The Children of Earth
... “The concern here is with the possibility of a theology of nature, that is, using the picture of reality coming to us from postmodern science as a way to reimagine the relationship between God and the world… ...
... “The concern here is with the possibility of a theology of nature, that is, using the picture of reality coming to us from postmodern science as a way to reimagine the relationship between God and the world… ...
Earth
... on the basis of their physical and chemical properties, by a variety of processes Solar System: ...
... on the basis of their physical and chemical properties, by a variety of processes Solar System: ...
Sidereal and Solar Time
... o During the course of a day the Earth travels a short distance in its orbit around the Sun. After the Earth has completed one rotation the Earth must turn for an extra 4 minutes in order to bring the Sun back to the same point in the sky. The time from Noon to Noon (the Solar Day) is longer tha ...
... o During the course of a day the Earth travels a short distance in its orbit around the Sun. After the Earth has completed one rotation the Earth must turn for an extra 4 minutes in order to bring the Sun back to the same point in the sky. The time from Noon to Noon (the Solar Day) is longer tha ...
What is the Solar System? I Arrangement The Sun – in the middle on
... II Presentation of the Solar System 1. Student 1 - introduction Welcome in the Universe. The address- the galaxy, Milky Way. We are the Solar System. There are our astronomical objects. The Sun in the centre and orbiting planets: Mars, Venus, Earth, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, Neptune. There is the Moo ...
... II Presentation of the Solar System 1. Student 1 - introduction Welcome in the Universe. The address- the galaxy, Milky Way. We are the Solar System. There are our astronomical objects. The Sun in the centre and orbiting planets: Mars, Venus, Earth, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, Neptune. There is the Moo ...
Volcanoes and Igneous Activity Earth
... groups of planets in the solar system. Describe the theory of the formation of the solar system. ...
... groups of planets in the solar system. Describe the theory of the formation of the solar system. ...
The most important questions to study for the exam
... • From the measured ages of "pristine" comets, i.e., those that are falling into the inner solar system for the first time • From the observed cratering ages of asteroids, such as Gaspra and Eros, that have been visited by spacecraft 9. Most of the meteoric material falling onto the Earth from space ...
... • From the measured ages of "pristine" comets, i.e., those that are falling into the inner solar system for the first time • From the observed cratering ages of asteroids, such as Gaspra and Eros, that have been visited by spacecraft 9. Most of the meteoric material falling onto the Earth from space ...
Planetarium Field Guide 2015-2016 Third Grade
... where the Earth fits in the larger picture. The Solar System a. What are the two things the Sun provides our planet that make life on Earth possible? a. Heat, light Terrestrial Planets and Gas Giants a. Terrestrial planets are those having rocky surfaces and cores made of iron, as Earth does. The te ...
... where the Earth fits in the larger picture. The Solar System a. What are the two things the Sun provides our planet that make life on Earth possible? a. Heat, light Terrestrial Planets and Gas Giants a. Terrestrial planets are those having rocky surfaces and cores made of iron, as Earth does. The te ...
Solar System knowledge
... future pioneers will have water supplies in situ or whether they will have to bring them from Earth, which would be very inconvenient not only from an economic point of view but also for the cumbersome weight. But Mars is not the only planet in the Solar System which could surprise us. Something new ...
... future pioneers will have water supplies in situ or whether they will have to bring them from Earth, which would be very inconvenient not only from an economic point of view but also for the cumbersome weight. But Mars is not the only planet in the Solar System which could surprise us. Something new ...
2.13 Understanding our Universe
... • If you are lucky you may see an object with a bright tail • This is likely to be a comet, which are made from rock, dry ice and frozen gases such as CO2 and CH4.They come from outside our Solar System • You may also see ‘shooting stars’ which are meteors, these are bits of dust and rock which ente ...
... • If you are lucky you may see an object with a bright tail • This is likely to be a comet, which are made from rock, dry ice and frozen gases such as CO2 and CH4.They come from outside our Solar System • You may also see ‘shooting stars’ which are meteors, these are bits of dust and rock which ente ...
Our Universe - Etiwanda E
... The small pieces of rock from comets moving through space are called meteoroids. A meteoroid that burns up in Earth’s atmosphere is called a meteor. A piece of a large meteoroid that does not burn up but hits Earth is called a meteorite. ...
... The small pieces of rock from comets moving through space are called meteoroids. A meteoroid that burns up in Earth’s atmosphere is called a meteor. A piece of a large meteoroid that does not burn up but hits Earth is called a meteorite. ...
the earth and other planets
... ~5.2AU from the sun Orbit =11.9 earth years 1 day =0.41 earth days ~61 moons; Ganymede is larger than Mercury; thin ring • Density =1.3g/ml • Gas giant planet mainly of Composite image of Jupiter by the Cassini probe. The black dot is the hydrogen and helium. shadow of Europa. Atmosphere banded with ...
... ~5.2AU from the sun Orbit =11.9 earth years 1 day =0.41 earth days ~61 moons; Ganymede is larger than Mercury; thin ring • Density =1.3g/ml • Gas giant planet mainly of Composite image of Jupiter by the Cassini probe. The black dot is the hydrogen and helium. shadow of Europa. Atmosphere banded with ...
PTYS/ASTR 206 – Section 3 – Homework1 – Assigned 1/22/09
... lecture notes find the perihelion and aphelion distances in AU. Based on these values, could this asteroid impact the Earth? Could it impact Mars? ...
... lecture notes find the perihelion and aphelion distances in AU. Based on these values, could this asteroid impact the Earth? Could it impact Mars? ...
Can you write numbers in scientific notation
... This “review sheet” has a list of questions that you can ask yourself to get a feel for your own comfort level on the different topics that we’ve covered in class. As with the second exam, you should be comfortable with reading/writing numbers in scientific notation & using your own scientific calcu ...
... This “review sheet” has a list of questions that you can ask yourself to get a feel for your own comfort level on the different topics that we’ve covered in class. As with the second exam, you should be comfortable with reading/writing numbers in scientific notation & using your own scientific calcu ...
DOC
... When our part of the Earth moves around so it is lit by the sun. The path an object takes around another object in space. A shape like a ball. A system of planets which revolve around a star (or sun) ...
... When our part of the Earth moves around so it is lit by the sun. The path an object takes around another object in space. A shape like a ball. A system of planets which revolve around a star (or sun) ...
Sun Moon and Stars Study Guide
... summer months? Would we have a greater amount of daylight in the summer months compared to the winter months? ...
... summer months? Would we have a greater amount of daylight in the summer months compared to the winter months? ...
Our solar system
... Meteoroid • rocky objects; smaller than asteroids and comets • Broken off pieces of planets, moons, asteroids, or comets ...
... Meteoroid • rocky objects; smaller than asteroids and comets • Broken off pieces of planets, moons, asteroids, or comets ...
"The Solar System" Slideshow
... due to collision with some other body) • Originally thought to be a star • Bright blue-green due to methane gas in its atmosphere • 64 Earths could fit inside it ...
... due to collision with some other body) • Originally thought to be a star • Bright blue-green due to methane gas in its atmosphere • 64 Earths could fit inside it ...
Asteroids • Small, rocky objects in orbit around the Sun. +
... The Oort Cloud & the Kuiper Belt • No comets have orbits coming from interstellar space. • Strong tendency for aphelia at ~ 50,000 AU • No preferential direction from which comets come ...
... The Oort Cloud & the Kuiper Belt • No comets have orbits coming from interstellar space. • Strong tendency for aphelia at ~ 50,000 AU • No preferential direction from which comets come ...
Earth-Space Vocabulary
... • The spin of something on its axis. • It takes the Earth one day to make one rotation. (23 hours, 56 minutes) ...
... • The spin of something on its axis. • It takes the Earth one day to make one rotation. (23 hours, 56 minutes) ...
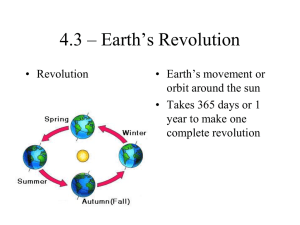
4.3 – Earth`s Revolution
... • Evidence the Earth is revolving around the sun • Stars seem to change position throughout the course of the year – look closer or father away • ACTUALLY!! Earth is moving – not the star ...
... • Evidence the Earth is revolving around the sun • Stars seem to change position throughout the course of the year – look closer or father away • ACTUALLY!! Earth is moving – not the star ...