Solar System Bead Distance Activity
... Our Solar System is immense in size by normal standards. We think of the planets as revolving around the Sun, but rarely consider how far each planet is from the Sun. Furthermore, we fail to appreciate the even greater distances to the other stars. Astronomers use the distance from the Sun to the Ea ...
... Our Solar System is immense in size by normal standards. We think of the planets as revolving around the Sun, but rarely consider how far each planet is from the Sun. Furthermore, we fail to appreciate the even greater distances to the other stars. Astronomers use the distance from the Sun to the Ea ...
The Solar System. The Inner Planets.
... and the Moon. Venus has very similar parameters to those of the Earth. However, it spins backwards (clockwise if looking from its north pole). Its atmosphere has 96% CO2, surface temperature 400740 K, surface pressure is 90 times the Earth’s one. It has volcanic activity, but probably no tectonic a ...
... and the Moon. Venus has very similar parameters to those of the Earth. However, it spins backwards (clockwise if looking from its north pole). Its atmosphere has 96% CO2, surface temperature 400740 K, surface pressure is 90 times the Earth’s one. It has volcanic activity, but probably no tectonic a ...
exercise 3
... Nine major planets are currently known. They are commonly divided into two groups: the inner planets (Mercury, Venus, Earth, and Mars) and the outer planets (Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune). The inner planets are small and are composed primarily of rock and iron. The outer planets are much lar ...
... Nine major planets are currently known. They are commonly divided into two groups: the inner planets (Mercury, Venus, Earth, and Mars) and the outer planets (Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune). The inner planets are small and are composed primarily of rock and iron. The outer planets are much lar ...
File
... are called the inner planets • Sometimes they are called terrestrial planets = Earth-like • They are relatively small and have solid cores and rocky crusts ...
... are called the inner planets • Sometimes they are called terrestrial planets = Earth-like • They are relatively small and have solid cores and rocky crusts ...
Introduction
... 2nd Law (1609): As a planet orbits the Sun, a line joining the Sun and the planet sweeps out equal areas in equal times Planets move faster in their orbits when closer to Sun (speed) ...
... 2nd Law (1609): As a planet orbits the Sun, a line joining the Sun and the planet sweeps out equal areas in equal times Planets move faster in their orbits when closer to Sun (speed) ...
Team 1:The Outer Planets and Comets, Asteroids, and Meteors
... of trace of methane in its atmosphere Its surrounded by a group of thin, round rings like Saturn only much less Its axis of rotation is tilted at an angle of 90 degrees ...
... of trace of methane in its atmosphere Its surrounded by a group of thin, round rings like Saturn only much less Its axis of rotation is tilted at an angle of 90 degrees ...
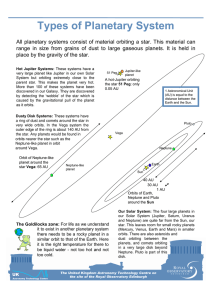
Types of Planetary System
... a ring of dust and comets around the star in very wide orbits. In the Vega system the outer edge of the ring is about 140 AU from the star. Any planets would be found in orbits nearer the star such as the Neptune-like planet in orbit around Vega. Orbit of Neptune-like planet around the star Vega: 65 ...
... a ring of dust and comets around the star in very wide orbits. In the Vega system the outer edge of the ring is about 140 AU from the star. Any planets would be found in orbits nearer the star such as the Neptune-like planet in orbit around Vega. Orbit of Neptune-like planet around the star Vega: 65 ...
astronomy review - Earth Science R: 1(A,C)
... Celestial Sphere- an imaginary sphere on which objects of the night sky appear Motions of the Stars and Planets Stars appear to rise in the _____________ and set in the ___________ Circumpolar planets appear to revolve around Polaris __________________ The apparent motion of the stars is c ...
... Celestial Sphere- an imaginary sphere on which objects of the night sky appear Motions of the Stars and Planets Stars appear to rise in the _____________ and set in the ___________ Circumpolar planets appear to revolve around Polaris __________________ The apparent motion of the stars is c ...
- mrzimmerman.org
... Key Idea 1: The Earth and celestial phenomena can be described by principles of relative motion and perspective. The universe is comprised of a wide array of objects, a few of which can be seen by the unaided eye. Others can only be observed with scientific instruments. These celestial objects, dist ...
... Key Idea 1: The Earth and celestial phenomena can be described by principles of relative motion and perspective. The universe is comprised of a wide array of objects, a few of which can be seen by the unaided eye. Others can only be observed with scientific instruments. These celestial objects, dist ...
Early Astronomy
... omitted, unless year a multiple of 400! i.e : 1600, 2000 leap years 1700, 1800, 1900 not leap years ...
... omitted, unless year a multiple of 400! i.e : 1600, 2000 leap years 1700, 1800, 1900 not leap years ...
Powerpoint
... – Argued that the planets move on spheres around the Earth (“geocentric” model) – Argues that the earth is spherical based on the shape of its shadow on the moon during lunar eclipses ...
... – Argued that the planets move on spheres around the Earth (“geocentric” model) – Argues that the earth is spherical based on the shape of its shadow on the moon during lunar eclipses ...
Terrestrial planets
... same way as other planets. Gas giants are larger and more massive than terrestrial planets, but much less dense, and are mainly composed of rock and metal. All four gas giants have ring systems made of dust and icy debris that orbit the planets. ...
... same way as other planets. Gas giants are larger and more massive than terrestrial planets, but much less dense, and are mainly composed of rock and metal. All four gas giants have ring systems made of dust and icy debris that orbit the planets. ...
Objects in the Sky Power Point
... On the first day of January 1801, Giuseppe Piazzi discovered an object which he first thought was a new comet. But after its orbit was better determined it was clear that it was not a comet but more like a small planet. Piazzi named it Ceres, after the Sicilian goddess of grain. Three other small b ...
... On the first day of January 1801, Giuseppe Piazzi discovered an object which he first thought was a new comet. But after its orbit was better determined it was clear that it was not a comet but more like a small planet. Piazzi named it Ceres, after the Sicilian goddess of grain. Three other small b ...
Name Period ______ Astronomy Unit Study Guide 1. _____
... following terms in your description: gravity, accretion, nebula.) ...
... following terms in your description: gravity, accretion, nebula.) ...
key
... telescope – a device that collects light to make distant objects appear closer and larger astronomer – someone who observes or studies the universe refraction – the bending of waves as they go from one substance to another reflection – the bouncing of waves off a surface rotation – one complete spin ...
... telescope – a device that collects light to make distant objects appear closer and larger astronomer – someone who observes or studies the universe refraction – the bending of waves as they go from one substance to another reflection – the bouncing of waves off a surface rotation – one complete spin ...
Pluto(2274km)- Pluto is a dwarf planet, and was classified as such in
... range in size from that of a fingernail to that of a car. The mean temperature on the surface of the clouds is -290°F and it is composed of mostly hydrogen and helium gas. Jupiter(1.4x10^5km)Jupiter is a gas giant. The average temperature at the cloud tops is -244°F. It has a very thick atmosphere a ...
... range in size from that of a fingernail to that of a car. The mean temperature on the surface of the clouds is -290°F and it is composed of mostly hydrogen and helium gas. Jupiter(1.4x10^5km)Jupiter is a gas giant. The average temperature at the cloud tops is -244°F. It has a very thick atmosphere a ...
word document
... If we consider the (m(r)) term, we see that for the earth is directed along the axis of the spinning earth, or in the direction of the North star (which at Memphis, is about 35 above the Northern horizon). The direction of r is straight up. Thus the direction of [r] will be {up and to the N ...
... If we consider the (m(r)) term, we see that for the earth is directed along the axis of the spinning earth, or in the direction of the North star (which at Memphis, is about 35 above the Northern horizon). The direction of r is straight up. Thus the direction of [r] will be {up and to the N ...
Space Science Chapter 1 Study Guide
... space. Visible light telescopes on Earth can be used to get a clearer view of distant objects in the sky. Visible light telescopes in space are not affected by Earth’s atmosphere. 11. What is an impact crater? A round pit left behind on the surface of a planet or other body in space after a smaller ...
... space. Visible light telescopes on Earth can be used to get a clearer view of distant objects in the sky. Visible light telescopes in space are not affected by Earth’s atmosphere. 11. What is an impact crater? A round pit left behind on the surface of a planet or other body in space after a smaller ...
2- Origin of the Universe
... • Contain thousands of icy and rocky objects • Kuiper Belt – Neptune to about 30 to 55 AU • Oort Cloud – from 5000 AU to 100000 AU Pluto and Eris are the best known dwarf planets found in Kuiper belt Pluto was reclassified as a dwarf planet in ...
... • Contain thousands of icy and rocky objects • Kuiper Belt – Neptune to about 30 to 55 AU • Oort Cloud – from 5000 AU to 100000 AU Pluto and Eris are the best known dwarf planets found in Kuiper belt Pluto was reclassified as a dwarf planet in ...