NS2-M3C13_-_The_Moon_Exam
... Apollo 13 landed the first humans on the Moon with Americans Lance Armstrong and Buzz Aldrin in 1969. (Input all that apply, then push the ENTER button.) A B C D ...
... Apollo 13 landed the first humans on the Moon with Americans Lance Armstrong and Buzz Aldrin in 1969. (Input all that apply, then push the ENTER button.) A B C D ...
Feb 2017 - Astronomical Society of Northern New England
... spend exactly one year in each of our 12 zodiac constellations. That is not a smooth eastward path, since it makes a retrograde loop for about 4 months in one of these constellations each year. That will happen on the 6th of this month. Jupiter will appear stationary that day and the very next day i ...
... spend exactly one year in each of our 12 zodiac constellations. That is not a smooth eastward path, since it makes a retrograde loop for about 4 months in one of these constellations each year. That will happen on the 6th of this month. Jupiter will appear stationary that day and the very next day i ...
The Transformation of Gas Giant Planets into Rocky Planets
... beyond the fringe of conventional astrophysical theory. However, the idea that stellar objects may in fact harbor solid cores is not inconsistent with the transformation hypothesis. On the other hand, his account of the Solar System’s formation from a supernova event must be rejected since it is, in ...
... beyond the fringe of conventional astrophysical theory. However, the idea that stellar objects may in fact harbor solid cores is not inconsistent with the transformation hypothesis. On the other hand, his account of the Solar System’s formation from a supernova event must be rejected since it is, in ...
Avogadro`s Number
... eye, but the number of stars swirling around you in the known universe is approximately equal to Avogadro’s number 6.02 x 1023. Just think, the known universe contains approximately a mole of stars. You don’t have to leave the Earth to encounter such a large number. The water in the Pacific Ocean ha ...
... eye, but the number of stars swirling around you in the known universe is approximately equal to Avogadro’s number 6.02 x 1023. Just think, the known universe contains approximately a mole of stars. You don’t have to leave the Earth to encounter such a large number. The water in the Pacific Ocean ha ...
Document
... Mercury is only 36 million miles from the Sun and orbits it every 88 days. It has a very elliptical orbit and moves approximately 30 miles per second. Mercury rotates very slowly and its “day” is 59 Earth days. Mercury has a rocky, crust surface with many craters. This gives it the appearance much l ...
... Mercury is only 36 million miles from the Sun and orbits it every 88 days. It has a very elliptical orbit and moves approximately 30 miles per second. Mercury rotates very slowly and its “day” is 59 Earth days. Mercury has a rocky, crust surface with many craters. This gives it the appearance much l ...
TRANSIT
... Found comet to northwest of Regulus. Quite large, quite bright. Easily seen with 15x70 bins. Also with 8x50 telescope finder. Very clear, quite large with 50mm lens. In the 32mm lens the coma is clear. There is definitely nebulosity/cometary material eastwards from the coma and relatively little to ...
... Found comet to northwest of Regulus. Quite large, quite bright. Easily seen with 15x70 bins. Also with 8x50 telescope finder. Very clear, quite large with 50mm lens. In the 32mm lens the coma is clear. There is definitely nebulosity/cometary material eastwards from the coma and relatively little to ...
16. Gravity and Space - Mr. Brick's Web Page
... The Moon. The Moon rotates about its own axis once every 27.5 days, which is the same time it takes for the Moon to orbit the Earth. This means that from Earth we always see the same side of the Moon. Humans have also launched many artificial satellites into Earth’s orbit. These are used for communi ...
... The Moon. The Moon rotates about its own axis once every 27.5 days, which is the same time it takes for the Moon to orbit the Earth. This means that from Earth we always see the same side of the Moon. Humans have also launched many artificial satellites into Earth’s orbit. These are used for communi ...
Large and small planets Journey through the Solar System
... dwarf planet. To qualify as a planet, an astronomical object must meet three conditions: It must move in an orbit around a sun; it must be massive enough for it to take on a round shape as a result of its own gravity; and finally it must not be part of a large collection of similar astronomical obje ...
... dwarf planet. To qualify as a planet, an astronomical object must meet three conditions: It must move in an orbit around a sun; it must be massive enough for it to take on a round shape as a result of its own gravity; and finally it must not be part of a large collection of similar astronomical obje ...
26.9 news and views feature mx
... massive than the Earth, but subsequent observations showed that it is less than 5% of the mass of Mercury, the smallest of the planets known before 1800 and itself less than 6% of the mass of the Earth. This realization, together with the discovery of many minor planets beyond Neptune during the pas ...
... massive than the Earth, but subsequent observations showed that it is less than 5% of the mass of Mercury, the smallest of the planets known before 1800 and itself less than 6% of the mass of the Earth. This realization, together with the discovery of many minor planets beyond Neptune during the pas ...
11 Celestial Objects and Events Every Stargazer Should See
... to any party for any loss, damage, or disruption caused by errors or omissions, whether such errors or omissions result from negligence, accident, or any other cause. ...
... to any party for any loss, damage, or disruption caused by errors or omissions, whether such errors or omissions result from negligence, accident, or any other cause. ...
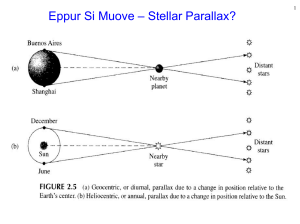
Eppur Si Muove – Stellar Parallax?
... 2. Planets moved faster when closer to the Sun in a way that a line between the Sun and planet swept out equal area in equal time. 3. The orbital period of a planet was related to its average distance from the Sun. P2=a3 ...
... 2. Planets moved faster when closer to the Sun in a way that a line between the Sun and planet swept out equal area in equal time. 3. The orbital period of a planet was related to its average distance from the Sun. P2=a3 ...
AST 301 Fall 2007 Review for Exam 3 This exam covers only
... planets (name them, explain them), but basically only one of them has been successful, so far, in detecting large numbers of extrasolar planets. Can you explain why that is? What do you learn from this technique? What could you learn about a planet from other techniques? Of the numerous extrasolar p ...
... planets (name them, explain them), but basically only one of them has been successful, so far, in detecting large numbers of extrasolar planets. Can you explain why that is? What do you learn from this technique? What could you learn about a planet from other techniques? Of the numerous extrasolar p ...
The Sky Tonight - Northern Stars Planetarium
... space. It’s the result of the death of an average star (like the Sun). The nebulosity you see is the outer layers of the star that have been blown out into space. Planetary nebula actually have no relationship to planets. They’re called planetary because of their appearance only, which led early ast ...
... space. It’s the result of the death of an average star (like the Sun). The nebulosity you see is the outer layers of the star that have been blown out into space. Planetary nebula actually have no relationship to planets. They’re called planetary because of their appearance only, which led early ast ...
Easy Science no 98
... vertical line across the middle of the poster paper. Write the directions north, south, east and west on the paper as shown. Use the modelling clay to make the pencil stand up at the spot where the two lines cross. You have now made a Sun tracker. On a sunny day, go out early and find an open space ...
... vertical line across the middle of the poster paper. Write the directions north, south, east and west on the paper as shown. Use the modelling clay to make the pencil stand up at the spot where the two lines cross. You have now made a Sun tracker. On a sunny day, go out early and find an open space ...
26A Phases of the Moon
... Now you are ready to look at variations in the light intensity that falls on each globe. The greater the light intensity, the more electricity your solar cell produces. Measuring the solar cell output allows us to find differences in light intensity at different places on the globes. Use the same so ...
... Now you are ready to look at variations in the light intensity that falls on each globe. The greater the light intensity, the more electricity your solar cell produces. Measuring the solar cell output allows us to find differences in light intensity at different places on the globes. Use the same so ...
Solar System - New Haven Science
... ways: they spin (rotate) and they change position relative to each other (revolve). The Sun is a star that produces light that travels in straight lines away from the sun in all directions. Light from the Sun illuminates objects that reflect light, including Earth and its moon. The side of the earth ...
... ways: they spin (rotate) and they change position relative to each other (revolve). The Sun is a star that produces light that travels in straight lines away from the sun in all directions. Light from the Sun illuminates objects that reflect light, including Earth and its moon. The side of the earth ...
Gravity-mod
... Explanation: If you neglect air resistance, objects falling near Earth’s surface fall with the same approximate acceleration 9.8 meters per second squared (9.8 m/s2, or g) due to Earth's gravity. All objects fall at the same rate, regardless of their mass How fast something falls isn't dependant on ...
... Explanation: If you neglect air resistance, objects falling near Earth’s surface fall with the same approximate acceleration 9.8 meters per second squared (9.8 m/s2, or g) due to Earth's gravity. All objects fall at the same rate, regardless of their mass How fast something falls isn't dependant on ...
The science behind our Sun and its interaction with Earth The
... about halfway through its lifespan (Frank, 2008). The Sun's light and heat are absolutely vital to human existence, yet most of us take them for granted. The Sun is the most important factor in Earth supporting life. We have come a long way in the study of our star, and have learned much. Understand ...
... about halfway through its lifespan (Frank, 2008). The Sun's light and heat are absolutely vital to human existence, yet most of us take them for granted. The Sun is the most important factor in Earth supporting life. We have come a long way in the study of our star, and have learned much. Understand ...
TLW explain how fossils provide evidence of the history of the Earth.
... star and gives enough energy to support life and drive our weather systems. While many other stars are larger, the sun appears prominent in the sky because it is so close to Earth. Earth: The Earth is a planet and does not produce its own light but reflects sunlight. Earth’s atmosphere, a mixture of ...
... star and gives enough energy to support life and drive our weather systems. While many other stars are larger, the sun appears prominent in the sky because it is so close to Earth. Earth: The Earth is a planet and does not produce its own light but reflects sunlight. Earth’s atmosphere, a mixture of ...
The Solar System (Ch. 6 in text) Consists of the sun (a typical star
... planets orbiting stars other than the sun have been discovered. There are several techniques available, but we’ll just discuss a few. 1. Direct detection—not possible at present. Reflected light from planet is about a billion times less than that of the star (less in the infrared, but still about a ...
... planets orbiting stars other than the sun have been discovered. There are several techniques available, but we’ll just discuss a few. 1. Direct detection—not possible at present. Reflected light from planet is about a billion times less than that of the star (less in the infrared, but still about a ...
EarthScience_Topic 3
... The right half of the Moon appears lighted and the left side of the Moon appears dark. During the time between the New Moon and the First Quarter Moon, the part of the Moon that appears lighted gets larger and larger every day, and will continue to grow until the Full Moon. ...
... The right half of the Moon appears lighted and the left side of the Moon appears dark. During the time between the New Moon and the First Quarter Moon, the part of the Moon that appears lighted gets larger and larger every day, and will continue to grow until the Full Moon. ...
Characteristics of Stars - Laconia School District
... Hertzsprung-Russell Diagram • People say about 100 years ago, two scientists were working alone and ...
... Hertzsprung-Russell Diagram • People say about 100 years ago, two scientists were working alone and ...
Astronomy
... 22. If the north celestial pole appears on your horizon, what is your latitude? 0 degrees at the equator ...
... 22. If the north celestial pole appears on your horizon, what is your latitude? 0 degrees at the equator ...
COORDINATES, TIME, AND THE SKY John Thorstensen
... approximation to what physicists call an inertial reference frame, which is not accelerating or (more appropriately for a system which specifies only directions) it is not rotating. As we’ll see later, it isn’t quite inertial, because the direction of the earth’s axis which defines the system is not ...
... approximation to what physicists call an inertial reference frame, which is not accelerating or (more appropriately for a system which specifies only directions) it is not rotating. As we’ll see later, it isn’t quite inertial, because the direction of the earth’s axis which defines the system is not ...
Geocentric model

In astronomy, the geocentric model (also known as geocentrism, or the Ptolemaic system) is a description of the cosmos where Earth is at the orbital center of all celestial bodies. This model served as the predominant cosmological system in many ancient civilizations such as ancient Greece including the noteworthy systems of Aristotle (see Aristotelian physics) and Ptolemy. As such, they believed that the Sun, Moon, stars, and naked eye planets circled Earth.Two commonly made observations supported the idea that Earth was the center of the Universe. The stars, the sun, and planets appear to revolve around Earth each day, making Earth the center of that system. The stars were thought to be on a celestial sphere, with the earth at its center, that rotated each day, using a line through the north and south pole as an axis. The stars closest to the equator appeared to rise and fall the greatest distance, but each star circled back to its rising point each day. The second observation supporting the geocentric model was that the Earth does not seem to move from the perspective of an Earth-bound observer, and that it is solid, stable, and unmoving.Ancient Roman and medieval philosophers usually combined the geocentric model with a spherical Earth. It is not the same as the older flat Earth model implied in some mythology, as was the case with the biblical and postbiblical Latin cosmology. The ancient Jewish Babylonian uranography pictured a flat Earth with a dome-shaped rigid canopy named firmament placed over it. (רקיע- rāqîa').However, the ancient Greeks believed that the motions of the planets were circular and not elliptical, a view that was not challenged in Western culture until the 17th century through the synthesis of theories by Copernicus and Kepler.The astronomical predictions of Ptolemy's geocentric model were used to prepare astrological and astronomical charts for over 1500 years. The geocentric model held sway into the early modern age, but from the late 16th century onward was gradually superseded by the heliocentric model of Copernicus, Galileo and Kepler. There was much resistance to the transition between these two theories. Christian theologians were reluctant to reject a theory that agreed with Bible passages (e.g. ""Sun, stand you still upon Gibeon"", Joshua 10:12 – King James 2000 Bible). Others felt a new, unknown theory could not subvert an accepted consensus for geocentrism.