Name: Astronomy Study Guide Part 1 Define Astronomy
... What keeps the planets from flying out into space? What keeps them from crashing into the sun? (2 answers) The suns gravity keeps the planets from flying into space, the inertia of the planets keeps them from going into the sun How are the following defined: day, month, year, calendar, leap year Day ...
... What keeps the planets from flying out into space? What keeps them from crashing into the sun? (2 answers) The suns gravity keeps the planets from flying into space, the inertia of the planets keeps them from going into the sun How are the following defined: day, month, year, calendar, leap year Day ...
Outer Space Study Guide
... This is another exciting theme to learn about. In the next few years ordinary people can travel to space thanks to Virgin Galactic’s idea. Anyone can view space from their computer thanks to the ISS. LINK. To top things off you can even explore Mars from home. LINK Scientist have estimated Earth to ...
... This is another exciting theme to learn about. In the next few years ordinary people can travel to space thanks to Virgin Galactic’s idea. Anyone can view space from their computer thanks to the ISS. LINK. To top things off you can even explore Mars from home. LINK Scientist have estimated Earth to ...
The movements of planets and other nearby objects are visible from
... Planet comes from a Greek word that means “wanderer.” Ancient Greek astronomers used this term because they noticed that planets move among the constellations. It is easiest to see the movements of Venus and Mars, the two planets closest to Earth. They change their positions in the sky from night to ...
... Planet comes from a Greek word that means “wanderer.” Ancient Greek astronomers used this term because they noticed that planets move among the constellations. It is easiest to see the movements of Venus and Mars, the two planets closest to Earth. They change their positions in the sky from night to ...
astro20 chap27 - Las Positas College
... fraction of planets with intelligent life that develops technology – don’t know how many early human civilizations failed to develop technology – the fact the many independent early civilizations did develop technology makes us believe ~ 1 ...
... fraction of planets with intelligent life that develops technology – don’t know how many early human civilizations failed to develop technology – the fact the many independent early civilizations did develop technology makes us believe ~ 1 ...
P1_Physics_Summary_Topic_3
... Keywords: red giant, supernova, white dwarf, black dwarf, fusion reactions, main sequence, neutron star ...
... Keywords: red giant, supernova, white dwarf, black dwarf, fusion reactions, main sequence, neutron star ...
Our Solar Neighbourhood
... “protoplanet hypothesis” = model to explain the birth of solar systems 1. cloud of dust and gas begins to swirl 2. most material accumulates in the center and forms the sun 3. remaining material accumulates in smaller clumps circling the center to form the planets ...
... “protoplanet hypothesis” = model to explain the birth of solar systems 1. cloud of dust and gas begins to swirl 2. most material accumulates in the center and forms the sun 3. remaining material accumulates in smaller clumps circling the center to form the planets ...
Lecture 1 The Big Picture: Origin of the Earth
... So, H, He most abundant, intermediate atoms are less, heavy elements are rare. ...
... So, H, He most abundant, intermediate atoms are less, heavy elements are rare. ...
Astronomy Objective 1 1. An asteroid is a small, rocky object that
... 10. A lunar eclipse is the passing of the moon through the Earth’s shadow at full moon. 11. A meteor is a bright streak of light that results when a meteoroid burns up in Earth’s atmosphere. 12. A meteorite is a meteoroid or any part of a meteoroid that is left when a meteoroid hits the Earth. 13. ...
... 10. A lunar eclipse is the passing of the moon through the Earth’s shadow at full moon. 11. A meteor is a bright streak of light that results when a meteoroid burns up in Earth’s atmosphere. 12. A meteorite is a meteoroid or any part of a meteoroid that is left when a meteoroid hits the Earth. 13. ...
Physical Geography Exam Review Part 2
... ѺThe Universe (Big Bang) ѺThe Solar System ѺThe Sun and the Earth ѺEarths Age and Uniqueness ѺThe Earth in Motion (Seasons) ...
... ѺThe Universe (Big Bang) ѺThe Solar System ѺThe Sun and the Earth ѺEarths Age and Uniqueness ѺThe Earth in Motion (Seasons) ...
36040345-1 - Space Medicine Association
... (3) They are totally different from life as we know it. 8 The second alternative arises from the possibility that completely independent biological systems originated with an identical chemical composition. Thus, the earth's system would be, so to say, universal. The hypothesis of panspermy, defende ...
... (3) They are totally different from life as we know it. 8 The second alternative arises from the possibility that completely independent biological systems originated with an identical chemical composition. Thus, the earth's system would be, so to say, universal. The hypothesis of panspermy, defende ...
Lecture 27 (pdf from the powerpoint)
... •Estimated by Drake as 0.5. It is now known from modern planet searches that at least 10% of sunlike stars have planets, and the true proportion may be much higher, since only planets gas-giant size and larger can be detected with current technology.[3] •ne = Estimated by Drake as 2. The same paper ...
... •Estimated by Drake as 0.5. It is now known from modern planet searches that at least 10% of sunlike stars have planets, and the true proportion may be much higher, since only planets gas-giant size and larger can be detected with current technology.[3] •ne = Estimated by Drake as 2. The same paper ...
General Science Class: ______ Earth Science
... 16. How will the composition of the sun change as billions of years pass? 17. What makes sunspots different from the rest of the surface of the sun? 18. What are solar flares? 19. Explain why scientists might be interested in knowing when the sunspot cycle is at its peak? 20. How do scientists class ...
... 16. How will the composition of the sun change as billions of years pass? 17. What makes sunspots different from the rest of the surface of the sun? 18. What are solar flares? 19. Explain why scientists might be interested in knowing when the sunspot cycle is at its peak? 20. How do scientists class ...
Origin and Age of the Universe
... 2. What do the majority of scientists believe was the origin of our Universe? ...
... 2. What do the majority of scientists believe was the origin of our Universe? ...
SNC 1PW - TeacherWeb
... 11. A _____________ is a lump of rock or metal that is trapped by Earth’s atmosphere. 12. A __________ is a chunk of frozen matter that travels in a very long orbit around the sun. Much of the orbit of a comet takes place ______________ our solar system. 13. A __________ _________ is the distance th ...
... 11. A _____________ is a lump of rock or metal that is trapped by Earth’s atmosphere. 12. A __________ is a chunk of frozen matter that travels in a very long orbit around the sun. Much of the orbit of a comet takes place ______________ our solar system. 13. A __________ _________ is the distance th ...
The Solar System
... The warming center is becoming a “protostar” of mostly hot hydrogen gas. Further out in the nebula other clumps of dust and debris are gathering into asteroid sized objects and “planetesimals”. ...
... The warming center is becoming a “protostar” of mostly hot hydrogen gas. Further out in the nebula other clumps of dust and debris are gathering into asteroid sized objects and “planetesimals”. ...
DO NOT WRITE ON THIS PAPER Standard 1 Objective 1 Study
... 15.The time it takes for half of a sample of a radioactive isotope to decay is called a Halflife. 16.Radioactive dating is used to determine the absolute age of rocks because radioactive decay happens at a relatively constant rate. 17.Radiometric dating is determining the age of a substance by compa ...
... 15.The time it takes for half of a sample of a radioactive isotope to decay is called a Halflife. 16.Radioactive dating is used to determine the absolute age of rocks because radioactive decay happens at a relatively constant rate. 17.Radiometric dating is determining the age of a substance by compa ...
knowledge quiz - Discovery Education
... A. our solar system and all other solar systems that exist B. nine planets, one sun, asteroids, and comets C. five solar systems D. just our sun http://www.discoveryschool.com/curriculumcenter/universe ...
... A. our solar system and all other solar systems that exist B. nine planets, one sun, asteroids, and comets C. five solar systems D. just our sun http://www.discoveryschool.com/curriculumcenter/universe ...
Document
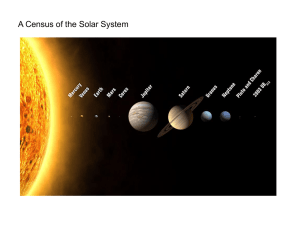
... including 58 residing in life-friendly orbits around their parent stars. The census, collected by NASA's Kepler Space Telescope after just four months of work, shows that small planets like Earth are much more prevalent than Jupiter-sized worlds and that multiple-planet systems are ...
... including 58 residing in life-friendly orbits around their parent stars. The census, collected by NASA's Kepler Space Telescope after just four months of work, shows that small planets like Earth are much more prevalent than Jupiter-sized worlds and that multiple-planet systems are ...
No Slide Title
... • If they are big enough, they will not totally burn up and will hit the earth. Meteors that survive are called METEORITES • Meteorites can cause damage. When they hit the earth they create CRATERS, just like on the moon. The earth has been hit by millions of meteorites in the past, their craters h ...
... • If they are big enough, they will not totally burn up and will hit the earth. Meteors that survive are called METEORITES • Meteorites can cause damage. When they hit the earth they create CRATERS, just like on the moon. The earth has been hit by millions of meteorites in the past, their craters h ...
Life2
... Quantum fluctuations in early universe produced “framework” of galaxy formation. Attracted gas and dark matter that coalesced to form first galaxies at only 500 million years. Formed in “cosmic web”. ...
... Quantum fluctuations in early universe produced “framework” of galaxy formation. Attracted gas and dark matter that coalesced to form first galaxies at only 500 million years. Formed in “cosmic web”. ...
Asteroids PP - MR D`S ICT CORNER
... • Asteroids are large chunks of rock (but smaller than planets) left over from the formation of the Solar System. Asteroids come from the Leonid asteroid belt, between Mars and Jupiter. Asteroids orbit the sun, and some asteroids cross the Earth’s orbit. At various times during the Earth’s history, ...
... • Asteroids are large chunks of rock (but smaller than planets) left over from the formation of the Solar System. Asteroids come from the Leonid asteroid belt, between Mars and Jupiter. Asteroids orbit the sun, and some asteroids cross the Earth’s orbit. At various times during the Earth’s history, ...
Panspermia
Panspermia (from Greek πᾶν (pan), meaning ""all"", and σπέρμα (sperma), meaning ""seed"") is the hypothesis that life exists throughout the Universe, distributed by meteoroids, asteroids, comets, planetoids and, also, by spacecraft in the form of unintended contamination by microorganisms.Panspermia is a hypothesis proposing that microscopic life forms that can survive the effects of space, such as extremophiles, become trapped in debris that is ejected into space after collisions between planets and small Solar System bodies that harbor life. Some organisms may travel dormant for an extended amount of time before colliding randomly with other planets or intermingling with protoplanetary disks. If met with ideal conditions on a new planet's surfaces, the organisms become active and the process of evolution begins. Panspermia is not meant to address how life began, just the method that may cause its distribution in the Universe.Pseudo-panspermia (sometimes called ""soft panspermia"" or ""molecular panspermia"") argues that the pre-biotic organic building blocks of life originated in space and were incorporated in the solar nebula from which the planets condensed and were further —and continuously— distributed to planetary surfaces where life then emerged (abiogenesis). From the early 1970s it was becoming evident that interstellar dust consisted of a large component of organic molecules. Interstellar molecules are formed by chemical reactions within very sparse interstellar or circumstellar clouds of dust and gas. The dust plays a critical role of shielding the molecules from the ionizing effect of ultraviolet radiation emitted by stars.Several simulations in laboratories and in low Earth orbit suggest that ejection, entry and impact is survivable for some simple organisms.