Glossary
... Patterns of perturbation of the atomic coordinates for which the molecule will behave like a simple spring (with linear restoring force) in response. A protein’s normal modes with the lowest frequency of oscillation can be identified, and tend to be similar to frequently observed patterns of large c ...
... Patterns of perturbation of the atomic coordinates for which the molecule will behave like a simple spring (with linear restoring force) in response. A protein’s normal modes with the lowest frequency of oscillation can be identified, and tend to be similar to frequently observed patterns of large c ...
Statistical Analysis Using Scaffold - Proteome Software
... • Name and size of the database searched (Swisprot or NCBI and the number of sequence entries) • Name and version of any additional software used for statistical analysis and an explanation of the analysis (Scaffold, #peptide requirements, probability settings) ...
... • Name and size of the database searched (Swisprot or NCBI and the number of sequence entries) • Name and version of any additional software used for statistical analysis and an explanation of the analysis (Scaffold, #peptide requirements, probability settings) ...
high quality protein wrapped
... evaluation twenty years after the introduction of the protein digestibility corrected amino acid score method. Br J Nutr. 2012; 108 Suppl. 2: S183-211. 4. Protein quality evaluation : report of the joint FAO/WHO expert consulation, FAO Food and Nutrition Paper No. 51, 1989 5 Protein quality evaluati ...
... evaluation twenty years after the introduction of the protein digestibility corrected amino acid score method. Br J Nutr. 2012; 108 Suppl. 2: S183-211. 4. Protein quality evaluation : report of the joint FAO/WHO expert consulation, FAO Food and Nutrition Paper No. 51, 1989 5 Protein quality evaluati ...
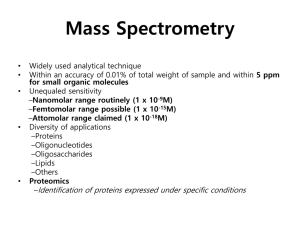
Mass Spectrometry
... A protein can be identified in a database by matching masses of a subset of the tryptic peptides against calculated values. ...
... A protein can be identified in a database by matching masses of a subset of the tryptic peptides against calculated values. ...
Chem 204
... Which of the following is least likely to result in protein denaturation, and explain why it is the least likely? A) Altering net charge by changing pH B) Changing the salt concentration C) Disruption of weak interactions by boiling D) Exposure to detergents E) Mixing with organic solvents such as a ...
... Which of the following is least likely to result in protein denaturation, and explain why it is the least likely? A) Altering net charge by changing pH B) Changing the salt concentration C) Disruption of weak interactions by boiling D) Exposure to detergents E) Mixing with organic solvents such as a ...
Tertiary structure
... The tertiary structure of a protein is stabilized by interactions between the R groups of the amino acids in one region of the polypeptide chain with R groups of amino acids in other regions of the protein. 1. Hydrophobic interactions are interactions between two nonpolar R groups. For example, hydr ...
... The tertiary structure of a protein is stabilized by interactions between the R groups of the amino acids in one region of the polypeptide chain with R groups of amino acids in other regions of the protein. 1. Hydrophobic interactions are interactions between two nonpolar R groups. For example, hydr ...
Immunogenicity
... developed involving computer algorithms that map the locations of MHC class I and class II-restricted T-cell epitopes within proteins of various origins. The in silico methods include frequency analysis, support-vector machines, hidden Markov models, and neural networks. MHC class II prediction meth ...
... developed involving computer algorithms that map the locations of MHC class I and class II-restricted T-cell epitopes within proteins of various origins. The in silico methods include frequency analysis, support-vector machines, hidden Markov models, and neural networks. MHC class II prediction meth ...
interrpo_nov16
... positions within a multiple sequence alignment • Patterns • Profiles • Profile HMMs Use these models (signatures) to infer relationships with the characterised sequences from which the alignment was constructed Approach used by a variety of databases: Pfam, TIGRFAMs, PANTHER, Prosite, etc ...
... positions within a multiple sequence alignment • Patterns • Profiles • Profile HMMs Use these models (signatures) to infer relationships with the characterised sequences from which the alignment was constructed Approach used by a variety of databases: Pfam, TIGRFAMs, PANTHER, Prosite, etc ...
printed handout sheet
... in turn promotes the release of glucose and free fatty acids into the bloodstream. 2. Short-term mechanisms based on catecholamine messengers and the autonomic nervous system are essential for the metabolic adaptation to physical exercise. Direct delivery of neurotransmitters to particular target ti ...
... in turn promotes the release of glucose and free fatty acids into the bloodstream. 2. Short-term mechanisms based on catecholamine messengers and the autonomic nervous system are essential for the metabolic adaptation to physical exercise. Direct delivery of neurotransmitters to particular target ti ...
2ABL
... Eigenvalue spectra for the matrix corresponding to the S1A serine protease family (top panel) and for a hundred trials for randomizing the S1A sequence alignment (bottom panel). The randomization process scrambles the order of amino acids in each alignment column independently; thus amino acid frequ ...
... Eigenvalue spectra for the matrix corresponding to the S1A serine protease family (top panel) and for a hundred trials for randomizing the S1A sequence alignment (bottom panel). The randomization process scrambles the order of amino acids in each alignment column independently; thus amino acid frequ ...
011S Product Info
... (H4) and heavy (D4) forms of the reagent differ by 4 deuterium atoms in heavy form instead of 4 hydrogen atoms of light form, and otherwise are chemically identical. Isotopic coding enables univocal detection of the PCAS-modified products in mass spectra. Reaction products of PCAS-H4/D4 will manifes ...
... (H4) and heavy (D4) forms of the reagent differ by 4 deuterium atoms in heavy form instead of 4 hydrogen atoms of light form, and otherwise are chemically identical. Isotopic coding enables univocal detection of the PCAS-modified products in mass spectra. Reaction products of PCAS-H4/D4 will manifes ...
Document
... Generation of a framework for the new sequence. Rebuild lacking loops. Complete and correct backbone. Correct and rebuild side chains. Verify model structure quality and check packing. Refine structure by energy minimisation and molecular dynamics. ...
... Generation of a framework for the new sequence. Rebuild lacking loops. Complete and correct backbone. Correct and rebuild side chains. Verify model structure quality and check packing. Refine structure by energy minimisation and molecular dynamics. ...
50695_1 - Griffith Research Online
... A protein is made up of a collection of amino acids, which are molecules that have both carboxyl and amino groups. An amino acid contains a carbon atom (Cα), and has four different connections, these include an amino group, carboxyl group, a hydrogen atom, and a side chain (this differs depending on ...
... A protein is made up of a collection of amino acids, which are molecules that have both carboxyl and amino groups. An amino acid contains a carbon atom (Cα), and has four different connections, these include an amino group, carboxyl group, a hydrogen atom, and a side chain (this differs depending on ...
inhibition of protein synthesis in cell-free systems by
... E. coli R2 was grown in shaking culture at 37 ° in a medium containing I 9'0 glucose, I 9'0 yeast extract, and 0.25 M potassium phosphate buffer (pH 6.5). The cells were harvested early in the log phase of growth in a Sharples centrifuge at IO ° and the paste obtained was stored at --20 °. The vario ...
... E. coli R2 was grown in shaking culture at 37 ° in a medium containing I 9'0 glucose, I 9'0 yeast extract, and 0.25 M potassium phosphate buffer (pH 6.5). The cells were harvested early in the log phase of growth in a Sharples centrifuge at IO ° and the paste obtained was stored at --20 °. The vario ...
Hydrophobic-Hydrophilic Forces and their Effects on Protein
... A protein is made up of a collection of amino acids, which are molecules that have both carboxyl and amino groups. An amino acid contains a carbon atom (Cα), and has four different connections, these include an amino group, carboxyl group, a hydrogen atom, and a side chain (this differs depending on ...
... A protein is made up of a collection of amino acids, which are molecules that have both carboxyl and amino groups. An amino acid contains a carbon atom (Cα), and has four different connections, these include an amino group, carboxyl group, a hydrogen atom, and a side chain (this differs depending on ...
Tumor Necrosis Factor- alpha (human, recombinant) CATALOG NO
... SUPPLIED AS: Sterile, filtered white lyophilized powder. The protein was lyophilized after extensive dialysis against 5mM Tris buffer pH 8.0. 10mg of HSA was added per mg TNF-alpha. RECONSTITUTION: Reconstitute the lyophilized TNF-alpha in sterile water to a concentration of 100µg/ml or higher, whic ...
... SUPPLIED AS: Sterile, filtered white lyophilized powder. The protein was lyophilized after extensive dialysis against 5mM Tris buffer pH 8.0. 10mg of HSA was added per mg TNF-alpha. RECONSTITUTION: Reconstitute the lyophilized TNF-alpha in sterile water to a concentration of 100µg/ml or higher, whic ...
Protein Structure and Function
... If the transition state can be bound more tightly than the substrate, activation energy will be reduced The differential binding of enzyme for these two state Is the driving force of reactions ...
... If the transition state can be bound more tightly than the substrate, activation energy will be reduced The differential binding of enzyme for these two state Is the driving force of reactions ...
File
... range of potential uses in construction and manufacturing. B The attraction of the silk spun by the spider is a combination of great strength and enormous elasticity, which man-made fibres have been unable to replicate. On an equal-weight basis, spider silk is far stronger than steel and it is estim ...
... range of potential uses in construction and manufacturing. B The attraction of the silk spun by the spider is a combination of great strength and enormous elasticity, which man-made fibres have been unable to replicate. On an equal-weight basis, spider silk is far stronger than steel and it is estim ...
Small G-protein
... Small GTP-binding proteins include (roles indicated): Compared to the subunit of heterotrimeric G-proteins, GTPase activity of the monomeric G-proteins is very low in the absence of interference. However, association with a protein of the GAP (GTPase-activating protein) type results in very rapid ...
... Small GTP-binding proteins include (roles indicated): Compared to the subunit of heterotrimeric G-proteins, GTPase activity of the monomeric G-proteins is very low in the absence of interference. However, association with a protein of the GAP (GTPase-activating protein) type results in very rapid ...
Erlanson et al. PNAS - UCSF Macromolecular Structure Group
... most are problematic because moderate affinity leads are difficult to obtain. Identifying and subsequently optimizing weaker binding compounds would improve the success rate, but screening at high concentrations is generally impractical because of compound insolubility and assay artifacts. Moreover, ...
... most are problematic because moderate affinity leads are difficult to obtain. Identifying and subsequently optimizing weaker binding compounds would improve the success rate, but screening at high concentrations is generally impractical because of compound insolubility and assay artifacts. Moreover, ...
Exam Questions_230516_final
... the normal translocation machinery. This protein has an N-terminal, 18-amino-acid hydrophilic segment that is located on the outside of the membrane, a 19-amino-acid hydrophobic transmembrane segment flanked by negatively and positively charged amino acids, and a C-terminal domain that resides inside ...
... the normal translocation machinery. This protein has an N-terminal, 18-amino-acid hydrophilic segment that is located on the outside of the membrane, a 19-amino-acid hydrophobic transmembrane segment flanked by negatively and positively charged amino acids, and a C-terminal domain that resides inside ...
Proteins are composed of amino acid subunits which form stable
... Proteins are composed of amino acid subunits which form stable three-dimensional structures. a. ...
... Proteins are composed of amino acid subunits which form stable three-dimensional structures. a. ...
Protein purification
Protein purification is a series of processes intended to isolate one or a few proteins from a complex mixture, usually cells, tissues or whole organisms. Protein purification is vital for the characterization of the function, structure and interactions of the protein of interest. The purification process may separate the protein and non-protein parts of the mixture, and finally separate the desired protein from all other proteins. Separation of one protein from all others is typically the most laborious aspect of protein purification. Separation steps usually exploit differences in protein size, physico-chemical properties, binding affinity and biological activity. The pure result may be termed protein isolate.The methods used in protein purification can roughly be divided into analytical and preparative methods. The distinction is not exact, but the deciding factor is the amount of protein that can practically be purified with that method. Analytical methods aim to detect and identify a protein in a mixture, whereas preparative methods aim to produce large quantities of the protein for other purposes, such as structural biology or industrial use. In general, the preparative methods can be used in analytical applications, but not the other way around.