Cloning of a T-Type Ca Channel Isoform in I n s u l i n
... The T-type Ca2+ channel gene deduced from -cells shares 96.3% amino acid identity with 1G, the neuronal isoform of the T-type Ca2+ channel (9). The four intramolecular homologous transmembrane domains of the -cell T-type Ca2+ channel 1-subunit are identical (except glycine 1667) to the 1G with each ...
... The T-type Ca2+ channel gene deduced from -cells shares 96.3% amino acid identity with 1G, the neuronal isoform of the T-type Ca2+ channel (9). The four intramolecular homologous transmembrane domains of the -cell T-type Ca2+ channel 1-subunit are identical (except glycine 1667) to the 1G with each ...
Prokaryotic features of a nucleus
... Plants have parallel pathways of sugar phosphate metabolism located on either side of the chloroplast envelope. As a consequence, many of these metabolic reactions are catalyzed by pairs of plastid/cytoplasmic isoenzymes, which can be separated on the basis of their charge differences [46]. Although ...
... Plants have parallel pathways of sugar phosphate metabolism located on either side of the chloroplast envelope. As a consequence, many of these metabolic reactions are catalyzed by pairs of plastid/cytoplasmic isoenzymes, which can be separated on the basis of their charge differences [46]. Although ...
Biochemistry of Ensiling - DigitalCommons@University of Nebraska
... Two or more (up to 10) monosaccharides linked together are referred to as oligosaccharides (Kandler & Hopf, 1980). This is a bit of an arbitrary definition to draw a distinction between oligosaccharides and polysaccharides. In most cases naturally occurring oligosaccharides that are not intermediate ...
... Two or more (up to 10) monosaccharides linked together are referred to as oligosaccharides (Kandler & Hopf, 1980). This is a bit of an arbitrary definition to draw a distinction between oligosaccharides and polysaccharides. In most cases naturally occurring oligosaccharides that are not intermediate ...
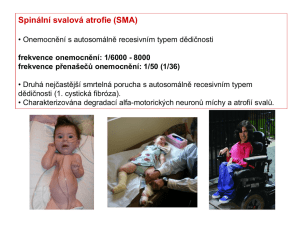
SMN1
... genes of the affected snRNPs are and how this specifically affects motor neuron function (indicated by a question mark (?)). One possibility is that the critical target gene is specific to motor neuron system. Alternatively, a function of critical importance to motor neurons could be disrupted. In a ...
... genes of the affected snRNPs are and how this specifically affects motor neuron function (indicated by a question mark (?)). One possibility is that the critical target gene is specific to motor neuron system. Alternatively, a function of critical importance to motor neurons could be disrupted. In a ...
Class17 1-31 Win16 Cell Cycle Notes
... – Is C a positive or negative regulator of B? – Is C a positive or negative regulator of its own expression? Challenge: Imagine that a new strain of E. coli is found that regulates lac operon expression based on levels of mercury in the environment. Design molecular interactions (or new molecules) ...
... – Is C a positive or negative regulator of B? – Is C a positive or negative regulator of its own expression? Challenge: Imagine that a new strain of E. coli is found that regulates lac operon expression based on levels of mercury in the environment. Design molecular interactions (or new molecules) ...
DNA methylation profiling identifies epigenetic dysregulation in
... of T2D in offspring (Inoue et al, 2009) while chronic high-fat diet in fathers programs b-cell dysfunction in female rat offspring (Ng et al, 2010). In humans, a reduced birth weight together with an accelerated growth in infancy has been associated with impaired glucose tolerance (IGT) in adulthood ...
... of T2D in offspring (Inoue et al, 2009) while chronic high-fat diet in fathers programs b-cell dysfunction in female rat offspring (Ng et al, 2010). In humans, a reduced birth weight together with an accelerated growth in infancy has been associated with impaired glucose tolerance (IGT) in adulthood ...
The fibrodysplasia ossificans progressiva R206H
... ACVR1 RNA into alk8–/– zebrafish embryos rescued approximately 80% of the injected embryos completely or partially (Figure 3, C and F), showing that human ACVR1 can function as a BMP type I receptor in this zebrafish model and substitute for Alk8. By contrast, microinjection of mutant ACVR1 RNA (enc ...
... ACVR1 RNA into alk8–/– zebrafish embryos rescued approximately 80% of the injected embryos completely or partially (Figure 3, C and F), showing that human ACVR1 can function as a BMP type I receptor in this zebrafish model and substitute for Alk8. By contrast, microinjection of mutant ACVR1 RNA (enc ...
Localization and structural analysis of the ribosomal RNA operons of
... post-transcriptional levels. The cellular content of specific mRNA and protein components unique to photosynthetic growth are either not detectable or present at extremely low levels in aerobically growing cells (3). Because of the apparent translational coupling between the synthesis of specific IC ...
... post-transcriptional levels. The cellular content of specific mRNA and protein components unique to photosynthetic growth are either not detectable or present at extremely low levels in aerobically growing cells (3). Because of the apparent translational coupling between the synthesis of specific IC ...
Boundary elements and nuclear organization
... 3. Insulators and transcriptional regulation The ability of boundary elements to prevent repression by blocking the spread of heterochromatin has been described for a variety of identified insulator elements (for a list of such elements, see West et al., 2002), suggestive of their role in preserving ...
... 3. Insulators and transcriptional regulation The ability of boundary elements to prevent repression by blocking the spread of heterochromatin has been described for a variety of identified insulator elements (for a list of such elements, see West et al., 2002), suggestive of their role in preserving ...
The Nature of Life – Chapter 1
... 14.1.2: Explain how sex is determined. (brief) 14.1.3: Explain how pedigrees are used to study human traits. 14.1.4: Describe examples of the inheritance of human traits. 14.1.5: Explain how small changes in DNA cause genetic disorders. Objectives: 14.2.1: Identify characteristics of human chromosom ...
... 14.1.2: Explain how sex is determined. (brief) 14.1.3: Explain how pedigrees are used to study human traits. 14.1.4: Describe examples of the inheritance of human traits. 14.1.5: Explain how small changes in DNA cause genetic disorders. Objectives: 14.2.1: Identify characteristics of human chromosom ...
Genetic and epigenetic risks of intracytoplasmic sperm injection
... senting the majority (60–70%) of the CF mutations in carriers and patients. In addition, polymorphisms reducing the production of the CFTR protein (5T, 7T) have been shown. In particular, the homozygous or heterozygous presence of the 5T allele is a frequent finding in CBAVD patients with incomplete ...
... senting the majority (60–70%) of the CF mutations in carriers and patients. In addition, polymorphisms reducing the production of the CFTR protein (5T, 7T) have been shown. In particular, the homozygous or heterozygous presence of the 5T allele is a frequent finding in CBAVD patients with incomplete ...
Recent advances in enzyme promiscuity | SpringerLink
... activity [44]. PTE mutant library was created by mutating 12 active-site residues of PTE in order to enhance its catalytic efficiency. The library was screened for catalytic activity against a new VX analogue, DEVX, which contains the same thiolate-leaving group of VX attached to a diethoxyphosphate ...
... activity [44]. PTE mutant library was created by mutating 12 active-site residues of PTE in order to enhance its catalytic efficiency. The library was screened for catalytic activity against a new VX analogue, DEVX, which contains the same thiolate-leaving group of VX attached to a diethoxyphosphate ...
The Johns Hopkins University - American University of Beirut
... • You need to understand the data they have, and how it is organized • There are often many ways to get to an answer. • Route to get there is not always obvious, but you need to think of alternatives and traps. • Use some query language – each system has its own. • Retrieve data in a specified forma ...
... • You need to understand the data they have, and how it is organized • There are often many ways to get to an answer. • Route to get there is not always obvious, but you need to think of alternatives and traps. • Use some query language – each system has its own. • Retrieve data in a specified forma ...
TEXT Definition Chromosomal alterations are variations from the
... Plants are more often aneuploid. In most plants, a single extra chromosome (or a missing chromosome) has a more severe effect on phenotype than the presence of a complete extra set of chromosomes. Each chromosome that is extra or missing, results in a characteristic phenotype. The first critical stu ...
... Plants are more often aneuploid. In most plants, a single extra chromosome (or a missing chromosome) has a more severe effect on phenotype than the presence of a complete extra set of chromosomes. Each chromosome that is extra or missing, results in a characteristic phenotype. The first critical stu ...
Redacted for Privacy
... the fibrous components of the extracellular matrix. Growth factors and cytokines expressed and released by foam cells, smooth muscle cells, and the endothelium itself promote lesion development to a more advanced state, the atheroma. Foam cells and lipids continue to accumulate in the core of the a ...
... the fibrous components of the extracellular matrix. Growth factors and cytokines expressed and released by foam cells, smooth muscle cells, and the endothelium itself promote lesion development to a more advanced state, the atheroma. Foam cells and lipids continue to accumulate in the core of the a ...
Further characterization of the lipoic acid enantiomers
... • Bis-methylation (in vitro models seem to have lower thiol methyl transferase activity than in vivo). • S-oxidation although B-lipoic is oxidized in vitro, no evidence in plasma, thiosulfinates and thiosulfonates formed subsequent to reduction. ...
... • Bis-methylation (in vitro models seem to have lower thiol methyl transferase activity than in vivo). • S-oxidation although B-lipoic is oxidized in vitro, no evidence in plasma, thiosulfinates and thiosulfonates formed subsequent to reduction. ...
The RNA world meets behavior: AfiI pre
... transcriptome remains unknown. Although we understand the chemical basis and are learning about both the mechanism and the preferred targets for this type of editing, an essential question remains: why do organisms recode mRNAs enzymatically rather than simply incorporating those changes into the ge ...
... transcriptome remains unknown. Although we understand the chemical basis and are learning about both the mechanism and the preferred targets for this type of editing, an essential question remains: why do organisms recode mRNAs enzymatically rather than simply incorporating those changes into the ge ...
Composite polymorphisms in the ryanodine receptor 2 gene
... Objective: Mutations in the cardiac ryanodine receptor (RYR2) gene have been reported to cause arrhythmogenic right ventricular cardiomyopathy (ARVC). The molecular mechanisms by which genetic modifications lead to ARVC are still not well understood. Methods: ARVC patients were screened for mutation ...
... Objective: Mutations in the cardiac ryanodine receptor (RYR2) gene have been reported to cause arrhythmogenic right ventricular cardiomyopathy (ARVC). The molecular mechanisms by which genetic modifications lead to ARVC are still not well understood. Methods: ARVC patients were screened for mutation ...
PDF
... by BLAST is expected to contain such homolog-specific and position-specific information. An MSA can be transformed into a position-specific scoring matrix (PSSM), which is a more sophisticated model for sequence similarity search than the substitution matrix because scores for amino-acids are modele ...
... by BLAST is expected to contain such homolog-specific and position-specific information. An MSA can be transformed into a position-specific scoring matrix (PSSM), which is a more sophisticated model for sequence similarity search than the substitution matrix because scores for amino-acids are modele ...
Gene Section HRK (harakiri, BCL2 interacting protein (contains only BH3 domain))
... Figure 2. HRK gene and promoter structure. A. Structure of the HRK gene. The structure of the human and rat HRK genes is shown. The HRK gene consists of two exons separated by a large intron. The transcriptional start site is indicated as +1 (see panel B for DNA sequence). Exon 1 contains the HRK op ...
... Figure 2. HRK gene and promoter structure. A. Structure of the HRK gene. The structure of the human and rat HRK genes is shown. The HRK gene consists of two exons separated by a large intron. The transcriptional start site is indicated as +1 (see panel B for DNA sequence). Exon 1 contains the HRK op ...
Fibrinogen Bern I: Substitution y 337 Asn + Lys Is
... bands at the same migration distance, corresponding to Lys (AAC + AAA). amino acid substitution y 337 Asn The purified double-stranded PCR-derived fragment was cloned and subjected to sequence analysis. Normal and mutated alleles of fibrinogen Bern I were obtained, showing a G + T transition in the ...
... bands at the same migration distance, corresponding to Lys (AAC + AAA). amino acid substitution y 337 Asn The purified double-stranded PCR-derived fragment was cloned and subjected to sequence analysis. Normal and mutated alleles of fibrinogen Bern I were obtained, showing a G + T transition in the ...
(..rignt click_Save Target As..)
... Genetics Theory: Chickens have 78 chromosomes. They are diploid animals, therefore the body cell chromosomes are grouped together in pairs- 39. For example, a chicken will have two Chromosome 1's, two chromosome 2's, two chromosome 3's, etc. The exception is the sex-chromosomes, Z and W, where roost ...
... Genetics Theory: Chickens have 78 chromosomes. They are diploid animals, therefore the body cell chromosomes are grouped together in pairs- 39. For example, a chicken will have two Chromosome 1's, two chromosome 2's, two chromosome 3's, etc. The exception is the sex-chromosomes, Z and W, where roost ...
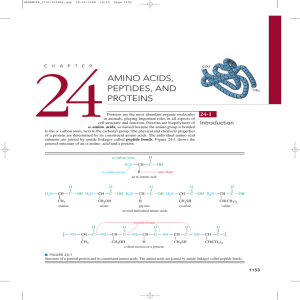
Amino Acids, Peptides, and Proteins
... those in meat, fish, milk, and eggs. About 50 g of complete protein per day is adequate for adult humans. Proteins that are severely deficient in one or more of the essential amino acids are called incomplete proteins. If the protein in a person’s diet comes mostly from one incomplete source, the am ...
... those in meat, fish, milk, and eggs. About 50 g of complete protein per day is adequate for adult humans. Proteins that are severely deficient in one or more of the essential amino acids are called incomplete proteins. If the protein in a person’s diet comes mostly from one incomplete source, the am ...
שקופית 1
... •When translated, the cryptic boCTP stretch does not prevent crucial aspects of hormone biosynthesis (the assembly of the heterodimer, formation of conformational-sensitive epitopes and the activation of the cognate receptor). However, this domain is missing the set of Olinked glycans and lacks the ...
... •When translated, the cryptic boCTP stretch does not prevent crucial aspects of hormone biosynthesis (the assembly of the heterodimer, formation of conformational-sensitive epitopes and the activation of the cognate receptor). However, this domain is missing the set of Olinked glycans and lacks the ...
International Journal on New Trends in Education and Their
... stopper codon. mRNA slips. tRNAs are synthesized through mRNAs. Afterwards, a peptide bond is created between tRNAs. Considering the expression of the pre-service teacher, it can be inferred that he/she assumes tRNAs are interconnected via peptide bonds. CONCLUSIONS AND DISCUSSION In consequence of ...
... stopper codon. mRNA slips. tRNAs are synthesized through mRNAs. Afterwards, a peptide bond is created between tRNAs. Considering the expression of the pre-service teacher, it can be inferred that he/she assumes tRNAs are interconnected via peptide bonds. CONCLUSIONS AND DISCUSSION In consequence of ...
Point mutation

A point mutation, or single base modification, is a type of mutation that causes a single nucleotide base change, insertion, or deletion of the genetic material, DNA or RNA. The term frameshift mutation indicates the addition or deletion of a base pair. A point mutant is an individual that is affected by a point mutation.Repeat induced point mutations are recurring point mutations, discussed below.