The Unseen Genome: Beyond DNA
... for the second layer, which consists of myriad “RNA only” genes sequestered within vast stretches of noncoding DNA. Science had dismissed such DNA as the useless detritus of evolution, because no proteins are made from it. But it turns out that these unconventional genes do give rise to active RNAs, ...
... for the second layer, which consists of myriad “RNA only” genes sequestered within vast stretches of noncoding DNA. Science had dismissed such DNA as the useless detritus of evolution, because no proteins are made from it. But it turns out that these unconventional genes do give rise to active RNAs, ...
Chapters 2-4
... 2. In codominance, alternative traits are both visible in the F1 hybrid 3. Variations on complete dominance do not negate Mendel’s law of segregation B. A gene may have more than two alleles mutations are the source of new alleles C. One gene may contribute to several visible characteristics. Some a ...
... 2. In codominance, alternative traits are both visible in the F1 hybrid 3. Variations on complete dominance do not negate Mendel’s law of segregation B. A gene may have more than two alleles mutations are the source of new alleles C. One gene may contribute to several visible characteristics. Some a ...
genes
... organism has. Gregor Mendel experimented with observable traits or characteristics. Each trait can be is controlled by at least two genes. Traits can be dominant or recessive depending upon the genes that make them up. ...
... organism has. Gregor Mendel experimented with observable traits or characteristics. Each trait can be is controlled by at least two genes. Traits can be dominant or recessive depending upon the genes that make them up. ...
Advanced Genetics: Karyotypes and Pedigrees
... • What is a karyotype? • What is the purpose of a karyotype? ...
... • What is a karyotype? • What is the purpose of a karyotype? ...
Mitochondrial Genome Evolution
... Mitochondrial phylogeny - a separate origin for plant mtDNA? Neurospora crassa Podospora anserina Aspergillus nidulans Saccharomyces cerevisiae ...
... Mitochondrial phylogeny - a separate origin for plant mtDNA? Neurospora crassa Podospora anserina Aspergillus nidulans Saccharomyces cerevisiae ...
Bio 102 Practice Problems
... 4. Sketch a purine nucleotide below. Label its three major parts, and indicate its 3´ and 5´ ends: 5. You have isolated the first bacterium from mars. Its DNA is a little different in structure from that of earthly organisms. Instead of our familiar A, T, C and G, you find that the organism’s DNA co ...
... 4. Sketch a purine nucleotide below. Label its three major parts, and indicate its 3´ and 5´ ends: 5. You have isolated the first bacterium from mars. Its DNA is a little different in structure from that of earthly organisms. Instead of our familiar A, T, C and G, you find that the organism’s DNA co ...
On the nature of the last common universal ancestor
... • No known virus has all the genes needed for the synthesis and replication of DNA. All viruses depend on the machineries of the infected cells. • Genes involved in DNA synthesis and replication have been transferred from the host cells towards the viruses that infect them. ...
... • No known virus has all the genes needed for the synthesis and replication of DNA. All viruses depend on the machineries of the infected cells. • Genes involved in DNA synthesis and replication have been transferred from the host cells towards the viruses that infect them. ...
Poster
... variable lengths for the sequences, but PreDetector doesn’t. It just takes the sequences « as it » and starts the generation of the matrix. The matrix should reflect the fact that nucleotides with higher frequencies at some position in the observed set should have a greater impact on the score on th ...
... variable lengths for the sequences, but PreDetector doesn’t. It just takes the sequences « as it » and starts the generation of the matrix. The matrix should reflect the fact that nucleotides with higher frequencies at some position in the observed set should have a greater impact on the score on th ...
Fall 2011 - Langara College
... 2. To understand the relationship between the structure and function of bacterial macromolecules. 3. To learn how bacteria differ from other organisms. 4. To learn to synthesize information and apply it to new situations.. 5. To enjoy and appreciate the microbial world! ...
... 2. To understand the relationship between the structure and function of bacterial macromolecules. 3. To learn how bacteria differ from other organisms. 4. To learn to synthesize information and apply it to new situations.. 5. To enjoy and appreciate the microbial world! ...
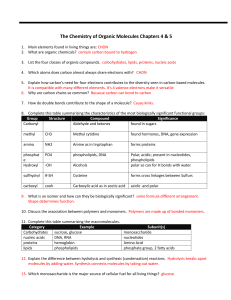
04-05 Biochem review sheet answers ws
... 3. List the four classes of organic compounds. carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, nucleic acids 4. Which atoms does carbon almost always share electrons with? CHON 5. Explain how carbon’s need for four electrons contributes to the diversity seen in carbon-based molecules. It is compatible with many di ...
... 3. List the four classes of organic compounds. carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, nucleic acids 4. Which atoms does carbon almost always share electrons with? CHON 5. Explain how carbon’s need for four electrons contributes to the diversity seen in carbon-based molecules. It is compatible with many di ...
File
... parent can produce at least 8 million different gametes. This is important for Variation. Then the 2 gametes combine during fertilization to produce a zygote (fertilized egg) with 2 sets of chromosomes (diploid). So all of us have 2 sets of information for each gene. These may be different alleles ...
... parent can produce at least 8 million different gametes. This is important for Variation. Then the 2 gametes combine during fertilization to produce a zygote (fertilized egg) with 2 sets of chromosomes (diploid). So all of us have 2 sets of information for each gene. These may be different alleles ...
APBiology 12
... Human lives are greatly affected by biotechnology, the manipulation of organisms or their components to make useful products. o Biotechnology includes such early practices as selective breeding of farm animals and the use of microorganisms to make wine and cheese. o Today, biotechnology also encom ...
... Human lives are greatly affected by biotechnology, the manipulation of organisms or their components to make useful products. o Biotechnology includes such early practices as selective breeding of farm animals and the use of microorganisms to make wine and cheese. o Today, biotechnology also encom ...
Chapter 20: Antimicrobial Drugs
... 5. The drug should be toxic to the undesired microorganisms and not harmful to the host (selective toxicity). The drug should be active against many microorganisms (broad spectrum). The drug should not produce hypersensitivity in the host. The drug should not produce drug resistance in the host. The ...
... 5. The drug should be toxic to the undesired microorganisms and not harmful to the host (selective toxicity). The drug should be active against many microorganisms (broad spectrum). The drug should not produce hypersensitivity in the host. The drug should not produce drug resistance in the host. The ...
the presentation
... colour, hair structure, overall construction anything that makes the dog different from the Asian Grey Wolf - are caused by mutations! ...
... colour, hair structure, overall construction anything that makes the dog different from the Asian Grey Wolf - are caused by mutations! ...
Schizophrenia and the prefrontal cortex
... Result: not really. There are gene expression changes as a result of intrauterine poly(I:C) exposure, but they are not common with the postmortem findings of ASD or schizophrenia. Question: is the immune activation seen in humans not an immune scar, but an active inflammatory process? ...
... Result: not really. There are gene expression changes as a result of intrauterine poly(I:C) exposure, but they are not common with the postmortem findings of ASD or schizophrenia. Question: is the immune activation seen in humans not an immune scar, but an active inflammatory process? ...
supplementary materials
... PCR from -710 to -1 nucleotides relative to the translation start site. The 5’ oligo is located 150 nucleotides in the RPP0 locus, an essential gene encoding a cytoplasmic component of the ribosome [6]. The 710 base-pair PCR construct containing the SPO77 promoter was cloned into the pCR2.1 TA cloni ...
... PCR from -710 to -1 nucleotides relative to the translation start site. The 5’ oligo is located 150 nucleotides in the RPP0 locus, an essential gene encoding a cytoplasmic component of the ribosome [6]. The 710 base-pair PCR construct containing the SPO77 promoter was cloned into the pCR2.1 TA cloni ...
Mutations - SchneiderSBI4U
... A point mutation could also result in the production of a stop codon in the middle of a gene If this occurs in an essential protein, such as hemoglobin, the mutation is lethal and is called a nonsense mutation Frameshift mutations are also normally lethal – the insertion or deletion of a nucleotide ...
... A point mutation could also result in the production of a stop codon in the middle of a gene If this occurs in an essential protein, such as hemoglobin, the mutation is lethal and is called a nonsense mutation Frameshift mutations are also normally lethal – the insertion or deletion of a nucleotide ...
Gene Set Enrichment Analysis
... Blue lines: various quantiles (same as before) across all GO class Compare with KS and modified KS (Right column. MIT, PNAS and Nature Gen.) Same data, same permutation!! ...
... Blue lines: various quantiles (same as before) across all GO class Compare with KS and modified KS (Right column. MIT, PNAS and Nature Gen.) Same data, same permutation!! ...
Chapter 6
... Mistakes in replication are rare, but each unrepaired mistake results in a mutation. Eucaryotic chromosomes are linear; however, in many bacteria (and all plasmids), the DNA is circular. On circular DNA, replication can be bidirectional; the two “replication forks,” traveling in opposite directions, ...
... Mistakes in replication are rare, but each unrepaired mistake results in a mutation. Eucaryotic chromosomes are linear; however, in many bacteria (and all plasmids), the DNA is circular. On circular DNA, replication can be bidirectional; the two “replication forks,” traveling in opposite directions, ...
Final lecture
... • HP1 is the key protein in forming mammalian heterochromatin, and acts by binding to methylated Structure from Protein Data Bank 1KNE. S. A. Jacobs histone H3. and S. Khorasanizadeh, Science 295 (2002): 20802083. ...
... • HP1 is the key protein in forming mammalian heterochromatin, and acts by binding to methylated Structure from Protein Data Bank 1KNE. S. A. Jacobs histone H3. and S. Khorasanizadeh, Science 295 (2002): 20802083. ...
Some Topics in Philosophy of Biology
... organisms are mobile and environments are not fixed (“niche construction” [see below] would need to be discussed here). This is not to deny that populations grow. Each population tends to produce more offspring that what would be necessary to replace the parent population. In other words, in general ...
... organisms are mobile and environments are not fixed (“niche construction” [see below] would need to be discussed here). This is not to deny that populations grow. Each population tends to produce more offspring that what would be necessary to replace the parent population. In other words, in general ...
Multicellularity
... “We were expecting many genes to be involved, working together in certain ways, because [the jump to multi-cellularity] seems like a really difficult thing to do,” he said. But it turned out that only one was needed: A single mutation that repurposed a certain type of protein. Instead of working as ...
... “We were expecting many genes to be involved, working together in certain ways, because [the jump to multi-cellularity] seems like a really difficult thing to do,” he said. But it turned out that only one was needed: A single mutation that repurposed a certain type of protein. Instead of working as ...
Technology Review (Cambridge, Mass
... After reading this chapter, you should be able to: ■ Describe how genes work, how they are expressed, and how they are inherited. Show the correlation between the chemical structure of a gene and its function. Discuss ways in which the location of a gene along a chromosome can be determined. Explain ...
... After reading this chapter, you should be able to: ■ Describe how genes work, how they are expressed, and how they are inherited. Show the correlation between the chemical structure of a gene and its function. Discuss ways in which the location of a gene along a chromosome can be determined. Explain ...
The Structure of DNA
... combinations of nitrogenous bases that form the “rungs” of DNA. • However, this does not restrict the sequence of nucleotides along each DNA strand. • The linear sequence of the four bases can be varied in countless ways. • Each gene has a unique order of nitrogen bases. • In April 1953, Watson and ...
... combinations of nitrogenous bases that form the “rungs” of DNA. • However, this does not restrict the sequence of nucleotides along each DNA strand. • The linear sequence of the four bases can be varied in countless ways. • Each gene has a unique order of nitrogen bases. • In April 1953, Watson and ...