
WK8
... "One of the most impressive discoveries was the origin of the energy of the stars. One of the men who discovered this was out with his girl friend the night after he realized that nuclear reactions must be going on in the stars in order to make them shine. She said "Look at how pretty the stars shin ...
... "One of the most impressive discoveries was the origin of the energy of the stars. One of the men who discovered this was out with his girl friend the night after he realized that nuclear reactions must be going on in the stars in order to make them shine. She said "Look at how pretty the stars shin ...
Solar System, Galaxy, and Universe (ES) V.4
... heavy and light elements, hot interiors of earth-like planets. Age of the solar system. Real-world contexts: Nebulas considered to be star-forming ...
... heavy and light elements, hot interiors of earth-like planets. Age of the solar system. Real-world contexts: Nebulas considered to be star-forming ...
Revolution: Earth`s orbit around the Sun
... Sun and Moon look equal in size in the sky because the Sun is 400 times larger but 400 times farther away The Moon will rise 50 minutes later each day because as the moon revolves around the Earth, the Earth is revolving and rotating Only one-half of the Moon is lit ALL the time, it is not Ful ...
... Sun and Moon look equal in size in the sky because the Sun is 400 times larger but 400 times farther away The Moon will rise 50 minutes later each day because as the moon revolves around the Earth, the Earth is revolving and rotating Only one-half of the Moon is lit ALL the time, it is not Ful ...
The Solar System
... • It has 16 moons, two of which are huge. • Its largest moon is called Ganymede. • Jupiter has a small ring system. • One day on Jupiter lasts nearly 10 Earth hours. • It takes 11.9 years to orbit the Sun. b4tea.com/information/jupiter-facts-and-infor ...
... • It has 16 moons, two of which are huge. • Its largest moon is called Ganymede. • Jupiter has a small ring system. • One day on Jupiter lasts nearly 10 Earth hours. • It takes 11.9 years to orbit the Sun. b4tea.com/information/jupiter-facts-and-infor ...
Types of Planetary System
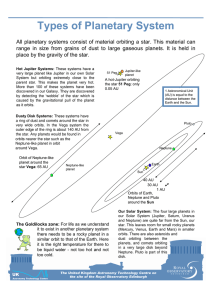
... a ring of dust and comets around the star in very wide orbits. In the Vega system the outer edge of the ring is about 140 AU from the star. Any planets would be found in orbits nearer the star such as the Neptune-like planet in orbit around Vega. Orbit of Neptune-like planet around the star Vega: 65 ...
... a ring of dust and comets around the star in very wide orbits. In the Vega system the outer edge of the ring is about 140 AU from the star. Any planets would be found in orbits nearer the star such as the Neptune-like planet in orbit around Vega. Orbit of Neptune-like planet around the star Vega: 65 ...
planet
... about this peculiar dwarf planet. • Unlike planets, dwarf planets lack the gravitational muscle to sweep up or scatter objects near their orbits. They end up orbiting the sun in zones of similar objects such as the asteroid and Kuiper belts. ...
... about this peculiar dwarf planet. • Unlike planets, dwarf planets lack the gravitational muscle to sweep up or scatter objects near their orbits. They end up orbiting the sun in zones of similar objects such as the asteroid and Kuiper belts. ...
The Solar System - Kennesaw State University
... The moon does not give off its own light. Instead, it reflects light from the sun. Half of the moon always faces the sun and so is always lit. As the moon moves through it’s orbit, different amounts of its lit half can be seen from Earth. That’s why the moon seems to have different shapes or phases. ...
... The moon does not give off its own light. Instead, it reflects light from the sun. Half of the moon always faces the sun and so is always lit. As the moon moves through it’s orbit, different amounts of its lit half can be seen from Earth. That’s why the moon seems to have different shapes or phases. ...
PRACTICE MINI-EXAM
... each), 3 mathematical problems (10 points each), and 1 essay question (25 points). This mini-exam contains 8 short-answer problems and 2 mathematical problems. ...
... each), 3 mathematical problems (10 points each), and 1 essay question (25 points). This mini-exam contains 8 short-answer problems and 2 mathematical problems. ...
In Retrospect: Kepler`s Astronomia Nova
... The 2009 International Year of Astronomy commemorates the 400th anniversary of two great discoveries: Galileo Galilei’s detection of Jupiter’s four major moons and the publication of Johannes Kepler’s monumental book Astronomia Nova. In this 1609 work, Kepler demonstrated that planets follow ellipti ...
... The 2009 International Year of Astronomy commemorates the 400th anniversary of two great discoveries: Galileo Galilei’s detection of Jupiter’s four major moons and the publication of Johannes Kepler’s monumental book Astronomia Nova. In this 1609 work, Kepler demonstrated that planets follow ellipti ...
Macmillan Natural and Social Science 1 [bold PB font]
... Your child is about to start unit 7 of Natural and Social Science 2. The topic of this unit is The Sun. In this unit, your child will learn to ...
... Your child is about to start unit 7 of Natural and Social Science 2. The topic of this unit is The Sun. In this unit, your child will learn to ...
Day 1 - Ch 1
... Apparent rotation of the celestial sphere is due to the rotation of the Earth. The Earth is rotating around an axis that goes from pole to pole through a center. Eventually, each day, the Sun sets in the west. If we suppose the Sun is the center of the solar system, it is fixed, so: Each point on t ...
... Apparent rotation of the celestial sphere is due to the rotation of the Earth. The Earth is rotating around an axis that goes from pole to pole through a center. Eventually, each day, the Sun sets in the west. If we suppose the Sun is the center of the solar system, it is fixed, so: Each point on t ...
Earth Rotation and Revolution Powerpoint
... The complete circular path can be seen for stars in the northern part of the sky around Polaris ...
... The complete circular path can be seen for stars in the northern part of the sky around Polaris ...
Summary of week 1:
... questions, come and chat for a minute or two with me, because I want to know who you are, what you are studying, how you are doing in the class, etc. 2) Make a brief presentation to the class (say, about a minute) based on one of the astronomy picures of the day (see link on class web site). Choose ...
... questions, come and chat for a minute or two with me, because I want to know who you are, what you are studying, how you are doing in the class, etc. 2) Make a brief presentation to the class (say, about a minute) based on one of the astronomy picures of the day (see link on class web site). Choose ...
Glossary - CW Perry School
... On June 21st from a point on the Arctic Circle, the Sun will appear to descend into the north-west, but instead of setting it will appear to skim the northern horizon and rise up again in the north-east. This never-setting sun known as the Midnight Sun. The further north you go the more days of Midn ...
... On June 21st from a point on the Arctic Circle, the Sun will appear to descend into the north-west, but instead of setting it will appear to skim the northern horizon and rise up again in the north-east. This never-setting sun known as the Midnight Sun. The further north you go the more days of Midn ...
solar_system
... Jupiter’s moons and is the fourth largest. It is slightly smaller than the Earth’s moon. The surface strongly resembles images of sea ice on Earth. There may be a liquid water sea under the crust. Europa is one of the five known moons in the solar system to have an ...
... Jupiter’s moons and is the fourth largest. It is slightly smaller than the Earth’s moon. The surface strongly resembles images of sea ice on Earth. There may be a liquid water sea under the crust. Europa is one of the five known moons in the solar system to have an ...
Lecture 1 Review Sheet
... Explain the significance of the cosmic microwave background radiation. What wavelength did it start out as? What does it record? Explain the nebular theory of planet formation Why is the Earth a sphere? List all the planets and dwarf planets from closest to farthest from the sun What does it mean wh ...
... Explain the significance of the cosmic microwave background radiation. What wavelength did it start out as? What does it record? Explain the nebular theory of planet formation Why is the Earth a sphere? List all the planets and dwarf planets from closest to farthest from the sun What does it mean wh ...
What part of the sun can we see only during a solar eclipse?
... earth is closer to the sun in the summer and further away in the winter. ...
... earth is closer to the sun in the summer and further away in the winter. ...
Unit 1
... • A body at rest stays at rest unless acted on by an outside force • b. F=ma • c. P^2=A^3 • d. Fg=mMG/R^2 ...
... • A body at rest stays at rest unless acted on by an outside force • b. F=ma • c. P^2=A^3 • d. Fg=mMG/R^2 ...
mary - Cal State LA - Instructional Web Server
... Planets travel around it in circular paths or orbits Holds the solar system together Filled with scorching, hot gases Provides energy that heats our world and makes life possible ...
... Planets travel around it in circular paths or orbits Holds the solar system together Filled with scorching, hot gases Provides energy that heats our world and makes life possible ...
Space Exploration Review Key
... Universal gravitation - Newton’s law states that all objects attract other objects and provides an explanation for the planets elliptical Reading Questions 1. a. Who invented the telescope and in what year? Hans Lippershry, 1608 b. What was the original purpose of the telescope? To magnify image-spe ...
... Universal gravitation - Newton’s law states that all objects attract other objects and provides an explanation for the planets elliptical Reading Questions 1. a. Who invented the telescope and in what year? Hans Lippershry, 1608 b. What was the original purpose of the telescope? To magnify image-spe ...
1 The Celestial Equator and the Ecliptic 2 Seasonal Changes in the
... We now know that this is due to the precession of the equinoxes. This is fundamentally due to the precession of the Earth’s rotation axis (see Figure 1.10). Precession occurs when a rotating object is subject to a torque. The precession period is 25800 years. Since the location of the north celestia ...
... We now know that this is due to the precession of the equinoxes. This is fundamentally due to the precession of the Earth’s rotation axis (see Figure 1.10). Precession occurs when a rotating object is subject to a torque. The precession period is 25800 years. Since the location of the north celestia ...
Geocentric model

In astronomy, the geocentric model (also known as geocentrism, or the Ptolemaic system) is a description of the cosmos where Earth is at the orbital center of all celestial bodies. This model served as the predominant cosmological system in many ancient civilizations such as ancient Greece including the noteworthy systems of Aristotle (see Aristotelian physics) and Ptolemy. As such, they believed that the Sun, Moon, stars, and naked eye planets circled Earth.Two commonly made observations supported the idea that Earth was the center of the Universe. The stars, the sun, and planets appear to revolve around Earth each day, making Earth the center of that system. The stars were thought to be on a celestial sphere, with the earth at its center, that rotated each day, using a line through the north and south pole as an axis. The stars closest to the equator appeared to rise and fall the greatest distance, but each star circled back to its rising point each day. The second observation supporting the geocentric model was that the Earth does not seem to move from the perspective of an Earth-bound observer, and that it is solid, stable, and unmoving.Ancient Roman and medieval philosophers usually combined the geocentric model with a spherical Earth. It is not the same as the older flat Earth model implied in some mythology, as was the case with the biblical and postbiblical Latin cosmology. The ancient Jewish Babylonian uranography pictured a flat Earth with a dome-shaped rigid canopy named firmament placed over it. (רקיע- rāqîa').However, the ancient Greeks believed that the motions of the planets were circular and not elliptical, a view that was not challenged in Western culture until the 17th century through the synthesis of theories by Copernicus and Kepler.The astronomical predictions of Ptolemy's geocentric model were used to prepare astrological and astronomical charts for over 1500 years. The geocentric model held sway into the early modern age, but from the late 16th century onward was gradually superseded by the heliocentric model of Copernicus, Galileo and Kepler. There was much resistance to the transition between these two theories. Christian theologians were reluctant to reject a theory that agreed with Bible passages (e.g. ""Sun, stand you still upon Gibeon"", Joshua 10:12 – King James 2000 Bible). Others felt a new, unknown theory could not subvert an accepted consensus for geocentrism.









![Macmillan Natural and Social Science 1 [bold PB font]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/006552150_1-744c96fecd477a0d4dbe6606035b9c8f-300x300.png)












