The Milky Way
... Earth. You can now imagine how Earth, the moon, and the sun move through space and how that produces the sights you see in the sky. But how did humanity first realize that we live on a planet moving through space? That required revolutionary overthrow of an ancient and honored theory of Earth’s plac ...
... Earth. You can now imagine how Earth, the moon, and the sun move through space and how that produces the sights you see in the sky. But how did humanity first realize that we live on a planet moving through space? That required revolutionary overthrow of an ancient and honored theory of Earth’s plac ...
astronomy notes2013
... c. Some of this oxygen formed _____________________________________ _____________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________ 3. The oceans a. The earth cooled enough for___________________________________ __________________________________ ...
... c. Some of this oxygen formed _____________________________________ _____________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________ 3. The oceans a. The earth cooled enough for___________________________________ __________________________________ ...
Astronomy powerpoint
... like Jupiter. • The are large, gaseous, less dense, and have many moons. • Jovian planets include: Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune. ...
... like Jupiter. • The are large, gaseous, less dense, and have many moons. • Jovian planets include: Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune. ...
Warm Up
... (b) At this speed, how long a track will the pi meson leave in the laboratory during its lifetime? The lifetime of a pi meson at rest in the laboratory 1.0 × 10!!" s ...
... (b) At this speed, how long a track will the pi meson leave in the laboratory during its lifetime? The lifetime of a pi meson at rest in the laboratory 1.0 × 10!!" s ...
Our solar system includes the sun and the eight
... of swirling gas that has lasted for hundreds of years. Jupiter does not have a solid surface - it is made up of gases. The bands that we see when looking at Jupiter are the tops of clouds high in its atmosphere. Saturn is the second largest planet in the Solar System. It has wide rings around its ce ...
... of swirling gas that has lasted for hundreds of years. Jupiter does not have a solid surface - it is made up of gases. The bands that we see when looking at Jupiter are the tops of clouds high in its atmosphere. Saturn is the second largest planet in the Solar System. It has wide rings around its ce ...
NIE10x301Sponsor Thank You (Page 1)
... discoveries of moons orbiting the planet Jupiter, and of the phases of Venus provided evidence for the sun-centered model. He also found that there were far more stars than was previously believed. Copernicus’ model gained acceptance, and with it came the awareness that, while the Sun may be the cen ...
... discoveries of moons orbiting the planet Jupiter, and of the phases of Venus provided evidence for the sun-centered model. He also found that there were far more stars than was previously believed. Copernicus’ model gained acceptance, and with it came the awareness that, while the Sun may be the cen ...
Ch 26-Studying Space
... – Evidence for Earth’s rotation – Explain how the change in apparent positions of constellations provides evidence of Earth’s rotation and revolution around the ...
... – Evidence for Earth’s rotation – Explain how the change in apparent positions of constellations provides evidence of Earth’s rotation and revolution around the ...
688 Chapter 21 Review - District 196 e
... Venus (mostly CO2). Why is Mars so cold while Venus is so hot? ...
... Venus (mostly CO2). Why is Mars so cold while Venus is so hot? ...
Earth and Space - Sun, Moon and Stars
... communicate information from careful observations and simple investigation through a variety of methods. ...
... communicate information from careful observations and simple investigation through a variety of methods. ...
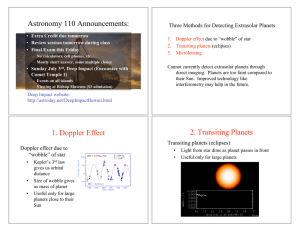
Astronomy 110 Announcements: 1. Doppler Effect 2. Transiting
... – Volcanism (outgassing). Leads to our oceans and atmosphere. ...
... – Volcanism (outgassing). Leads to our oceans and atmosphere. ...
Asteroids, Comets, Meteors…what`s the difference
... Asteroids are rocky or metallic objects, most of which orbit the ________________________ in the asteroid belt between the planets ________________________ and Jupiter. A few asteroids approach the Sun more closely. Asteroids are also known as ________________________ or minor planets. The first ___ ...
... Asteroids are rocky or metallic objects, most of which orbit the ________________________ in the asteroid belt between the planets ________________________ and Jupiter. A few asteroids approach the Sun more closely. Asteroids are also known as ________________________ or minor planets. The first ___ ...
2015-16 Space Week 1 and 2 ppt
... 13.Why is the Moon lopsided? 14.Who is second-in-command on a Shuttle mission? 15.What was the name of the first space probe to visit Mercury? 16.How much are astronauts paid? 17.What two states are involved in the transmission of information to and from Hubble Space Telescope? 18.Stephen Hawking or ...
... 13.Why is the Moon lopsided? 14.Who is second-in-command on a Shuttle mission? 15.What was the name of the first space probe to visit Mercury? 16.How much are astronauts paid? 17.What two states are involved in the transmission of information to and from Hubble Space Telescope? 18.Stephen Hawking or ...
1. Evolution of the Solar System— Nebular hypothesis, p 10 a
... Evolution of the Solar System— Nebular hypothesis, p 10 a. Cloud of atoms, mostly hydrogen and helium b. Gravitational collapse contracted it into rotating disc c. Heat of conversion of gravitational to thermal energy fired Sun into star in center of nebular cloud d. Cooling allowed condensation of ...
... Evolution of the Solar System— Nebular hypothesis, p 10 a. Cloud of atoms, mostly hydrogen and helium b. Gravitational collapse contracted it into rotating disc c. Heat of conversion of gravitational to thermal energy fired Sun into star in center of nebular cloud d. Cooling allowed condensation of ...
Chapter 4: The Origin of Modern Astronomy - Otto
... Earth. You can now imagine how Earth, the moon, and the sun move through space and how that produces the sights you see in the sky. But how did humanity first realize that we live on a planet moving through space? That required revolutionary overthrow of an ancient and honored theory of Earth’s plac ...
... Earth. You can now imagine how Earth, the moon, and the sun move through space and how that produces the sights you see in the sky. But how did humanity first realize that we live on a planet moving through space? That required revolutionary overthrow of an ancient and honored theory of Earth’s plac ...
The Solar System
... changes in the orbit of Uranus led Alexis Bouvard to deduce that its orbit was subject to gravitational perturbation by an unknown planet. Neptune was subsequently observed by Johann Galle within a degree of the position predicted by Urbain Le Verrier, and its largest moon, Triton, was discovered sh ...
... changes in the orbit of Uranus led Alexis Bouvard to deduce that its orbit was subject to gravitational perturbation by an unknown planet. Neptune was subsequently observed by Johann Galle within a degree of the position predicted by Urbain Le Verrier, and its largest moon, Triton, was discovered sh ...
Where are we at within the Universe? Earth
... metal object (although gravity is not as strong as electromagnetic forces). He also determined that gravity holds planets and moon in their orbits. Newton wrote two famous laws about gravity: The Law of Inertia and the Law of Universal Gravitation. The Law of Inertia says that a body in motion tends ...
... metal object (although gravity is not as strong as electromagnetic forces). He also determined that gravity holds planets and moon in their orbits. Newton wrote two famous laws about gravity: The Law of Inertia and the Law of Universal Gravitation. The Law of Inertia says that a body in motion tends ...
Take a Grand Tour of the solar system at twice the speed of light
... supply in Riley, because the end of the line is many millions of miles ahead. We end our scale model in Mt. Horeb with Pluto, although the Sun’s influence continues far beyond this point. Pluto’s orbit is highly elliptical, coming as close to the Sun as Neptune’s orbit, but going out as far as 50 ti ...
... supply in Riley, because the end of the line is many millions of miles ahead. We end our scale model in Mt. Horeb with Pluto, although the Sun’s influence continues far beyond this point. Pluto’s orbit is highly elliptical, coming as close to the Sun as Neptune’s orbit, but going out as far as 50 ti ...
The Size of the Solar System
... Use the scale factors to calculate the size of your object and the distance of the object from the Sun (round two decimal digits). Fill in these values in table 2. To make it easier to make the model, find the distance from the previous object to the current object. Again, record the distance in tab ...
... Use the scale factors to calculate the size of your object and the distance of the object from the Sun (round two decimal digits). Fill in these values in table 2. To make it easier to make the model, find the distance from the previous object to the current object. Again, record the distance in tab ...
PHY 121 Astronomy
... Classical astronomers concluded that Earth had to be motionless because they could not see any parallax on the stars. They started with the wrong premise that the stars are on a sphere which is not too large in its diameter and so the stars were assumed to be much closer than they actually are. Star ...
... Classical astronomers concluded that Earth had to be motionless because they could not see any parallax on the stars. They started with the wrong premise that the stars are on a sphere which is not too large in its diameter and so the stars were assumed to be much closer than they actually are. Star ...
HR.MOON.doc
... The Sun is made of gases. The Sun has been burning for 5,000,000 years. The Sun is 93,000,000 miles away. It takes 3.5 years to get to the Sun from the Earth The Earth would be to hot if it was a planet like Mercury but it would be too cold if it was a planet like Mars. ...
... The Sun is made of gases. The Sun has been burning for 5,000,000 years. The Sun is 93,000,000 miles away. It takes 3.5 years to get to the Sun from the Earth The Earth would be to hot if it was a planet like Mercury but it would be too cold if it was a planet like Mars. ...
How did our solar system get here?
... • Orbits the Sun in 248 years, and makes one full rotation in 6 hours 7minutes. Also has not made it fully around the Sun since it was discovered in 1930. • Between 1979 and 1999, Pluto was closer to the Sun than Neptune; this gave us a good opportunity for study this planet and it’s moon. • Not con ...
... • Orbits the Sun in 248 years, and makes one full rotation in 6 hours 7minutes. Also has not made it fully around the Sun since it was discovered in 1930. • Between 1979 and 1999, Pluto was closer to the Sun than Neptune; this gave us a good opportunity for study this planet and it’s moon. • Not con ...
AUST – HORIZON AND BEYOND part 1
... Most of the universe is empty space, called a vacuum, but it is an imperfect vacuum. There are clouds of interstellar dust and the tiny particles that make up the solar wind. There are many isolated particles and hydrogen atoms, which sometimes form clouds over a billion kilometres wide called "nebu ...
... Most of the universe is empty space, called a vacuum, but it is an imperfect vacuum. There are clouds of interstellar dust and the tiny particles that make up the solar wind. There are many isolated particles and hydrogen atoms, which sometimes form clouds over a billion kilometres wide called "nebu ...
Kiwi and Tinker Crate_February
... 1st-ESS1.A- The Universe and its Stars- Patterns of the motion of the sun, moon, stars in the sky can be observed, described, and predicted. 5th- ESS1.A- The Universe and its Stars- The sun is a star that appears larger and brighter than other stars because it is closer. Stars range greatly in their ...
... 1st-ESS1.A- The Universe and its Stars- Patterns of the motion of the sun, moon, stars in the sky can be observed, described, and predicted. 5th- ESS1.A- The Universe and its Stars- The sun is a star that appears larger and brighter than other stars because it is closer. Stars range greatly in their ...