Astronomy Unit Test Review Sheet
... 2. What is an optical telescope? What is the difference between a reflecting and a refracting telescope? What other types of telescopes do scientists use to gather information? Optical telescopes are used to see visible light from far away. Refracting uses a glass lens and a reflecting telescope use ...
... 2. What is an optical telescope? What is the difference between a reflecting and a refracting telescope? What other types of telescopes do scientists use to gather information? Optical telescopes are used to see visible light from far away. Refracting uses a glass lens and a reflecting telescope use ...
Study Guide for Unit 4: Stars and Solar System
... Rotation- the act of spinning Revolution- when one object travels around another Axis-a real or imaginary line that an object spins around Orbit-the path a revolving object takes Phases-the apparent shape of the moon in the sky Concepts to know: *The Earth rotates on an imaginary axis. This action c ...
... Rotation- the act of spinning Revolution- when one object travels around another Axis-a real or imaginary line that an object spins around Orbit-the path a revolving object takes Phases-the apparent shape of the moon in the sky Concepts to know: *The Earth rotates on an imaginary axis. This action c ...
1700_orbits
... • Astronomers knew the relative distances of the planets, but not the absolute distances. • Known: Jupiter is 5 times farther from the Sun than the Earth is. It takes Jupiter 12 times longer to go around the Sun than it does for the Earth. • Not known: How many kilometers (or miles) are the Earth an ...
... • Astronomers knew the relative distances of the planets, but not the absolute distances. • Known: Jupiter is 5 times farther from the Sun than the Earth is. It takes Jupiter 12 times longer to go around the Sun than it does for the Earth. • Not known: How many kilometers (or miles) are the Earth an ...
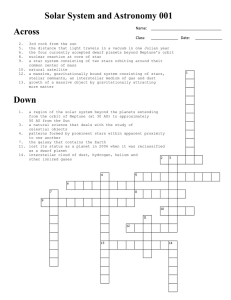
Solar System and Astronomy puzzle 001
... a star system consisting of two stars orbiting around their common center of mass 10. natural satellite 12. a massive, gravitationally bound system consisting of stars, stellar remnants, an interstellar medium of gas and dust 13. growth of a massive object by gravitationally attracting more matter ...
... a star system consisting of two stars orbiting around their common center of mass 10. natural satellite 12. a massive, gravitationally bound system consisting of stars, stellar remnants, an interstellar medium of gas and dust 13. growth of a massive object by gravitationally attracting more matter ...
Genetics: The Science of Heredity
... ______ 7. Earth has seasons because a. it rotates on its axis. b. the distance between Earth and the sun changes. c. its axis is tilted as it moves around the sun. d. the temperature of the sun changes. ...
... ______ 7. Earth has seasons because a. it rotates on its axis. b. the distance between Earth and the sun changes. c. its axis is tilted as it moves around the sun. d. the temperature of the sun changes. ...
Genetics: The Science of Heredity
... a. Like the moon, the stars move around Earth. b. As Earth revolves around the sun, we have a different view of the stars. c. As the Earth rotates on its axis, we see different parts of the sky. d. Just as the seasons on Earth change, so do the seasons on stars. ...
... a. Like the moon, the stars move around Earth. b. As Earth revolves around the sun, we have a different view of the stars. c. As the Earth rotates on its axis, we see different parts of the sky. d. Just as the seasons on Earth change, so do the seasons on stars. ...
Astronomy Comprehensive Test
... the spectra of most galaxies shifted toward the red end of the spectrum. Another American astronomer, Edwin Hubble, later interpreted this discovery as evidence that __________________________________ ...
... the spectra of most galaxies shifted toward the red end of the spectrum. Another American astronomer, Edwin Hubble, later interpreted this discovery as evidence that __________________________________ ...
File - Teaching Through E
... • Mars is the God of War • Sometimes referred to as the Red Planet • Even though Mars is much smaller than Earth, its surface area is about the same as the land surface area of Earth. ...
... • Mars is the God of War • Sometimes referred to as the Red Planet • Even though Mars is much smaller than Earth, its surface area is about the same as the land surface area of Earth. ...
Chapter 2 History
... Aristotelian theory of motion, and only managed to account for the observed planetary positions by a combination of deferents and epicycles centred on the stationary sun. It was the moving earth that annoyed his peers. Tycho Brahe, the great astronomer of the next generation clearly appreciated the ...
... Aristotelian theory of motion, and only managed to account for the observed planetary positions by a combination of deferents and epicycles centred on the stationary sun. It was the moving earth that annoyed his peers. Tycho Brahe, the great astronomer of the next generation clearly appreciated the ...
The Solar System
... • Solar System: The sun together with the eight planets and all other celestial bodies that orbit the sun. • Outer Planets: Any of the four planets, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, Neptune, with orbits outside that of Mars. • Inner Planets: Any of the four planets, Mercury, Venus, Earth, and Mars, whose or ...
... • Solar System: The sun together with the eight planets and all other celestial bodies that orbit the sun. • Outer Planets: Any of the four planets, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, Neptune, with orbits outside that of Mars. • Inner Planets: Any of the four planets, Mercury, Venus, Earth, and Mars, whose or ...
Document
... stars revolve around the Earth which is fixed) “Geocentric Universe”: fixed relationship between stars Ptolemy (c. 100 A.D.) refined the system introduced (most notably) by Hipparchus to explain the observed motions of the stars and planets. Copernicus (1473-1543) proposed a heliocentric model of pl ...
... stars revolve around the Earth which is fixed) “Geocentric Universe”: fixed relationship between stars Ptolemy (c. 100 A.D.) refined the system introduced (most notably) by Hipparchus to explain the observed motions of the stars and planets. Copernicus (1473-1543) proposed a heliocentric model of pl ...
Lecture 3
... • Heliocentric parallax uses the sun as a base. • Take a photo with telescope at two different seasons come back to later for stars • Geocentric parallax uses the earth as a base. • Make a measurement two or more times in one night. • Use for planets/Sun/Moon Brahe’s data also had distances to p ...
... • Heliocentric parallax uses the sun as a base. • Take a photo with telescope at two different seasons come back to later for stars • Geocentric parallax uses the earth as a base. • Make a measurement two or more times in one night. • Use for planets/Sun/Moon Brahe’s data also had distances to p ...
Contributions of astronomy to all of science
... and taking from this Earth, from the rest of the world that we call “The Environment.” We live in a complex and interconnected world. At times this can be overwhelming and occasionally, we are tempted to, and perhaps even need to, retreat into a view of the world that is simpler, isolated and c ...
... and taking from this Earth, from the rest of the world that we call “The Environment.” We live in a complex and interconnected world. At times this can be overwhelming and occasionally, we are tempted to, and perhaps even need to, retreat into a view of the world that is simpler, isolated and c ...
Slide 1
... places that are far, far away. time light Telescopes are _________ machines, because the _________ that comes to you through them left their star or galaxy ...
... places that are far, far away. time light Telescopes are _________ machines, because the _________ that comes to you through them left their star or galaxy ...
Grade 8 Science Astronomy Benchmark DO NOT WRITE ON THIS
... 1. The Sun is higher in the sky, daylight is shorter 2. The Sun is higher in the Sky, daylight is longer 3. The Sun is lower in sky, daylight is longer 4. The Sun is lower in the sky, daylight is shorter ...
... 1. The Sun is higher in the sky, daylight is shorter 2. The Sun is higher in the Sky, daylight is longer 3. The Sun is lower in sky, daylight is longer 4. The Sun is lower in the sky, daylight is shorter ...
34_alone
... • Why only us? • How could the Universe be so big and so so lonely? • What is our destiny? If we kill ourselves, what has it all been for? • All those worlds we can not detect. What are they for? • “It would be a great waste of space”. ...
... • Why only us? • How could the Universe be so big and so so lonely? • What is our destiny? If we kill ourselves, what has it all been for? • All those worlds we can not detect. What are they for? • “It would be a great waste of space”. ...
Minerals
... In NYS, the sun is almost always in the southern sky; therefore shadows always point north. For anything about seasons: IT’S ALL IN THE TILT – 23 ½ o Earth’s eccentricity is very slight, so it is not quite a circle, it’s an oblate sphere or a slightly eccentric ellipse; BUT . . . A diagram of Earth’ ...
... In NYS, the sun is almost always in the southern sky; therefore shadows always point north. For anything about seasons: IT’S ALL IN THE TILT – 23 ½ o Earth’s eccentricity is very slight, so it is not quite a circle, it’s an oblate sphere or a slightly eccentric ellipse; BUT . . . A diagram of Earth’ ...
Assessment - hrsbstaff.ednet.ns.ca
... (a) the space shuttle is falling freely toward Earth (b) the space shuttle is not affected by Earth’s gravity (c) the mass of the space shuttle decreases as the distance from Earth increases (d) the space shuttle is moving away from Earth 5. The force of gravity exerts a ___ on an orbiting satellite ...
... (a) the space shuttle is falling freely toward Earth (b) the space shuttle is not affected by Earth’s gravity (c) the mass of the space shuttle decreases as the distance from Earth increases (d) the space shuttle is moving away from Earth 5. The force of gravity exerts a ___ on an orbiting satellite ...
Assessment - hrsbstaff.ednet.ns.ca
... (a) the space shuttle is falling freely toward Earth (b) the space shuttle is not affected by Earth’s gravity (c) the mass of the space shuttle decreases as the distance from Earth increases (d) the space shuttle is moving away from Earth 5. The force of gravity exerts a ___ on an orbiting satellite ...
... (a) the space shuttle is falling freely toward Earth (b) the space shuttle is not affected by Earth’s gravity (c) the mass of the space shuttle decreases as the distance from Earth increases (d) the space shuttle is moving away from Earth 5. The force of gravity exerts a ___ on an orbiting satellite ...
Video: National Geographic: Journey to the Edge of the Universe
... 59. Light travels at ____ trillion miles per year. 60. The star Epsilon Eridani is located just ____ light years from Earth 61. Star Gliese 581 is located ______ light years from Earth 62. Comets are _____________________ and ______________________. 63. The atmosphere of Bellerophon is being __ ...
... 59. Light travels at ____ trillion miles per year. 60. The star Epsilon Eridani is located just ____ light years from Earth 61. Star Gliese 581 is located ______ light years from Earth 62. Comets are _____________________ and ______________________. 63. The atmosphere of Bellerophon is being __ ...
Chapter 20
... kinetic energy is transformed to (a) stopping energy. (b) potential energy. (c) heat energy. (d) energy of rest. ...
... kinetic energy is transformed to (a) stopping energy. (b) potential energy. (c) heat energy. (d) energy of rest. ...
EarthScience1stNineWeeks
... 22. Why would a person weigh more on the Earth than on the moon? (notes) 23. The Southern Hemisphere is warmer in January than in July because— (23, 664) 24. If the Earth is in the winter solstice position for the northern hemisphere, what part of the Earth would receive the most direct sunlight? 25 ...
... 22. Why would a person weigh more on the Earth than on the moon? (notes) 23. The Southern Hemisphere is warmer in January than in July because— (23, 664) 24. If the Earth is in the winter solstice position for the northern hemisphere, what part of the Earth would receive the most direct sunlight? 25 ...
Geocentric model

In astronomy, the geocentric model (also known as geocentrism, or the Ptolemaic system) is a description of the cosmos where Earth is at the orbital center of all celestial bodies. This model served as the predominant cosmological system in many ancient civilizations such as ancient Greece including the noteworthy systems of Aristotle (see Aristotelian physics) and Ptolemy. As such, they believed that the Sun, Moon, stars, and naked eye planets circled Earth.Two commonly made observations supported the idea that Earth was the center of the Universe. The stars, the sun, and planets appear to revolve around Earth each day, making Earth the center of that system. The stars were thought to be on a celestial sphere, with the earth at its center, that rotated each day, using a line through the north and south pole as an axis. The stars closest to the equator appeared to rise and fall the greatest distance, but each star circled back to its rising point each day. The second observation supporting the geocentric model was that the Earth does not seem to move from the perspective of an Earth-bound observer, and that it is solid, stable, and unmoving.Ancient Roman and medieval philosophers usually combined the geocentric model with a spherical Earth. It is not the same as the older flat Earth model implied in some mythology, as was the case with the biblical and postbiblical Latin cosmology. The ancient Jewish Babylonian uranography pictured a flat Earth with a dome-shaped rigid canopy named firmament placed over it. (רקיע- rāqîa').However, the ancient Greeks believed that the motions of the planets were circular and not elliptical, a view that was not challenged in Western culture until the 17th century through the synthesis of theories by Copernicus and Kepler.The astronomical predictions of Ptolemy's geocentric model were used to prepare astrological and astronomical charts for over 1500 years. The geocentric model held sway into the early modern age, but from the late 16th century onward was gradually superseded by the heliocentric model of Copernicus, Galileo and Kepler. There was much resistance to the transition between these two theories. Christian theologians were reluctant to reject a theory that agreed with Bible passages (e.g. ""Sun, stand you still upon Gibeon"", Joshua 10:12 – King James 2000 Bible). Others felt a new, unknown theory could not subvert an accepted consensus for geocentrism.