DiRex Digital Imaging - Quantum Medical Imaging
... radiography combined with positioning flexibility inherent of a cassettebased system. Improved workflow, excellent image quality, and flexibility equal exceptional patient care, offered at an affordable total cost of ownership (TCO). ...
... radiography combined with positioning flexibility inherent of a cassettebased system. Improved workflow, excellent image quality, and flexibility equal exceptional patient care, offered at an affordable total cost of ownership (TCO). ...
In-laboratory diffraction-enhanced x-ray imaging (DEXI
... A detailed description of the laboratory-based DEXI instrument used in this work can be found in a previous publication [7]. In summary, the DEXI instrument utilizes a 2.2-kW silver x-ray source, which is operated at a voltage of 55 kV and a current of 35 mA. A mismatched, twocrystal monochromator i ...
... A detailed description of the laboratory-based DEXI instrument used in this work can be found in a previous publication [7]. In summary, the DEXI instrument utilizes a 2.2-kW silver x-ray source, which is operated at a voltage of 55 kV and a current of 35 mA. A mismatched, twocrystal monochromator i ...
How do we achieve Optimization?
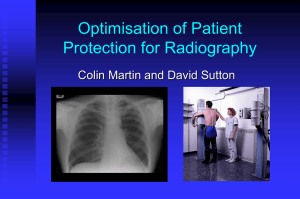
... Provide recommendations for: speed index of film screen system filtration tube potential anti-scatter grid AEC exposure time ...
... Provide recommendations for: speed index of film screen system filtration tube potential anti-scatter grid AEC exposure time ...
Date approved or revised
... L. Exposure Indicator Determination M. Gross Exposure Error (e.g., mottle, light or dark, low contrast) ...
... L. Exposure Indicator Determination M. Gross Exposure Error (e.g., mottle, light or dark, low contrast) ...
The Advanced Modalities ~ Computed
... a specific tissue. • Helical (spiral): The gantry rotates 360 degrees around the patient as the table moves through it continuously, rather than taking one slice at a time. • Multidetector CT: A scanner that has more than one detector (up to 64) and thus can obtain more than one image (or slice) at ...
... a specific tissue. • Helical (spiral): The gantry rotates 360 degrees around the patient as the table moves through it continuously, rather than taking one slice at a time. • Multidetector CT: A scanner that has more than one detector (up to 64) and thus can obtain more than one image (or slice) at ...
BASIC CONCEPTS IN DIAGNOSTIC IMAGING
... • Performed with Speech Pathologist • Barium administered in various bolus consistencies ranging from liquid to solid ...
... • Performed with Speech Pathologist • Barium administered in various bolus consistencies ranging from liquid to solid ...
Varian TrueBeam
... • Overall, better image uniformity • Cupping artifact has been minimized - apparent when performing window and level • Improvement in the skin line definition • Better HU accuracy under all conditions ...
... • Overall, better image uniformity • Cupping artifact has been minimized - apparent when performing window and level • Improvement in the skin line definition • Better HU accuracy under all conditions ...
Clinical Performance of a Spatiotemporally Accelerated Motion
... Purpose: Contrast-enhanced MR Angiography (CE-MRA) is ideal for pediatric abdominal vascular imaging due to the lack of ionizing radiation. However, pediatric CE-MRA is usually limited by motion and compromised spatiotemporal resolution. General anesthesia (GA) with periods of suspended respiration ...
... Purpose: Contrast-enhanced MR Angiography (CE-MRA) is ideal for pediatric abdominal vascular imaging due to the lack of ionizing radiation. However, pediatric CE-MRA is usually limited by motion and compromised spatiotemporal resolution. General anesthesia (GA) with periods of suspended respiration ...
No Slide Title
... rays. The shorter UV rays can be damaging to life. Beyond UV (still shorter wavelength or higher frequency) are X-rays and the even more powerful gamma rays. Their high energy allows them to penetrate through solid matter. They can cause serious damage to the macromolecules of life. X-rays (also cal ...
... rays. The shorter UV rays can be damaging to life. Beyond UV (still shorter wavelength or higher frequency) are X-rays and the even more powerful gamma rays. Their high energy allows them to penetrate through solid matter. They can cause serious damage to the macromolecules of life. X-rays (also cal ...
Radiography4.32 MB
... Compton scattering occurs when the incident x-ray photon is deflected from its original path by an interaction with an electron. The electron gains energy and is ejected from its orbital position. The x-ray photon loses energy due to the interaction but continues to travel through the material al ...
... Compton scattering occurs when the incident x-ray photon is deflected from its original path by an interaction with an electron. The electron gains energy and is ejected from its orbital position. The x-ray photon loses energy due to the interaction but continues to travel through the material al ...
Computed Tomography in the Diagnostic Radiography Curriculum
... • The first and second generations of CT were very similar. • Both used a scanning technique called translate/rotate in order to move around the patient. • The first generation scanner used a single detector and thin beam. While the second generation scanner use several detectors and a fan beam. – T ...
... • The first and second generations of CT were very similar. • Both used a scanning technique called translate/rotate in order to move around the patient. • The first generation scanner used a single detector and thin beam. While the second generation scanner use several detectors and a fan beam. – T ...
EL CAMINO COLLEGE RADIOLOGIC TECHNOLOGY PROGRAM
... • Committee on Accreditation of Allied Health Education Programs (CAAHEP) in collaboration with the Joint Review Committee on Education in Diagnostic Medical Sonography (JRC-DMS) ...
... • Committee on Accreditation of Allied Health Education Programs (CAAHEP) in collaboration with the Joint Review Committee on Education in Diagnostic Medical Sonography (JRC-DMS) ...
normal-ultrasound-protocol-thyroid
... Give the patient a clear explanation of the examination and results delivery. o This makes the patient aware of what you are going to do before you do and also gives the patient to ask any question. Make it clear to the patient that they may breathe and swallow normally through the examination but k ...
... Give the patient a clear explanation of the examination and results delivery. o This makes the patient aware of what you are going to do before you do and also gives the patient to ask any question. Make it clear to the patient that they may breathe and swallow normally through the examination but k ...
Slajd 1
... Murphy, M.J., et al., The management of imaging dose during imageguided radiotherapy: report of the AAPM Task Group 75. Med Phys, ...
... Murphy, M.J., et al., The management of imaging dose during imageguided radiotherapy: report of the AAPM Task Group 75. Med Phys, ...
X-ray - Pharos University in Alexandria
... images of the body. Sonography uses highfrequency sound waves to create crosssectional still or real-time (motion) images of the body. ...
... images of the body. Sonography uses highfrequency sound waves to create crosssectional still or real-time (motion) images of the body. ...
Pediatric - Upper GI - Department of Radiology
... The technologist will position your child on the x-ray table. Sometimes it is necessary to wrap young children in a blanket or other positioning devices to help keep your child still. The technologist will take an x-ray of the abdomen. The technologist will make you and your child as comfortable as ...
... The technologist will position your child on the x-ray table. Sometimes it is necessary to wrap young children in a blanket or other positioning devices to help keep your child still. The technologist will take an x-ray of the abdomen. The technologist will make you and your child as comfortable as ...
Generation of x-rays (cont) - gnssn
... chemically processed to create a visible image. Film processing may be manual or automatic. • The sensitivity (or the speed) of a film or film-screen system is the reciprocal of the radiation dose required to produce a given density on the film. ...
... chemically processed to create a visible image. Film processing may be manual or automatic. • The sensitivity (or the speed) of a film or film-screen system is the reciprocal of the radiation dose required to produce a given density on the film. ...
Document
... chemically processed to create a visible image. Film processing may be manual or automatic. • The sensitivity (or the speed) of a film or film-screen system is the reciprocal of the radiation dose required to produce a given density on the film. ...
... chemically processed to create a visible image. Film processing may be manual or automatic. • The sensitivity (or the speed) of a film or film-screen system is the reciprocal of the radiation dose required to produce a given density on the film. ...
RADIOLOGICAL PHYSICS CENTER
... manual or automatic registration with the planning-CT image. Use of MV EPID or film images as a visual comparison to DRRs does not meet this definition. ...
... manual or automatic registration with the planning-CT image. Use of MV EPID or film images as a visual comparison to DRRs does not meet this definition. ...
File - Mackay Education
... provides excellent soft tissue images, detecting edema in the brain, providing direct imaging of the spinal cord, detecting tumors in the chest & abdomen, & visualizing the cardiovascular system. MRI is contraindicated for patients with pacemakers or metallic implants because the powerful magnet c ...
... provides excellent soft tissue images, detecting edema in the brain, providing direct imaging of the spinal cord, detecting tumors in the chest & abdomen, & visualizing the cardiovascular system. MRI is contraindicated for patients with pacemakers or metallic implants because the powerful magnet c ...
CAREERS IN RADIOLOGIC TECHNOLOGY (FINAL) • RADIOLOGIC
... Single Photon Emission Computed Tomography ...
... Single Photon Emission Computed Tomography ...
Fluoroscopy

Fluoroscopy /flɔrˈɒskəpi/ is an imaging technique that uses X-rays to obtain real-time moving images of the interior of an object. In its primary application of medical imaging, a fluoroscope /ˈflɔrɵˌskoʊp/ allows a physician to see the internal structure and function of a patient, so that the pumping action of the heart or the motion of swallowing, for example, can be watched. This is useful for both diagnosis and therapy and occurs in general radiology, interventional radiology, and image-guided surgery. In its simplest form, a fluoroscope consists of an X-ray source and a fluorescent screen, between which a patient is placed. However, since the 1950s most fluoroscopes have included X-ray image intensifiers and cameras as well, to improve the image's visibility and make it available on a remote display screen. For many decades fluoroscopy tended to produce live pictures that were not recorded, but since the 1960s, as technology improved, recording and playback became the norm.Fluoroscopy is similar to radiography and X-ray computed tomography (X-ray CT) in that it generates images using X-rays. The original difference was that radiography fixed still images on film whereas fluoroscopy provided live moving pictures that were not stored. However, today radiography, CT, and fluoroscopy are all digital imaging modes with image analysis software and data storage and retrieval. The use of X-rays, a form of ionizing radiation, requires the potential risks from a procedure to be carefully balanced with the benefits of the procedure to the patient. Because the patient must be exposed to a continuous source of x-rays instead of a momentary pulse, a fluoroscopy procedure generally subjects a patient to a higher absorbed dose of radiation than an ordinary (still) radiograph. Much research has been directed toward reducing radiation exposure, and recent advances in fluoroscopy technology such as digital image processing and flat panel detectors, have resulted in much lower radiation doses than former procedures.The type of fluoroscopy used in airport security (to check for hidden weapons or bombs) uses lower doses of radiation than medical fluoroscopy. It was formerly also used in retail stores in the form of shoe-fitting fluoroscopes, but such use was discontinued because it is no longer considered acceptable to use radiation exposure, however small the dose, for nonessential purposes. Only important applications such as health care, bodily safety, food safety, nondestructive testing, and scientific research meet the risk-benefit threshold for use. The reason for higher doses in medical applications is that they are more demanding about tissue contrast, and for the same reason they sometimes require contrast media.