For Chapter 16 on November 26, 2012
... • The large percent of CO2 in the atmosphere results in high surface temperatures (477o C) due the “greenhouse effect” • Radar images have revealed relatively few impact craters • Most of these craters are fairly large, because the smaller incoming objects are consumed by Venus’s thick atmosphere ...
... • The large percent of CO2 in the atmosphere results in high surface temperatures (477o C) due the “greenhouse effect” • Radar images have revealed relatively few impact craters • Most of these craters are fairly large, because the smaller incoming objects are consumed by Venus’s thick atmosphere ...
Totally Crazy SOL Study Sheet Here are a few friendly reminders to
... Planets in order of size: Pluto, Mercury, Mars, Venus, Earth, Neptune, Uranus, Saturn, Jupiter Planets closest to the sun orbit the fastest Full moon during a lunar eclipse; new moon during a solar eclipse Full and New Moon = Spring tide (highest); 1st and 3rd quarter = Neap tide Dark areas of the m ...
... Planets in order of size: Pluto, Mercury, Mars, Venus, Earth, Neptune, Uranus, Saturn, Jupiter Planets closest to the sun orbit the fastest Full moon during a lunar eclipse; new moon during a solar eclipse Full and New Moon = Spring tide (highest); 1st and 3rd quarter = Neap tide Dark areas of the m ...
8th Grade Science FOCUS on Achievement
... and reproduce. Their roots help to hold soil in place and slow down erosion while their leaves can stop direct sunlight from reaching the ground. Of all these functions and uses, which shows an interaction between the geosphere and the biosphere? roots slowing down erosion B. leaves stopping direct ...
... and reproduce. Their roots help to hold soil in place and slow down erosion while their leaves can stop direct sunlight from reaching the ground. Of all these functions and uses, which shows an interaction between the geosphere and the biosphere? roots slowing down erosion B. leaves stopping direct ...
File
... and the largest planet within the Solar System. One of the storm is called the Great Red Spot Jupiter is classified as a gas giant along with Saturn, Uranus and Neptune but it is the biggest of the gas giant and Jupiter have stronger winds and storms than Earth . Together, these four planets are som ...
... and the largest planet within the Solar System. One of the storm is called the Great Red Spot Jupiter is classified as a gas giant along with Saturn, Uranus and Neptune but it is the biggest of the gas giant and Jupiter have stronger winds and storms than Earth . Together, these four planets are som ...
Where`s Earth 2.0? - Institute of Astronomy
... system, we have been searching for Earth 2.0. In this talk we’ll explore what makes our own planet Earth such a haven for life and what this really means for the habitability of Earth 2.0. We’ll be talking about our solar system, exoplanet atmospheres, why Earth is covered in water and extinction ev ...
... system, we have been searching for Earth 2.0. In this talk we’ll explore what makes our own planet Earth such a haven for life and what this really means for the habitability of Earth 2.0. We’ll be talking about our solar system, exoplanet atmospheres, why Earth is covered in water and extinction ev ...
Yung_Parkinson_PSseminar04 - Division of Geological and
... and can change the composition of planetary atmospheres from primordial values irreversibly •hydrogen escape is of particular importance as it affects the oxidation state of the atmosphere and because it results in the loss of water vapour ...
... and can change the composition of planetary atmospheres from primordial values irreversibly •hydrogen escape is of particular importance as it affects the oxidation state of the atmosphere and because it results in the loss of water vapour ...
Chapter 4
... peaks at a wavelength much longer than wavelengths in the visible part of the spectrum. This means that a. the object is not visible but might be detected with equipment sensitive to nonvisible radiation. b. the object, like all blackbodies, emits no radiation. c. the object emits visible radiation, ...
... peaks at a wavelength much longer than wavelengths in the visible part of the spectrum. This means that a. the object is not visible but might be detected with equipment sensitive to nonvisible radiation. b. the object, like all blackbodies, emits no radiation. c. the object emits visible radiation, ...
out of this world: comets asteroids, and meteoroids
... is composed of the sun, eight planets, and moons. Most people disregard the smaller celestial bodies called asteroids, comets, and meteoroids that fill our solar system. ...
... is composed of the sun, eight planets, and moons. Most people disregard the smaller celestial bodies called asteroids, comets, and meteoroids that fill our solar system. ...
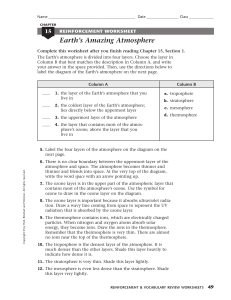
Earth`s Amazing Atmosphere
... 7. The ozone layer is in the upper part of the atmospheric layer that contains most of the atmosphere’s ozone. Use the symbol for ozone to draw in the ozone layer on the diagram. 8. The ozone layer is important because it absorbs ultraviolet radiation. Draw a wavy line coming from space to represent ...
... 7. The ozone layer is in the upper part of the atmospheric layer that contains most of the atmosphere’s ozone. Use the symbol for ozone to draw in the ozone layer on the diagram. 8. The ozone layer is important because it absorbs ultraviolet radiation. Draw a wavy line coming from space to represent ...
Greenhouse Effect - hs science @ cchs
... • The Ozone (O3) Layer is located between the stratosphere and the troposphere and helps protect us from UV light from the sun. • Ozone depletion is caused by human-made compounds called chlorofluorocarbons (CFC’s) – Many CFCs have been widely used as refrigerants and propellants (in aerosol applica ...
... • The Ozone (O3) Layer is located between the stratosphere and the troposphere and helps protect us from UV light from the sun. • Ozone depletion is caused by human-made compounds called chlorofluorocarbons (CFC’s) – Many CFCs have been widely used as refrigerants and propellants (in aerosol applica ...
Our Solar System
... There are stream drainage patterns found on the planet from running water at some point long ago. ...
... There are stream drainage patterns found on the planet from running water at some point long ago. ...
Tropical Horticulture: Lecture 3 1 Lecture 3
... Sun’s temperature = 12,000°F (6,000°K) Earth intercepts 1/5 billionth of this energy Solar energy is the engine which drives the earth’s atmosphere and oceanic circulation. Radiant energy travels through space as electric magnetic waves traveling at 186,000 miles per second. ...
... Sun’s temperature = 12,000°F (6,000°K) Earth intercepts 1/5 billionth of this energy Solar energy is the engine which drives the earth’s atmosphere and oceanic circulation. Radiant energy travels through space as electric magnetic waves traveling at 186,000 miles per second. ...
Layers of the Earth Drawing The Earth is much too big to draw it on
... The thermosphere is the second-highest layer of Earth's atmosphere. It extends from the mesopause (which separates it from the mesosphere) at an altitude of about 80 km (50 mi; 260,000 ft) up to the thermopause at an altitude range of 500–1,000 km (310–620 mi; 1,600,000–3,300,000 ft). The height of ...
... The thermosphere is the second-highest layer of Earth's atmosphere. It extends from the mesopause (which separates it from the mesosphere) at an altitude of about 80 km (50 mi; 260,000 ft) up to the thermopause at an altitude range of 500–1,000 km (310–620 mi; 1,600,000–3,300,000 ft). The height of ...
The surface of Venus is rather smooth in many places, though not
... There are high-velocity winds in the upper atmosphere, but the atmosphere below the cloud deck appears to be relatively stagnant, with only very weak winds blowing at the surface. Convection driven by differential solar heating should give rise to winds of only a few meters per second, so the high v ...
... There are high-velocity winds in the upper atmosphere, but the atmosphere below the cloud deck appears to be relatively stagnant, with only very weak winds blowing at the surface. Convection driven by differential solar heating should give rise to winds of only a few meters per second, so the high v ...
The surface of Venus is rather smooth in many places, though not
... There are high-velocity winds in the upper atmosphere, but the atmosphere below the cloud deck appears to be relatively stagnant, with only very weak winds blowing at the surface. Convection driven by differential solar heating should give rise to winds of only a few meters per second, so the high v ...
... There are high-velocity winds in the upper atmosphere, but the atmosphere below the cloud deck appears to be relatively stagnant, with only very weak winds blowing at the surface. Convection driven by differential solar heating should give rise to winds of only a few meters per second, so the high v ...
The Solar System and its Planets
... (B) has sufficient mass for its self-gravity to overcome rigid body forces so that it assumes a hydrostatic equilibrium (nearly round) shape (C) has not cleared the neighbourhood around its orbit (D) is not a satellite (moon) ...
... (B) has sufficient mass for its self-gravity to overcome rigid body forces so that it assumes a hydrostatic equilibrium (nearly round) shape (C) has not cleared the neighbourhood around its orbit (D) is not a satellite (moon) ...
Energy in our Atmosphere Study Guide
... 22. Explain the concept of the Earth’s Energy budget. The way Earth absorbs, reflects and uses solar energy. It should be 50% absorbed and used and 50% reflected to maintain an balanced energy budget. 23. What things reflect, absorb and scatter the Sun’s radiation Ground, Oceans/water source, Clouds ...
... 22. Explain the concept of the Earth’s Energy budget. The way Earth absorbs, reflects and uses solar energy. It should be 50% absorbed and used and 50% reflected to maintain an balanced energy budget. 23. What things reflect, absorb and scatter the Sun’s radiation Ground, Oceans/water source, Clouds ...
Lecture 4 - Twin Cities - University of Minnesota
... The End of Planet Formation • Eventually the solar wind pushed all of the gas out into interstellar space • Sun was spinning much more quickly • Eventually the Sun’s magnetic field dispersed its angular momentum ...
... The End of Planet Formation • Eventually the solar wind pushed all of the gas out into interstellar space • Sun was spinning much more quickly • Eventually the Sun’s magnetic field dispersed its angular momentum ...
Grade 7 Science
... 6. Use masking tape to label the ball ―Sun.‖ 7. Place the large, closed box in the center of the circle. Set the roll of masking tape flat on top of the box. 8. Place the ball on top of the roll of masking tape so that the ball stays in place. 9. Stand inside the circle of chairs. You will represent ...
... 6. Use masking tape to label the ball ―Sun.‖ 7. Place the large, closed box in the center of the circle. Set the roll of masking tape flat on top of the box. 8. Place the ball on top of the roll of masking tape so that the ball stays in place. 9. Stand inside the circle of chairs. You will represent ...
Chapter 6 The Archean Eon of Precambrian Time I. Introduction
... 1. Material that had been pulled into the central region of the nebula condensed, shrank, and was heated to several million degrees by gravitational compression a. the Sun was born when pressures and temperatures within the core became sufficiently high, thermonuclear reactions began b. Solar radiat ...
... 1. Material that had been pulled into the central region of the nebula condensed, shrank, and was heated to several million degrees by gravitational compression a. the Sun was born when pressures and temperatures within the core became sufficiently high, thermonuclear reactions began b. Solar radiat ...
Unit 6 Notes Part 1
... I. Wind, precipitation, warming and cooling depend on how much energy is in the atmosphere and where that energy is located. II. Much more energy from the Sun reaches low latitudes (near the equator) than high latitudes (nearer the poles) III. Insolation – the amount of solar radiation that reaches ...
... I. Wind, precipitation, warming and cooling depend on how much energy is in the atmosphere and where that energy is located. II. Much more energy from the Sun reaches low latitudes (near the equator) than high latitudes (nearer the poles) III. Insolation – the amount of solar radiation that reaches ...
Venus
... Greenhouse Effect • Visible light passes through atmosphere and warms planet’s surface. • Surface heats up from incoming light. • Surface reemits in shorter infrared waves. • Atmosphere and absorbs this infrared light from surface, trapping heat. ...
... Greenhouse Effect • Visible light passes through atmosphere and warms planet’s surface. • Surface heats up from incoming light. • Surface reemits in shorter infrared waves. • Atmosphere and absorbs this infrared light from surface, trapping heat. ...
Chapter 2
... •Early in the history of the Solar System, the solar wind stripped the inner planets of their primitive atmospheres •In this image, the modern solar wind “ blows” the geomagnetic field into a streamlined shape with the blunt end facing into the solar wind and the tail extending downwind ...
... •Early in the history of the Solar System, the solar wind stripped the inner planets of their primitive atmospheres •In this image, the modern solar wind “ blows” the geomagnetic field into a streamlined shape with the blunt end facing into the solar wind and the tail extending downwind ...
Unit 6 Part 1 Notes
... The temperature is highest near the surface of the Earth and decreases with altitude. Earth’s surface is a major source of heat Rock, soil, and water on Earth absorb the Sun’s light and radiate it back into the atmosphere as heat The temperature is also higher near the surface because of the ...
... The temperature is highest near the surface of the Earth and decreases with altitude. Earth’s surface is a major source of heat Rock, soil, and water on Earth absorb the Sun’s light and radiate it back into the atmosphere as heat The temperature is also higher near the surface because of the ...
ecology - nutrient cycles
... The Carbon Cycle In the carbon dioxide cycle, carbon dioxide is returned to the atmosphere primarily by the activity of _______________. ...
... The Carbon Cycle In the carbon dioxide cycle, carbon dioxide is returned to the atmosphere primarily by the activity of _______________. ...