File - Wildcat Biology Review
... A group of individuals belonging to a single species that lives together in a defined area is termed a(an) ...
... A group of individuals belonging to a single species that lives together in a defined area is termed a(an) ...
Cells - SchoolRack
... – takes fluid from the spaces between cells and returns it to the circulatory system. It also filters bacteria and other microorganisms from this fluid. Reproductive – produces gamete cells (males = sperm, females = eggs) Respiratory – moves oxygen into the body and carbon dioxide out of the ...
... – takes fluid from the spaces between cells and returns it to the circulatory system. It also filters bacteria and other microorganisms from this fluid. Reproductive – produces gamete cells (males = sperm, females = eggs) Respiratory – moves oxygen into the body and carbon dioxide out of the ...
CH 20 DNA TECHNOLOGY - Ed W. Clark High School
... A. Recombinant DNA is DNA in which nucleotide sequences from two different sources are combined into one DNA molecule. B. The methods for making recombinant DNA is called genetic engjneering C. Biotechnology allows for the manipulation of organisms and their components to make useful products. II. U ...
... A. Recombinant DNA is DNA in which nucleotide sequences from two different sources are combined into one DNA molecule. B. The methods for making recombinant DNA is called genetic engjneering C. Biotechnology allows for the manipulation of organisms and their components to make useful products. II. U ...
RNAi - University of Maryland, College Park
... along with its use of genome sequence information, has dramatically changed how these tests are done. RNAi is a form of reverse genetics, meaning researchers can systematically pick genes rather than beginning with mutants and then searching for the genes affected. One major advantage of this method ...
... along with its use of genome sequence information, has dramatically changed how these tests are done. RNAi is a form of reverse genetics, meaning researchers can systematically pick genes rather than beginning with mutants and then searching for the genes affected. One major advantage of this method ...
II. Principles of Cell
... number of independent clones = genome size/average size insert For a human genomic DNA library of 40 kb average insert size ...
... number of independent clones = genome size/average size insert For a human genomic DNA library of 40 kb average insert size ...
Overview
... DoTS Gene Indices Are Based on Clustering and Assembling ESTs Identify new sequences In GenBank and dbEST •Remove vector, polyA tails, ribosomal and poor quality sequences •Mask repeats with RepeatMasker “Quality” AssemblySequences •BLAST N vs self •BLASTN vs DoT S •Connected components analysis to ...
... DoTS Gene Indices Are Based on Clustering and Assembling ESTs Identify new sequences In GenBank and dbEST •Remove vector, polyA tails, ribosomal and poor quality sequences •Mask repeats with RepeatMasker “Quality” AssemblySequences •BLAST N vs self •BLASTN vs DoT S •Connected components analysis to ...
BIG IDEA 3 3.A.1 Genetic information is transmitted from one
... iii. Each codon encodes a specific amino acid, which can be deduced by using a genetic code chart (it will be given to you). Many amino acids have more than one codon. v. tRNA brings the correct amino acid to the correct place on the mRNA. vi. The amino acid is transferred to the growing peptide cha ...
... iii. Each codon encodes a specific amino acid, which can be deduced by using a genetic code chart (it will be given to you). Many amino acids have more than one codon. v. tRNA brings the correct amino acid to the correct place on the mRNA. vi. The amino acid is transferred to the growing peptide cha ...
Chapter 13: The Genetic Code and Transcription
... Chemically similar amino acids often share one or two “middle” bases in the triplet encoding them. Hydrophobic amino acids, like valine and alanine, have either a U or C in their second position. Hydrophilic amino acids, like serine or threonine, are specified with either a G or C in the second posi ...
... Chemically similar amino acids often share one or two “middle” bases in the triplet encoding them. Hydrophobic amino acids, like valine and alanine, have either a U or C in their second position. Hydrophilic amino acids, like serine or threonine, are specified with either a G or C in the second posi ...
DNA/RNA/Protein Synthesis Study Guide
... and ______ have specific roles in this process. Structure B/G, known as __________, is important because it carries the DNA message from the (A)_____________ to the _______________. There, the (G) _________ attaches to the surface of (C) ___________, which is made partly of the second type of RNA, _ ...
... and ______ have specific roles in this process. Structure B/G, known as __________, is important because it carries the DNA message from the (A)_____________ to the _______________. There, the (G) _________ attaches to the surface of (C) ___________, which is made partly of the second type of RNA, _ ...
Protein Synthesis - BLI-Research-SynBio-2016-session-2
... RNA polymerase- complex of enzymes with 2 functions: • Unwind DNA sequence • Produce primary transcript by stringing together the chain of RNA nucleotides ...
... RNA polymerase- complex of enzymes with 2 functions: • Unwind DNA sequence • Produce primary transcript by stringing together the chain of RNA nucleotides ...
File
... A selectable marker will protect the organism from a selective agent that would normally kill it or prevent its growth. In most applications, only one in a several million or billion cells will take up DNA. Rather than checking every single cell, scientists use a selective agent to kill all cells th ...
... A selectable marker will protect the organism from a selective agent that would normally kill it or prevent its growth. In most applications, only one in a several million or billion cells will take up DNA. Rather than checking every single cell, scientists use a selective agent to kill all cells th ...
DNA and Cell Division - Student Note
... gives the directions to the cell directs cell growth, cell death, responses to changes in the environment and message to other cells ...
... gives the directions to the cell directs cell growth, cell death, responses to changes in the environment and message to other cells ...
Gene Tagging with Transposons
... • Transposable elements are stretches of DNA that can move to new locations in a genome • These elements can contain genes or be non-coding • Large portions of higher eukaryotes’ genomes are composed of either inert or active transposons (often as repetitive DNA) • Transposons are thus important evo ...
... • Transposable elements are stretches of DNA that can move to new locations in a genome • These elements can contain genes or be non-coding • Large portions of higher eukaryotes’ genomes are composed of either inert or active transposons (often as repetitive DNA) • Transposons are thus important evo ...
Document
... The final step in genetic engineering is to sequence a piece of DNA, or to read the sequence of bases. Only one strand of DNA double helix is used in this process. However, many copies of this strand is needed. Multiple copies of DNA strands can be produced by the process of DNA cloning. ...
... The final step in genetic engineering is to sequence a piece of DNA, or to read the sequence of bases. Only one strand of DNA double helix is used in this process. However, many copies of this strand is needed. Multiple copies of DNA strands can be produced by the process of DNA cloning. ...
DNA Lab Techniques
... of a group of genetically identical cells • May be produced by asexual reproduction (mitosis) ...
... of a group of genetically identical cells • May be produced by asexual reproduction (mitosis) ...
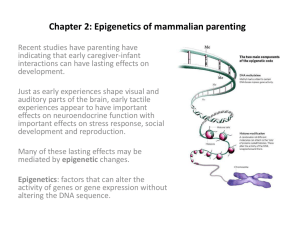
Chapter 2: Epigenetics of mammalian parenting
... • All these effects are traceable to changes in neurotransmitter receptor and activity levels in the brain. ...
... • All these effects are traceable to changes in neurotransmitter receptor and activity levels in the brain. ...
Ch 18 - Quia
... -Contains a 400-fold reduction in gaps -99% of euchromatic sequence -Error rate = 1 per 100,000 bases ...
... -Contains a 400-fold reduction in gaps -99% of euchromatic sequence -Error rate = 1 per 100,000 bases ...
Gral Regents Review Part 2
... Changes in chromosome structure may also cause disorders. For example, a chromosome may break, leading to a variety of new arrangements that affect its genes. ...
... Changes in chromosome structure may also cause disorders. For example, a chromosome may break, leading to a variety of new arrangements that affect its genes. ...