The Solar System
... everything going around it. We now know that this is not correct. The idea that fits scientific observations and allows us to predict the movement of the planets is called the heliocentric model. This just means that the Sun is at the centre of the solar system, and the Earth and other planets go ar ...
... everything going around it. We now know that this is not correct. The idea that fits scientific observations and allows us to predict the movement of the planets is called the heliocentric model. This just means that the Sun is at the centre of the solar system, and the Earth and other planets go ar ...
Exam Name___________________________________
... B) A theory cannot be taken seriously by scientists if it contradicts other theories developed by scientists over the past several hundred years. C) If even a single new fact is discovered that contradicts what we expect according to a particular theory, then the theory must be revised or discar ...
... B) A theory cannot be taken seriously by scientists if it contradicts other theories developed by scientists over the past several hundred years. C) If even a single new fact is discovered that contradicts what we expect according to a particular theory, then the theory must be revised or discar ...
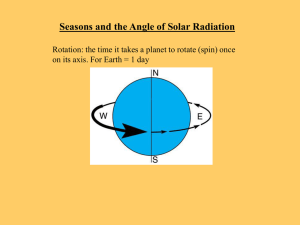
Seasons
... Billions of years ago, before there was life on Earth, a planet about the size of Mars smashed into us. It knocked the Earth over, so instead of rotating around an axis that is straight up and down, we are tilted by ...
... Billions of years ago, before there was life on Earth, a planet about the size of Mars smashed into us. It knocked the Earth over, so instead of rotating around an axis that is straight up and down, we are tilted by ...
Earth, Moon, Space, Solar System and Sun Study Guide Vocabulary
... Rotation- The spinning of a planet or moon on its axis. Ex- Earth rotates once every 24 hours on its axis. Earth rotates from west to east. ...
... Rotation- The spinning of a planet or moon on its axis. Ex- Earth rotates once every 24 hours on its axis. Earth rotates from west to east. ...
Lec 7 Copernicus I
... If everything is going in a circle, why do bodies fall to earth? Why can’t we detect stellar parallax? Why does the moon orbit the earth? Shouldn’t we see Phases of Venus? If Copernicus and Ptolemy both use epicycles, then how do we choose between them? 8. Scripture declares the universe to be geoce ...
... If everything is going in a circle, why do bodies fall to earth? Why can’t we detect stellar parallax? Why does the moon orbit the earth? Shouldn’t we see Phases of Venus? If Copernicus and Ptolemy both use epicycles, then how do we choose between them? 8. Scripture declares the universe to be geoce ...
Document
... earth, carrying around it with it the sun and moon. • The sun and moon must slowly drift with respect to the celestial sphere over the course of a month (moon) and year (sun). ...
... earth, carrying around it with it the sun and moon. • The sun and moon must slowly drift with respect to the celestial sphere over the course of a month (moon) and year (sun). ...
Chapter 16: Our Solar System
... _____ 11. Which of the following terrestrial planets has retrograde rotation? a. Mercury b. Venus c. Earth d. Mars _____ 12. Which of the following planets in the outer solar system is tipped on its side? a. Jupiter c. Uranus b. Saturn d. Neptune _____ 13. Which of the following moons of Jupiter is ...
... _____ 11. Which of the following terrestrial planets has retrograde rotation? a. Mercury b. Venus c. Earth d. Mars _____ 12. Which of the following planets in the outer solar system is tipped on its side? a. Jupiter c. Uranus b. Saturn d. Neptune _____ 13. Which of the following moons of Jupiter is ...
Lecture on Planetary Configurations
... “Take the orbits of any two planets and draw a line between the two planet positions every few days. Because the inner planet orbits faster than the outer planet, interesting patterns evolve. Each planetary pairing has its own unique dance rhythm. For example, the Earth-Venus dance returns to the ...
... “Take the orbits of any two planets and draw a line between the two planet positions every few days. Because the inner planet orbits faster than the outer planet, interesting patterns evolve. Each planetary pairing has its own unique dance rhythm. For example, the Earth-Venus dance returns to the ...
Stars
... Observed motions of the Sun can be described if either 1) The Sun goes around the Earth once per day, or 2) The Earth rotates about its axis. ...
... Observed motions of the Sun can be described if either 1) The Sun goes around the Earth once per day, or 2) The Earth rotates about its axis. ...
Ancient Astronomy
... First to point a telescope skyward (3X) then (30X) Profound discoveries 1. Milky Way had many more stars in it 2. Jupiter, now a small round disk, had four orbiting moons 3. Venus had phases 4. Sun had sunspots 5. Moon covered with craters and mountains These discoveries proved that Copernicus was r ...
... First to point a telescope skyward (3X) then (30X) Profound discoveries 1. Milky Way had many more stars in it 2. Jupiter, now a small round disk, had four orbiting moons 3. Venus had phases 4. Sun had sunspots 5. Moon covered with craters and mountains These discoveries proved that Copernicus was r ...
overview - Butlins
... space could lead to something that changes life on Earth. For example, if scientists can understand what happens outside of Earth’s atmosphere in the stars and galaxies, they might be able to stop global warming or they might be able to harness a new form of energy! It’s impossible to have a full un ...
... space could lead to something that changes life on Earth. For example, if scientists can understand what happens outside of Earth’s atmosphere in the stars and galaxies, they might be able to stop global warming or they might be able to harness a new form of energy! It’s impossible to have a full un ...
Know wonder sunmoonearth
... Things besides planets orbit the sun. Pluto is now a dwarf planet Because they thought it was way too small. It’s not close enough to our solar system. It takes the earth 365 to go around the sun. A new planet X. Sun is a huge star. Made out of burning gasses. The earth is an Inner core outer core a ...
... Things besides planets orbit the sun. Pluto is now a dwarf planet Because they thought it was way too small. It’s not close enough to our solar system. It takes the earth 365 to go around the sun. A new planet X. Sun is a huge star. Made out of burning gasses. The earth is an Inner core outer core a ...
The movements of planets and other nearby objects are
... bird and a plane flew overhead at the same time, you might think that the bird was faster. You would have this impression because the farther away a moving object is from you, the less it seems to move. Stars are always moving, but they are so far away that you cannot see their movements. Observers ...
... bird and a plane flew overhead at the same time, you might think that the bird was faster. You would have this impression because the farther away a moving object is from you, the less it seems to move. Stars are always moving, but they are so far away that you cannot see their movements. Observers ...
Science 9 – Space Exploration
... 11. In the 1920’s two scientists began comparing the surface temperature of stars with the star’s luminosity. They graphed their results in what is referred to as the … A. Solar Shift Model B. Hertzsprung-Russell Diagram C. Wegener-Darwin Illustration D. Helio-Solar Diagram 12. A star has a definite ...
... 11. In the 1920’s two scientists began comparing the surface temperature of stars with the star’s luminosity. They graphed their results in what is referred to as the … A. Solar Shift Model B. Hertzsprung-Russell Diagram C. Wegener-Darwin Illustration D. Helio-Solar Diagram 12. A star has a definite ...
The Newtonian Revolution: The discovery of natural law
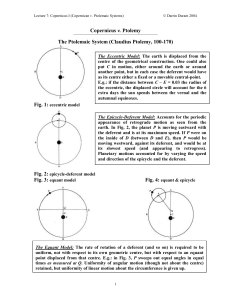
... Ptolemy – Greek (Egyptian) Astronomer 100AD made first decent quantitative model of the planets’ motion • It had the Earth at the center • It placed the planets Mercury and Venus carefully to match the observed angle offsets between the sun and these planets. • Accounted for retrograde motion with ...
... Ptolemy – Greek (Egyptian) Astronomer 100AD made first decent quantitative model of the planets’ motion • It had the Earth at the center • It placed the planets Mercury and Venus carefully to match the observed angle offsets between the sun and these planets. • Accounted for retrograde motion with ...
Decline of Western Civilization (extended) knowledge of ancient
... (orbital speed) x (distance to sun) = constant fastest at perihelion, slowest at aphelion ...
... (orbital speed) x (distance to sun) = constant fastest at perihelion, slowest at aphelion ...
We live in a solar system that consists of a star we call the Sun and
... Asteroid Minor planet. Comets Balls of dusty ice that orbit the Sun. Galaxy A catherine wheel made up from billions of stars which the Sun is one. Meteorite Pieces of rock or metal which strike Earth’s atmosphere. Eclipse When the Moon blocks the sunlight to the Earth (Solar Eclipse) or when the Ear ...
... Asteroid Minor planet. Comets Balls of dusty ice that orbit the Sun. Galaxy A catherine wheel made up from billions of stars which the Sun is one. Meteorite Pieces of rock or metal which strike Earth’s atmosphere. Eclipse When the Moon blocks the sunlight to the Earth (Solar Eclipse) or when the Ear ...
Part I: Moons, Asteroids, and Comets
... 3. Do all planets have moons? _________________________________________________________________________ 4. What is an asteroid? _________________________________________________________________________ 5. Where are most asteroids located? __________________________________________________________ ...
... 3. Do all planets have moons? _________________________________________________________________________ 4. What is an asteroid? _________________________________________________________________________ 5. Where are most asteroids located? __________________________________________________________ ...
Astro 205 Ch. 2
... • “Occam’s Razor” is a principle which states that simplicity is an important part of scienBfic theory. ...
... • “Occam’s Razor” is a principle which states that simplicity is an important part of scienBfic theory. ...
ch. 5 study guide
... o Why do we see different stars during different seasons? As Earth revolves around the Sun, it passes different groups of stars. o What is one constellation from our science book? The constellations in our science book include the Big Dipper, the Little Dipper, Orion, Cassiopeia, and Scorpius. Know ...
... o Why do we see different stars during different seasons? As Earth revolves around the Sun, it passes different groups of stars. o What is one constellation from our science book? The constellations in our science book include the Big Dipper, the Little Dipper, Orion, Cassiopeia, and Scorpius. Know ...
Document
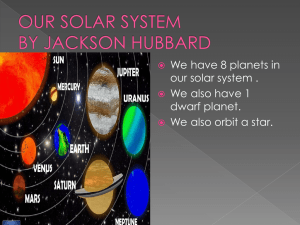
... We have 8 planets in our solar system . We also have 1 dwarf planet. We also orbit a star. ...
... We have 8 planets in our solar system . We also have 1 dwarf planet. We also orbit a star. ...
How do we know how the Solar System is
... Copernicus, a Polish astronomer, suggested a dramatically different model of the Solar System, a heliocentric model, with the Sun at the center Copernicus preserved the idea that planets orbited in circular orbits around the Sun, however. Big debate ensued, between geocentric and heliocentric mode ...
... Copernicus, a Polish astronomer, suggested a dramatically different model of the Solar System, a heliocentric model, with the Sun at the center Copernicus preserved the idea that planets orbited in circular orbits around the Sun, however. Big debate ensued, between geocentric and heliocentric mode ...
Copernican Revolution Part 1
... (7 Planetes* - Sun, Moon, Mercury, Venus, Mars, Jupiter, Saturn) No science in ancient Greece (comparison of theories & evidence) Pythagoras of Samos ~500 BCE Earth is a sphere* Mathematical perfection,* (Note: separation of ideal from reality) All complex phenomena must result from basic simple one ...
... (7 Planetes* - Sun, Moon, Mercury, Venus, Mars, Jupiter, Saturn) No science in ancient Greece (comparison of theories & evidence) Pythagoras of Samos ~500 BCE Earth is a sphere* Mathematical perfection,* (Note: separation of ideal from reality) All complex phenomena must result from basic simple one ...
Geocentric model

In astronomy, the geocentric model (also known as geocentrism, or the Ptolemaic system) is a description of the cosmos where Earth is at the orbital center of all celestial bodies. This model served as the predominant cosmological system in many ancient civilizations such as ancient Greece including the noteworthy systems of Aristotle (see Aristotelian physics) and Ptolemy. As such, they believed that the Sun, Moon, stars, and naked eye planets circled Earth.Two commonly made observations supported the idea that Earth was the center of the Universe. The stars, the sun, and planets appear to revolve around Earth each day, making Earth the center of that system. The stars were thought to be on a celestial sphere, with the earth at its center, that rotated each day, using a line through the north and south pole as an axis. The stars closest to the equator appeared to rise and fall the greatest distance, but each star circled back to its rising point each day. The second observation supporting the geocentric model was that the Earth does not seem to move from the perspective of an Earth-bound observer, and that it is solid, stable, and unmoving.Ancient Roman and medieval philosophers usually combined the geocentric model with a spherical Earth. It is not the same as the older flat Earth model implied in some mythology, as was the case with the biblical and postbiblical Latin cosmology. The ancient Jewish Babylonian uranography pictured a flat Earth with a dome-shaped rigid canopy named firmament placed over it. (רקיע- rāqîa').However, the ancient Greeks believed that the motions of the planets were circular and not elliptical, a view that was not challenged in Western culture until the 17th century through the synthesis of theories by Copernicus and Kepler.The astronomical predictions of Ptolemy's geocentric model were used to prepare astrological and astronomical charts for over 1500 years. The geocentric model held sway into the early modern age, but from the late 16th century onward was gradually superseded by the heliocentric model of Copernicus, Galileo and Kepler. There was much resistance to the transition between these two theories. Christian theologians were reluctant to reject a theory that agreed with Bible passages (e.g. ""Sun, stand you still upon Gibeon"", Joshua 10:12 – King James 2000 Bible). Others felt a new, unknown theory could not subvert an accepted consensus for geocentrism.