High Energy Radiography for Inspection of the Lid Weld in
... copper is briefly addresses and compared to other materials. Copper has a higher linear coefficient of attenuation than iron, the percentual difference being 51 % at 50 keV, 11 % at 1 MeV and 17 % at 10 MeV. Due to an estimate based on a canister drawing the X-rays need to penetrate varying thicknes ...
... copper is briefly addresses and compared to other materials. Copper has a higher linear coefficient of attenuation than iron, the percentual difference being 51 % at 50 keV, 11 % at 1 MeV and 17 % at 10 MeV. Due to an estimate based on a canister drawing the X-rays need to penetrate varying thicknes ...
R8 - American College of Radiology
... tubes, and peritoneal cavity during injection of contrast media with fluoroscopic visualization. It should be done with the minimum radiation exposure necessary to provide sufficient anatomic detail for diagnosis of normal or abnormal findings. Adherence to the following practice parameters will max ...
... tubes, and peritoneal cavity during injection of contrast media with fluoroscopic visualization. It should be done with the minimum radiation exposure necessary to provide sufficient anatomic detail for diagnosis of normal or abnormal findings. Adherence to the following practice parameters will max ...
COURSE SYLLABUS TM 220 COMPUTED TOMOGRAPHY PHYSICS
... processing system, CT gantry, display, storage and recording devices. CSLO #9 Evaluate the techniques used for image manipulation in CT. CSLO #10 Identify the properties which effect image quality in CT Scanning. CSLO #11 Discuss biological effects of CT and adhere to radiation protection guidelines ...
... processing system, CT gantry, display, storage and recording devices. CSLO #9 Evaluate the techniques used for image manipulation in CT. CSLO #10 Identify the properties which effect image quality in CT Scanning. CSLO #11 Discuss biological effects of CT and adhere to radiation protection guidelines ...
see p. D49 - Viktor`s Notes for the Neurosurgery Resident
... – for axial head CT, gantry is angled parallel to orbitomeatal line. – for coronal head CT, patient is either supine or prone with neck hyperextended (impossible for intubated patients, patients with cervical spine disease, airway obstruction, or obesity). detectors 180° opposite beam measure X-ray ...
... – for axial head CT, gantry is angled parallel to orbitomeatal line. – for coronal head CT, patient is either supine or prone with neck hyperextended (impossible for intubated patients, patients with cervical spine disease, airway obstruction, or obesity). detectors 180° opposite beam measure X-ray ...
Planar X-Ray Imaging - I: Basics (1) Sketch the basic imaging setup
... How is the number of X-ray quanta generated by the X-ray tube distributed? Why? How are mean value and variance of a Poisson distribution related? What are the major factors determining the mean number of X-ray quanta generated? Describe the SNR at input and output of an efficiency stage. What does ...
... How is the number of X-ray quanta generated by the X-ray tube distributed? Why? How are mean value and variance of a Poisson distribution related? What are the major factors determining the mean number of X-ray quanta generated? Describe the SNR at input and output of an efficiency stage. What does ...
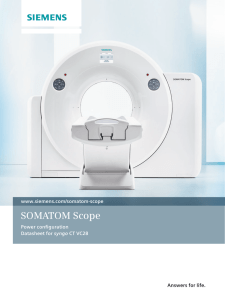
SOMATOM Scope
... Scope provides excellent image detail even at low radiation doses. This industry-leading material* – which is also used in our top-of-theline scanners – achieves exceptional overall efficiency thanks to high X-ray absorption combined with extremely effective conversion of X-ray energy into visible l ...
... Scope provides excellent image detail even at low radiation doses. This industry-leading material* – which is also used in our top-of-theline scanners – achieves exceptional overall efficiency thanks to high X-ray absorption combined with extremely effective conversion of X-ray energy into visible l ...
radiology coding basics - Silverdale WA Local AAPC
... CT imaging combines special x-ray equipment with sophisticated computers to produce multiple images or pictures of the inside of the body. These cross-sectional images of the area being studied can then be examined on a computer monitor and provide greater clarity and reveal more details than regula ...
... CT imaging combines special x-ray equipment with sophisticated computers to produce multiple images or pictures of the inside of the body. These cross-sectional images of the area being studied can then be examined on a computer monitor and provide greater clarity and reveal more details than regula ...
Physics Radiology In-Training Test Questions for Diagnostic
... by the sampling pitch (distance between detector elements D. Incorrect: Image contrast with a digital system is freely adjustable as long as there is sufficient signal to noise ratio of the statistical information in the image. That is why the digital detectors are often referred to as “SNR limited” ...
... by the sampling pitch (distance between detector elements D. Incorrect: Image contrast with a digital system is freely adjustable as long as there is sufficient signal to noise ratio of the statistical information in the image. That is why the digital detectors are often referred to as “SNR limited” ...
Segmentation of Thyroid Scintography Using Edge Detection and
... camera is composed of a collimator, a scintillator crystal usually made of NaI (or CsI), the photomultiplier tubes, the electronic circuits and a computer equipped with the suitable software to depict the nuclear medicine examinations. In planar imaging, the patient, having being delivered with the ...
... camera is composed of a collimator, a scintillator crystal usually made of NaI (or CsI), the photomultiplier tubes, the electronic circuits and a computer equipped with the suitable software to depict the nuclear medicine examinations. In planar imaging, the patient, having being delivered with the ...
ct for techs_1 system components
... space. A busy CT practice could store a year’s worth of cases on one or two bookshelves. Optical disks use a laser beam to write (burn) data as binary code into the surface of a metallic disk. Two types of disks are used: the write-once-read-many (WORM) disk with a storage capacity from 122 megabyte ...
... space. A busy CT practice could store a year’s worth of cases on one or two bookshelves. Optical disks use a laser beam to write (burn) data as binary code into the surface of a metallic disk. Two types of disks are used: the write-once-read-many (WORM) disk with a storage capacity from 122 megabyte ...
Diagnostic Medical Imaging Radiation Exposure and Risk of
... of tumorigenesis, and a dose-dependent relationship exists between radiation dose and induction of DNA damage in cells.8 No large-scale epidemiologic study of cancer induction by diagnostic radiation is reported in the literature.9 Therefore, the greatest amount of information regarding human exposu ...
... of tumorigenesis, and a dose-dependent relationship exists between radiation dose and induction of DNA damage in cells.8 No large-scale epidemiologic study of cancer induction by diagnostic radiation is reported in the literature.9 Therefore, the greatest amount of information regarding human exposu ...
application/msword
... to produce an adaptive x-ray imaging system for healthcare, homeland security and industrial quality assessment. The system consists of Intelligent Imaging Sensors, combined with state-of-the-art in digital radiographic imaging with a unique feedback mechanism which is able to optimise the image acq ...
... to produce an adaptive x-ray imaging system for healthcare, homeland security and industrial quality assessment. The system consists of Intelligent Imaging Sensors, combined with state-of-the-art in digital radiographic imaging with a unique feedback mechanism which is able to optimise the image acq ...
A Novel In-Office Cone Beam Computed Tomography (CBCT
... for up to 20 days from the onset of infection, or until the bony density is reduced by 30-50%.3 Nuclear imaging scans possess limited specificity and spatial resolution, and are expensive and time-consuming.4 Though magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is presently considered the most reliable imaging t ...
... for up to 20 days from the onset of infection, or until the bony density is reduced by 30-50%.3 Nuclear imaging scans possess limited specificity and spatial resolution, and are expensive and time-consuming.4 Though magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is presently considered the most reliable imaging t ...
MINISTRY OF EDUCATION AND SCIENCE OF THE RUSSIAN
... individual features of the structure of a healthy body, as well as changes in various diseases of organs. To be able to: independently identify the image of all human organs and indicate their main anatomical structures on radiographs, angiograms, computer x-ray and an MRI, Ultrasound, postglacial. ...
... individual features of the structure of a healthy body, as well as changes in various diseases of organs. To be able to: independently identify the image of all human organs and indicate their main anatomical structures on radiographs, angiograms, computer x-ray and an MRI, Ultrasound, postglacial. ...
j35-2004-ieeetmi-panorama
... acquires overlapping images by precise simultaneous translation of the X-ray source and image intensifier. The images are aligned by semi-automatically detecting and matching semantically meaningful features on a reconstruction plane. Composed images of objects that are not on that plane will have p ...
... acquires overlapping images by precise simultaneous translation of the X-ray source and image intensifier. The images are aligned by semi-automatically detecting and matching semantically meaningful features on a reconstruction plane. Composed images of objects that are not on that plane will have p ...
Best Practices in Computerized Tomography
... version was replaced with an electronic version that is archived within the order entry software program. Both the patient’s history and current list of medications are recorded. On subsequent visits, the previous questionnaire pops up to be updated. The method shortens the interview time and increa ...
... version was replaced with an electronic version that is archived within the order entry software program. Both the patient’s history and current list of medications are recorded. On subsequent visits, the previous questionnaire pops up to be updated. The method shortens the interview time and increa ...
Ongoing quality control in digital radiography: Report of AAPM
... been demonstrated between different types of hospitals.24 One would expect a lower rejected image rate for a commonly performed view such as a PA chest as compared to a seldomperformed, technically challenging view such as facial bones, and this has been demonstrated.14,16 The presence of trainees w ...
... been demonstrated between different types of hospitals.24 One would expect a lower rejected image rate for a commonly performed view such as a PA chest as compared to a seldomperformed, technically challenging view such as facial bones, and this has been demonstrated.14,16 The presence of trainees w ...
Tomographic Image Reconstruction 1 Introduction
... Tomography is a non-invasive imaging technique allowing for the visualization of the internal structures of an object without the superposition of over- and under-lying structures that usually plagues conventional projection images. For example, in a conventional chest radiograph, the heart, lungs, ...
... Tomography is a non-invasive imaging technique allowing for the visualization of the internal structures of an object without the superposition of over- and under-lying structures that usually plagues conventional projection images. For example, in a conventional chest radiograph, the heart, lungs, ...
22 COMPUTER VISION APPLIED
... the 35 mm cine lm standard with a digital medium capable of ful lling the same role as archival and exchange medium. As digital systems were being introduced into the marketplace, several competing solutions were o ered by manufacturers and adopted by clinicians, resulting in incompatibilities betwe ...
... the 35 mm cine lm standard with a digital medium capable of ful lling the same role as archival and exchange medium. As digital systems were being introduced into the marketplace, several competing solutions were o ered by manufacturers and adopted by clinicians, resulting in incompatibilities betwe ...
Fluoroscopy

Fluoroscopy /flɔrˈɒskəpi/ is an imaging technique that uses X-rays to obtain real-time moving images of the interior of an object. In its primary application of medical imaging, a fluoroscope /ˈflɔrɵˌskoʊp/ allows a physician to see the internal structure and function of a patient, so that the pumping action of the heart or the motion of swallowing, for example, can be watched. This is useful for both diagnosis and therapy and occurs in general radiology, interventional radiology, and image-guided surgery. In its simplest form, a fluoroscope consists of an X-ray source and a fluorescent screen, between which a patient is placed. However, since the 1950s most fluoroscopes have included X-ray image intensifiers and cameras as well, to improve the image's visibility and make it available on a remote display screen. For many decades fluoroscopy tended to produce live pictures that were not recorded, but since the 1960s, as technology improved, recording and playback became the norm.Fluoroscopy is similar to radiography and X-ray computed tomography (X-ray CT) in that it generates images using X-rays. The original difference was that radiography fixed still images on film whereas fluoroscopy provided live moving pictures that were not stored. However, today radiography, CT, and fluoroscopy are all digital imaging modes with image analysis software and data storage and retrieval. The use of X-rays, a form of ionizing radiation, requires the potential risks from a procedure to be carefully balanced with the benefits of the procedure to the patient. Because the patient must be exposed to a continuous source of x-rays instead of a momentary pulse, a fluoroscopy procedure generally subjects a patient to a higher absorbed dose of radiation than an ordinary (still) radiograph. Much research has been directed toward reducing radiation exposure, and recent advances in fluoroscopy technology such as digital image processing and flat panel detectors, have resulted in much lower radiation doses than former procedures.The type of fluoroscopy used in airport security (to check for hidden weapons or bombs) uses lower doses of radiation than medical fluoroscopy. It was formerly also used in retail stores in the form of shoe-fitting fluoroscopes, but such use was discontinued because it is no longer considered acceptable to use radiation exposure, however small the dose, for nonessential purposes. Only important applications such as health care, bodily safety, food safety, nondestructive testing, and scientific research meet the risk-benefit threshold for use. The reason for higher doses in medical applications is that they are more demanding about tissue contrast, and for the same reason they sometimes require contrast media.