired gene with the same ...
... What is the correct order? ____ Insert recombinant DNA into bacteria cells ____ Isolate desired product from bacteria cells ____ Cut plasmid and desired gene with the same ...
Leukaemia Section t(1;14)(q21;q32) IRTA1/IGH Atlas of Genetics and Cytogenetics in Oncology and Haematology
... alpha fusion protein results from this. The predicted fusion protein fuses the signal peptide and first two extracellular residues of IRTA1 to the C alpha encoded transmembrane and cytoplasmic domains. Overexpression of IRTA1 was not observed in other myeloma or lymphoma cell lines, regardless of th ...
... alpha fusion protein results from this. The predicted fusion protein fuses the signal peptide and first two extracellular residues of IRTA1 to the C alpha encoded transmembrane and cytoplasmic domains. Overexpression of IRTA1 was not observed in other myeloma or lymphoma cell lines, regardless of th ...