Introduction to Biology II
... Takayasu's arteritis is a disorder that results in the narrowing of the lumen of arteries. Temporal arteritis (also known as "giant cell arteritis") is an inflammation of blood vessels, most commonly the large and medium arteries of the head. Untreated, the disorder can lead to significant vision lo ...
... Takayasu's arteritis is a disorder that results in the narrowing of the lumen of arteries. Temporal arteritis (also known as "giant cell arteritis") is an inflammation of blood vessels, most commonly the large and medium arteries of the head. Untreated, the disorder can lead to significant vision lo ...
Human Biology
... immune response • Chemokines – involved with the inflammatory response – They lead to chemotaxis and activation ...
... immune response • Chemokines – involved with the inflammatory response – They lead to chemotaxis and activation ...
Multiple Sclerosis Is an Inflammatory T-Cell–Mediated - Direct-MS
... helpful. And all of the authors acknowledge that MS is a complex disorder with multiple clinical patterns that could be initiated through more than one mechanism. Neither side mentions another intriguing idea: that the immune response in MS could result from a chronic vi- ...
... helpful. And all of the authors acknowledge that MS is a complex disorder with multiple clinical patterns that could be initiated through more than one mechanism. Neither side mentions another intriguing idea: that the immune response in MS could result from a chronic vi- ...
Cholesterol Reduction Complex
... Fact: About 40% of Canadian adults have high cholesterol, which can affect anyone at any age, and can negatively impact heart health and cardiovascular function over time. People with high cholesterol have a higher risk of developing heart disease compared with those with optimal levels. Among the c ...
... Fact: About 40% of Canadian adults have high cholesterol, which can affect anyone at any age, and can negatively impact heart health and cardiovascular function over time. People with high cholesterol have a higher risk of developing heart disease compared with those with optimal levels. Among the c ...
Formation of White Blood Cells and Platelets
... o Loss of __________________________ causes weakness o Loss of ___________________________ causes shock, which can be fatal Transfusions are given for _______________________, _________________________________, or for _____________________ Human Blood Groups Blood contains genetically determined ...
... o Loss of __________________________ causes weakness o Loss of ___________________________ causes shock, which can be fatal Transfusions are given for _______________________, _________________________________, or for _____________________ Human Blood Groups Blood contains genetically determined ...
SI PPT: Blood
... Small ones called… arterioles venules Other features higher blood pressure one-way valves Arteries smaller ...
... Small ones called… arterioles venules Other features higher blood pressure one-way valves Arteries smaller ...
Basic Laboratory Tests Complete Blood Counts (CBC)
... radiation treatment and some forms of leukemia. Reduced counts are found with immunodeficiency diseases, severe sepsis, systemic lupus, bone marrow failure, medication reactions and the late stages HIV infection. Monocyte (Monos) Monocytes are the largest of the white blood cells. Monocytes digest d ...
... radiation treatment and some forms of leukemia. Reduced counts are found with immunodeficiency diseases, severe sepsis, systemic lupus, bone marrow failure, medication reactions and the late stages HIV infection. Monocyte (Monos) Monocytes are the largest of the white blood cells. Monocytes digest d ...
phys chapter 35 [12-11
... membranes into kidney tubules; if amount is still slight, it can be reabsorbed through tubular epithelium into blood and cause no harm, but if great, then only small percentage reabsorbed Water continues to be reabsorbed, causing tubular Hgb concentration to rise so high that Hgb precipitates and ...
... membranes into kidney tubules; if amount is still slight, it can be reabsorbed through tubular epithelium into blood and cause no harm, but if great, then only small percentage reabsorbed Water continues to be reabsorbed, causing tubular Hgb concentration to rise so high that Hgb precipitates and ...
Cardiovascular Disaster in Hemodialysis patients
... Inadequate capillary density + increased oxygen demand >> relative hypoxia >> fibrosis ...
... Inadequate capillary density + increased oxygen demand >> relative hypoxia >> fibrosis ...
Hemostasis and hemocoagulation
... Integrity of blood vessels protects from blood loss – it contains potent anticoagulative surface. Endothel is formed with one continuous layer on basal membrane and so it forms the first barrier against hemostasis and thrombosis Integrity is dependant also on subendothelial and extracellular mat ...
... Integrity of blood vessels protects from blood loss – it contains potent anticoagulative surface. Endothel is formed with one continuous layer on basal membrane and so it forms the first barrier against hemostasis and thrombosis Integrity is dependant also on subendothelial and extracellular mat ...
allergies - West Campus | Pima Community College, Tucson
... blood platelets, which are essential for clotting, are coated w/ drug molecules that function as haptens If Ab’s develop against these haptens cause destruction of the platelets In hemolytic anemia, the body may form AB’s against its own blood cells Immune-caused destruction of WBC’s is called agran ...
... blood platelets, which are essential for clotting, are coated w/ drug molecules that function as haptens If Ab’s develop against these haptens cause destruction of the platelets In hemolytic anemia, the body may form AB’s against its own blood cells Immune-caused destruction of WBC’s is called agran ...
5 Secrets to Lower Cholesterol Naturally
... concludes, in patients with high cholesterol.12 Sterols vs. cholesterol Plant sterols actually compete in the body with cholesterol to be absorbed. In this way, they reduce the amount of cholesterol in the bloodstream. The more of these healthy natural elements you take in, the less cholesterol you ...
... concludes, in patients with high cholesterol.12 Sterols vs. cholesterol Plant sterols actually compete in the body with cholesterol to be absorbed. In this way, they reduce the amount of cholesterol in the bloodstream. The more of these healthy natural elements you take in, the less cholesterol you ...
State - Wild about Bio
... – Is characterized either by a deficiency of insulin or, more commonly, by reduced responsiveness of target cells due to some change in insulin receptors – Adults – Body produces insulin, pancreas either cant produce enough or body cant use it adequately (glucose cant get into cells so there is a bu ...
... – Is characterized either by a deficiency of insulin or, more commonly, by reduced responsiveness of target cells due to some change in insulin receptors – Adults – Body produces insulin, pancreas either cant produce enough or body cant use it adequately (glucose cant get into cells so there is a bu ...
detailed lecture outline
... Eosinophils (acidophils) make up about 2-4 percent of circulating WBCs. Their main mode of attack is to excrete toxic compounds such as nitric oxide and cytotoxic enzymes, which are effective against parasites that are too large to ...
... Eosinophils (acidophils) make up about 2-4 percent of circulating WBCs. Their main mode of attack is to excrete toxic compounds such as nitric oxide and cytotoxic enzymes, which are effective against parasites that are too large to ...
Termination of the Acute Inflammatory Response
... Exogenous (from outside the body) such as silica, which can result in silicosis (chronic lung disease) if inhaled for a prolonged period of time. Endogenous (from inside the body) such as LDLs; once the concentration of these molecules are high enough they pass through the vascular wall, accumulate ...
... Exogenous (from outside the body) such as silica, which can result in silicosis (chronic lung disease) if inhaled for a prolonged period of time. Endogenous (from inside the body) such as LDLs; once the concentration of these molecules are high enough they pass through the vascular wall, accumulate ...
Document
... Enzymes enhance motility Antibiotics Chemicals that suppress the female immune system Clotting factors that coagulate semen so it sticks to vagina Fibrinolysin then dissolves that mass ...
... Enzymes enhance motility Antibiotics Chemicals that suppress the female immune system Clotting factors that coagulate semen so it sticks to vagina Fibrinolysin then dissolves that mass ...
Regents Biology - Nick Williams` San Marin Science
... the B cells in the blood & infects some of your cells? You need trained assassins to kill off these infected cells! ...
... the B cells in the blood & infects some of your cells? You need trained assassins to kill off these infected cells! ...
Chapter 19 Disorders Associated with the Immune System
... A development that promises to transform transplantation medicine is the use of stem cells. These are pluripotent—that is, they can generate cell types such as nerve, blood, or other cells. Stem cells first appear in the embryo as embryonic stem cells. In principle, they could be cultured indefinite ...
... A development that promises to transform transplantation medicine is the use of stem cells. These are pluripotent—that is, they can generate cell types such as nerve, blood, or other cells. Stem cells first appear in the embryo as embryonic stem cells. In principle, they could be cultured indefinite ...
Chapter 12
... c. Basophils migrate to damaged tissues and release histamine to promote inflammation and heparin to inhibit blood clotting. d. Lymphocytes are the major players in specific immune reactions and some produce ...
... c. Basophils migrate to damaged tissues and release histamine to promote inflammation and heparin to inhibit blood clotting. d. Lymphocytes are the major players in specific immune reactions and some produce ...
Blood word
... fibrinogen into net like insoluble fibrin causing the blood cells to catch. The amount of prothrombin activator formed is proportional to the amount of tissue damage. Once a blood clot forms, it promotes still more clotting through a positive ...
... fibrinogen into net like insoluble fibrin causing the blood cells to catch. The amount of prothrombin activator formed is proportional to the amount of tissue damage. Once a blood clot forms, it promotes still more clotting through a positive ...
Acute inflammation - immunology.unideb.hu
... cells and damaged tissues resulting from the original insult, and to initiate the process of repair. ...
... cells and damaged tissues resulting from the original insult, and to initiate the process of repair. ...
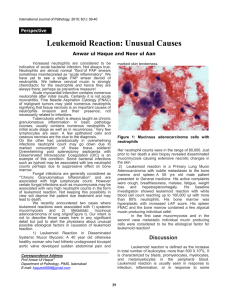
Leukemoid Reaction: Unusual Causes
... neutrophils invasion and their presence; not necessarily related to infections. Tuberculosis which is always taught as chronic granulomatous inflammation in basic pathology courses, usually contains numerous neutrophils in initial acute stage as well as in recurrences.1 Very few lymphocytes are seen ...
... neutrophils invasion and their presence; not necessarily related to infections. Tuberculosis which is always taught as chronic granulomatous inflammation in basic pathology courses, usually contains numerous neutrophils in initial acute stage as well as in recurrences.1 Very few lymphocytes are seen ...
Blood and Body Fluids
... to secrete your blood type antigens into body fluids and secretions. In other words secretors put blood type antigens into the blood and nonsecretors put little to no blood type antigens into the blood. Persons who are secretors can have their body fluids tested for blood type. These people also te ...
... to secrete your blood type antigens into body fluids and secretions. In other words secretors put blood type antigens into the blood and nonsecretors put little to no blood type antigens into the blood. Persons who are secretors can have their body fluids tested for blood type. These people also te ...
What Is Gingivitis?
... GINGIVITIS S Your immune system was created to fight off infection, and that starts with fighting invasions of any foreign object. When plaque, bacteria and food invade the gum line your immune system goes to work. It sends blood vessels to the site of the invasion that hold antibodies and cells tha ...
... GINGIVITIS S Your immune system was created to fight off infection, and that starts with fighting invasions of any foreign object. When plaque, bacteria and food invade the gum line your immune system goes to work. It sends blood vessels to the site of the invasion that hold antibodies and cells tha ...
Atherosclerosis
Atherosclerosis (also known as arteriosclerotic vascular disease or ASVD) is a specific form of arteriosclerosis in which an artery wall thickens as a result of invasion and accumulation of white blood cells (WBCs) (foam cell) and proliferation of intimal smooth muscle cell creating a fibrofatty plaque.The accumulation of the WBCs is termed ""fatty streaks"" early on because of the appearance being similar to that of marbled steak. These accumulations contain both living, active WBCs (producing inflammation) and remnants of dead cells, including cholesterol and triglycerides. The remnants eventually include calcium and other crystallized materials within the outermost and oldest plaque. The ""fatty streaks"" reduce the elasticity of the artery walls. However, they do not affect blood flow for decades because the artery muscular wall enlarges at the locations of plaque. The wall stiffening may eventually increase pulse pressure; widened pulse pressure is one possible result of advanced disease within the major arteries.Atherosclerosis is therefore a syndrome affecting arterial blood vessels due to a chronic inflammatory response of WBCs in the walls of arteries. This is promoted by low-density lipoproteins (LDL, plasma proteins that carry cholesterol and triglycerides) without adequate removal of fats and cholesterol from the macrophages by functional high-density lipoproteins (HDL). It is commonly referred to as a ""hardening"" or furring of the arteries. It is caused by the formation of multiple atheromatous plaques within the arteries.The plaque is divided into three distinct components: The atheroma (""lump of gruel"", from Greek ἀθήρα (athera), meaning ""gruel""), which is the nodular accumulation of a soft, flaky, yellowish material at the center of large plaques, composed of macrophages nearest the lumen of the artery Underlying areas of cholesterol crystals Calcification at the outer base of older or more advanced lesions.Atherosclerosis is a chronic disease that remains asymptomatic for decades. Atherosclerotic lesions, or atherosclerotic plaques, are separated into two broad categories: Stable and unstable (also called vulnerable). The pathobiology of atherosclerotic lesions is very complicated, but generally, stable atherosclerotic plaques, which tend to be asymptomatic, are rich in extracellular matrix and smooth muscle cells. On the other hand, unstable plaques are rich in macrophages and foam cells, and the extracellular matrix separating the lesion from the arterial lumen (also known as the fibrous cap) is usually weak and prone to rupture. Ruptures of the fibrous cap expose thrombogenic material, such as collagen, to the circulation and eventually induce thrombus formation in the lumen. Upon formation, intraluminal thrombi can occlude arteries outright (e.g., coronary occlusion), but more often they detach, move into the circulation, and eventually occlude smaller downstream branches causing thromboembolism. Apart from thromboembolism, chronically expanding atherosclerotic lesions can cause complete closure of the lumen. Chronically expanding lesions are often asymptomatic until lumen stenosis is so severe (usually over 80%) that blood supply to downstream tissue(s) is insufficient, resulting in ischemia.These complications of advanced atherosclerosis are chronic, slowly progressive and cumulative. Most commonly, soft plaque suddenly ruptures (see vulnerable plaque), causing the formation of a thrombus that will rapidly slow or stop blood flow, leading to death of the tissues fed by the artery in approximately five minutes. This catastrophic event is called an infarction. One of the most common recognized scenarios is called coronary thrombosis of a coronary artery, causing myocardial infarction (a heart attack). The same process in an artery to the brain is commonly called stroke. Another common scenario in very advanced disease is claudication from insufficient blood supply to the legs. Atherosclerosis affects the entire artery tree, but mostly larger, high-pressure vessels such as the coronary, renal, femoral, cerebral, and carotid arteries. These are termed ""clinically silent"" because the person having the infarction does not notice the problem and does not seek medical help, or when they do, physicians do not recognize what has happened.