Earth Science
... a) traces and remains of ancient, often extinct, life are preserved by various means in many sedimentary rocks; b) superposition, cross-cutting relationships, index fossils, and radioactive decay are methods of dating bodies of rock; c) absolute and relative dating have different applications but ca ...
... a) traces and remains of ancient, often extinct, life are preserved by various means in many sedimentary rocks; b) superposition, cross-cutting relationships, index fossils, and radioactive decay are methods of dating bodies of rock; c) absolute and relative dating have different applications but ca ...
TAKS Study Guide - Northwest ISD Moodle
... 11. What processes does it take to form a metamorphic rock? 12. Give 2 examples for how catastrophic events can change the Earth’s surface. a. b. 13. What is the theory for how dinosaurs became extinct? 14. What are the 2 main factors that affect climate? ...
... 11. What processes does it take to form a metamorphic rock? 12. Give 2 examples for how catastrophic events can change the Earth’s surface. a. b. 13. What is the theory for how dinosaurs became extinct? 14. What are the 2 main factors that affect climate? ...
Graphing the Big Dipper Although they look close together from
... Graphing the Big Dipper Although they look close together from Earth, the stars in the Big Dipper are actually very far apart. They also vary tremendously in their distances from Earth. In this activity, you will graph the stars of the Big Dipper to make these differences clearer. Materials Graphing ...
... Graphing the Big Dipper Although they look close together from Earth, the stars in the Big Dipper are actually very far apart. They also vary tremendously in their distances from Earth. In this activity, you will graph the stars of the Big Dipper to make these differences clearer. Materials Graphing ...
PHYS 390 Lectures 1/2 - The Big Picture 1/2
... in its orbit around the Sun (first used in 1838 by Freidrich Wilhelm Bessel). Below, the Earth is shown in its orbit at two extreme positions 6 months apart, labelled by the letters A and B, and a nearby star is at position S. The direction towards a very distant star is indicated by the two vertica ...
... in its orbit around the Sun (first used in 1838 by Freidrich Wilhelm Bessel). Below, the Earth is shown in its orbit at two extreme positions 6 months apart, labelled by the letters A and B, and a nearby star is at position S. The direction towards a very distant star is indicated by the two vertica ...
138KB - NZQA
... ago, a collision is thought to have happened with a smaller planetary body that was in the same orbit round the sun. The collision occurred because the smaller planetary body was travelling faster than Earth. This collision caused both planets to melt and the outer layers of both planets to be eject ...
... ago, a collision is thought to have happened with a smaller planetary body that was in the same orbit round the sun. The collision occurred because the smaller planetary body was travelling faster than Earth. This collision caused both planets to melt and the outer layers of both planets to be eject ...
58KB - NZQA
... ago, a collision is thought to have happened with a smaller planetary body that was in the same orbit round the sun. The collision occurred because the smaller planetary body was travelling faster than Earth. This collision caused both planets to melt and the outer layers of both planets to be eject ...
... ago, a collision is thought to have happened with a smaller planetary body that was in the same orbit round the sun. The collision occurred because the smaller planetary body was travelling faster than Earth. This collision caused both planets to melt and the outer layers of both planets to be eject ...
Universe 8/e Chapter 2 - Physics and Astronomy
... celestial sphere appears to rotate around the Earth once in each 24-hour period. In fact, it is actually the Earth that is rotating. The poles and equator of the celestial sphere are determined by extending the axis of rotation and the equatorial plane of the Earth out to the celestial sphere. The p ...
... celestial sphere appears to rotate around the Earth once in each 24-hour period. In fact, it is actually the Earth that is rotating. The poles and equator of the celestial sphere are determined by extending the axis of rotation and the equatorial plane of the Earth out to the celestial sphere. The p ...
28. Planet Earth - Brigham Young University
... turn, of rock and ice in chunks a few meters across to dust-size. The ring system is extremely thin, only two to five kilometers thick, and over 400,000 kilometers from inner to outer edge. (Put another way, if Saturn’s rings were only as wide as this page, they would be less than three one-hundredt ...
... turn, of rock and ice in chunks a few meters across to dust-size. The ring system is extremely thin, only two to five kilometers thick, and over 400,000 kilometers from inner to outer edge. (Put another way, if Saturn’s rings were only as wide as this page, they would be less than three one-hundredt ...
ISP 205: Visions of the Universe
... 1. about six hours after they rise. 2. about twelve hours after they rise. 3. about twenty four hours after they rise. 4. never. 5. at different times, depending on the star. * Either North or South ...
... 1. about six hours after they rise. 2. about twelve hours after they rise. 3. about twenty four hours after they rise. 4. never. 5. at different times, depending on the star. * Either North or South ...
Additional Problems
... You are explaining to friends why astronauts feel weightless orbiting in the space shuttle, and they respond that they thought gravity was just a lot weaker up there. Convince them and yourself that it isn’t so by calculating how much weaker gravity is 300 km above the Earth’s surface. ...
... You are explaining to friends why astronauts feel weightless orbiting in the space shuttle, and they respond that they thought gravity was just a lot weaker up there. Convince them and yourself that it isn’t so by calculating how much weaker gravity is 300 km above the Earth’s surface. ...
Careful measurements reveal that the earth has a slight difference in
... equator in order to be able to see both Polaris and the Southern cross. ...
... equator in order to be able to see both Polaris and the Southern cross. ...
earth science review
... When Earth, Moon, & Sun are in line (New/Full Moon) Very high tide, Very low tide When the Moon and Sun are working against each other we get small tides (First/Third Quarter) 2 high tides 2 low tides ...
... When Earth, Moon, & Sun are in line (New/Full Moon) Very high tide, Very low tide When the Moon and Sun are working against each other we get small tides (First/Third Quarter) 2 high tides 2 low tides ...
15asteroids6s
... These are a particular type of crystal that forms only by very slow cooling (millions of years) Helps to distinguish true meteorites from terrestrial rocks ...
... These are a particular type of crystal that forms only by very slow cooling (millions of years) Helps to distinguish true meteorites from terrestrial rocks ...
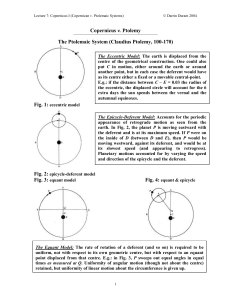
Lec 7 Copernicus I
... the deferent and is at its maximum speed. If P were on the inside of D (between D and E), then P would be moving westward, against its deferent, and would be at its slowest speed (and appearing to retrogress). Planetary motions accounted for by varying the speed and direction of the epicycle and the ...
... the deferent and is at its maximum speed. If P were on the inside of D (between D and E), then P would be moving westward, against its deferent, and would be at its slowest speed (and appearing to retrogress). Planetary motions accounted for by varying the speed and direction of the epicycle and the ...
WhatsInSolarSystem - School
... Comets are objects which display a coma, a fuzzy atmosphere, when they are close to the Sun. They are balls of dust, rock and ice. Centaurs These objects which have crossed the orbits of one or more of the giant planets. As centaurs in mythology were half man and half horse these objects behave like ...
... Comets are objects which display a coma, a fuzzy atmosphere, when they are close to the Sun. They are balls of dust, rock and ice. Centaurs These objects which have crossed the orbits of one or more of the giant planets. As centaurs in mythology were half man and half horse these objects behave like ...
Chpt4b
... gasses escape from the nucleus caring dust with it. Comets shine by reflected solar light Finally comets are divided into two large classes of short-term and long term ...
... gasses escape from the nucleus caring dust with it. Comets shine by reflected solar light Finally comets are divided into two large classes of short-term and long term ...
9 Weeks Standards being Taught 1st 9 Weeks Vocabulary
... and electromagnetic waves. 8-6.3 Summarize factors that influence the basic properties of waves (including frequency, amplitude, wavelength, and speed). 8-6.4 Summarize the behaviors of waves (including refraction, reflection, transmission, and ...
... and electromagnetic waves. 8-6.3 Summarize factors that influence the basic properties of waves (including frequency, amplitude, wavelength, and speed). 8-6.4 Summarize the behaviors of waves (including refraction, reflection, transmission, and ...
Summer 2008 Astronomical Calendar
... will be as close as they will get to each other all year, it’s not the distance between the two worlds that makes Jupiter so bright. Jupiter’s size and brightly reflective clouds make it dazzle. Jupiter is 11 times as wide as the Earth, with about 121 times more surface area. The best time to view J ...
... will be as close as they will get to each other all year, it’s not the distance between the two worlds that makes Jupiter so bright. Jupiter’s size and brightly reflective clouds make it dazzle. Jupiter is 11 times as wide as the Earth, with about 121 times more surface area. The best time to view J ...
ASTRONOMY 12 Problem Set 1 – Due Thursday, January 21, 2016
... 4) Consider an astronaut descending feet first into a ten solar mass (one solar mass is 1.99 × 1033 gm) black hole. Assume the astronaut is tall (she soon will be) and has a height of 200 cm and has a mass of 60 kg (6 × 104 gm). a) What would be the tidal force between the bottom of her feet and the ...
... 4) Consider an astronaut descending feet first into a ten solar mass (one solar mass is 1.99 × 1033 gm) black hole. Assume the astronaut is tall (she soon will be) and has a height of 200 cm and has a mass of 60 kg (6 × 104 gm). a) What would be the tidal force between the bottom of her feet and the ...
Solar Noon
... When the new moon, Earth, and Sun are not completely aligned and viewers on Earth are located in the penumbra of the Moon’s shadow; causes a solar eclipse where the new moon temporarily blocks part of the Sun’s disk. ...
... When the new moon, Earth, and Sun are not completely aligned and viewers on Earth are located in the penumbra of the Moon’s shadow; causes a solar eclipse where the new moon temporarily blocks part of the Sun’s disk. ...
History of Astronomy
... c) The geocentric model couldn’t account for day and night. d) The Earth revolved around the Sun. e) The Sun orbited Earth. ...
... c) The geocentric model couldn’t account for day and night. d) The Earth revolved around the Sun. e) The Sun orbited Earth. ...