Lesson 1: The Immune System - Lecture Notes | Vaccine Education
... 4) remembering pathogens to prevent disease from recurring. Introduction to the Immune System 1. The immune system is a dynamic communication network of cells, tissues and organs that defend the body against attacks by foreign organisms. Some of these organisms can cause disease and are known as pat ...
... 4) remembering pathogens to prevent disease from recurring. Introduction to the Immune System 1. The immune system is a dynamic communication network of cells, tissues and organs that defend the body against attacks by foreign organisms. Some of these organisms can cause disease and are known as pat ...
Physiology Lecture 10
... migrate to the bone marrow. The hematopoietic stem cells form a population of relatively undifferentiated, multi-potent stem cells that give rise to all of the specialized blood cells. The hematopoietic stem cells are self-renewing, duplicating themselves by mitosis. Erythropoiesis refers to the for ...
... migrate to the bone marrow. The hematopoietic stem cells form a population of relatively undifferentiated, multi-potent stem cells that give rise to all of the specialized blood cells. The hematopoietic stem cells are self-renewing, duplicating themselves by mitosis. Erythropoiesis refers to the for ...
anatomy of the immune system passive immunity
... • they bind to cells using an antibody “bridge”, then kill it by secreting a chemical (perforin) that makes holes in the cell membrane of the target cell. • With enough holes, the cell will die, because water rushing inside the cell will induce osmotic swelling, and an influx of calcium may trigger ...
... • they bind to cells using an antibody “bridge”, then kill it by secreting a chemical (perforin) that makes holes in the cell membrane of the target cell. • With enough holes, the cell will die, because water rushing inside the cell will induce osmotic swelling, and an influx of calcium may trigger ...
IN THIS ISSUE Precursor loss triggers AIDS A MyD88 meddles with
... How a young T cell is educated may dictate its future function, according to a new report by Li et al. (page 2145). Young T cells receive survival signals through their T cell receptors during development. These signals are normally provided by epithelial cells in the thymus. But recent reports show ...
... How a young T cell is educated may dictate its future function, according to a new report by Li et al. (page 2145). Young T cells receive survival signals through their T cell receptors during development. These signals are normally provided by epithelial cells in the thymus. But recent reports show ...
Immunology of the tonsil: a review
... chemical barriers, phagocytic cells and humoral factors, such as complement and interferon. Superimposed on this primitive system in vertebrates is adaptive immunity, where the response, which is mediated by lymphocytes and antibodies, improves on second and subsequent contact with the same organism ...
... chemical barriers, phagocytic cells and humoral factors, such as complement and interferon. Superimposed on this primitive system in vertebrates is adaptive immunity, where the response, which is mediated by lymphocytes and antibodies, improves on second and subsequent contact with the same organism ...
What is the role of class II MHC proteins on donor cells in graft
... -636. Each of the following is a characteristic of antibodies, EXCEPT which one? A.they are proteins with variable and constant regions B.they contain carbohydrates C.they are only secreted by T-cells D.they can combine very specifically with antigen E.they are structurally organized in globular do ...
... -636. Each of the following is a characteristic of antibodies, EXCEPT which one? A.they are proteins with variable and constant regions B.they contain carbohydrates C.they are only secreted by T-cells D.they can combine very specifically with antigen E.they are structurally organized in globular do ...
Nature of The Immune System
... A series of serum proteins involved in mediation of inflammation but also involved in ...
... A series of serum proteins involved in mediation of inflammation but also involved in ...
Tumoricidal activity of human dendritic cells
... Through their role in the induction of antigen specific CTLs and through their capacity to harness the cytotoxic activity of innate immune cells (NK cells, NKT cells, and ϒð T cells), DCs can elicit potent cytotoxic immune responses towards tumor cells Evidence from animal and human studies indi ...
... Through their role in the induction of antigen specific CTLs and through their capacity to harness the cytotoxic activity of innate immune cells (NK cells, NKT cells, and ϒð T cells), DCs can elicit potent cytotoxic immune responses towards tumor cells Evidence from animal and human studies indi ...
Autoimmune T cells—not always the bad guys
... Autoimmune T cells—not always the bad guys Autoimmune attack of central nervous system (CNS) components is associated with devastating neurodegenerative diseases such as multiple sclerosis. Although autoimmune T cells are usually viewed as detrimental, Schwartz and colleagues report on page 49 of th ...
... Autoimmune T cells—not always the bad guys Autoimmune attack of central nervous system (CNS) components is associated with devastating neurodegenerative diseases such as multiple sclerosis. Although autoimmune T cells are usually viewed as detrimental, Schwartz and colleagues report on page 49 of th ...
Unit 10 p4
... **A VACCINE consists of bacteria or viruses that have been _______ so they a cannot cause a serious infection; or could include a toxoid or toxin that has been chemically altered to destroy its toxic effects -includes antigens that stimulate a but does not produce the severe symptoms of disease 2) P ...
... **A VACCINE consists of bacteria or viruses that have been _______ so they a cannot cause a serious infection; or could include a toxoid or toxin that has been chemically altered to destroy its toxic effects -includes antigens that stimulate a but does not produce the severe symptoms of disease 2) P ...
HBImmunity
... Antibody. Engages B and T cells.It involves the antigen-antibody response that creates a type of memory. The specific response is more effective. It is characterized by specificity, memory and prompt response to an antigen. Immunity: “Free from burden”. Ability of an organism to recognize and defend ...
... Antibody. Engages B and T cells.It involves the antigen-antibody response that creates a type of memory. The specific response is more effective. It is characterized by specificity, memory and prompt response to an antigen. Immunity: “Free from burden”. Ability of an organism to recognize and defend ...
Immune System 2 Non-Specific External and Internal Defenses(1)
... The outer surface of the skin consists of dry, dead cells filled with tough proteins that do not allow the microbes to obtain the water and nutrients they need to survive ...
... The outer surface of the skin consists of dry, dead cells filled with tough proteins that do not allow the microbes to obtain the water and nutrients they need to survive ...
2014 stem cell symposium - Translational Research Institute
... He directs a large group of researchers who focus on the development of new repair strategies in stem cell therapy and gene therapy in orthopaedics. ...
... He directs a large group of researchers who focus on the development of new repair strategies in stem cell therapy and gene therapy in orthopaedics. ...
Chapter 12
... of blood-borne macromolecules known as complement; (2) macrophages and neutrophils, which phagocytose invaders; (3) and natural killer cells (NK cells), which kill tumor cells, virally infected cells, bacteria, and parasites. The adaptive immune system eliminates threats from specific invaders. It n ...
... of blood-borne macromolecules known as complement; (2) macrophages and neutrophils, which phagocytose invaders; (3) and natural killer cells (NK cells), which kill tumor cells, virally infected cells, bacteria, and parasites. The adaptive immune system eliminates threats from specific invaders. It n ...
Ref. Infectious agents or immunomodulatory molecules Host cell
... immunostimulatory chemicals [4]. Cells were exposed to heat-killed E. coli, S. aureus and Bordatella pertussis bacteria for six, twelve, or twenty-four hours and five to seven time-points were collected. Additional experiments were done using live virulent B. pertussis, avirulent strains, and LPS fr ...
... immunostimulatory chemicals [4]. Cells were exposed to heat-killed E. coli, S. aureus and Bordatella pertussis bacteria for six, twelve, or twenty-four hours and five to seven time-points were collected. Additional experiments were done using live virulent B. pertussis, avirulent strains, and LPS fr ...
Every 300 generations: Randomly store 100 sequences from
... first strand until cross-over position, switch to second strand and copy until the end. Replace the two parent virus strands with the new recombinant. 9. Update the tracker for number of latent generations at each site at each of NC cells • Immune response: if t ≥ 30 1. Draw a random sample r = 5000 ...
... first strand until cross-over position, switch to second strand and copy until the end. Replace the two parent virus strands with the new recombinant. 9. Update the tracker for number of latent generations at each site at each of NC cells • Immune response: if t ≥ 30 1. Draw a random sample r = 5000 ...
THE WWW OF WHITE BLOOD CELLS: CLINICAL PATHOLOGY
... present from birth, and does not involve the production of antibodies. They mature in the bone marrow, lymph nodes, spleen, tonsils, and thymus. They destroy all cells in the same manner, and do not have memory of previous antigens. They tend to destroy cancer or infected cells. They also release ch ...
... present from birth, and does not involve the production of antibodies. They mature in the bone marrow, lymph nodes, spleen, tonsils, and thymus. They destroy all cells in the same manner, and do not have memory of previous antigens. They tend to destroy cancer or infected cells. They also release ch ...
File
... no harm to the body. Immediate Allergic Response – can occur within seconds of contact with the antigen. The response is caused by the release of histamine by cells which brings about the allergic symptoms. Anaphylactic shock – an immediate allergic response that occurs because the allergen has ente ...
... no harm to the body. Immediate Allergic Response – can occur within seconds of contact with the antigen. The response is caused by the release of histamine by cells which brings about the allergic symptoms. Anaphylactic shock – an immediate allergic response that occurs because the allergen has ente ...
Document
... organs and differentiate into CTL effector cells. CTLs can kill targets independently of costimulation. Once a CTL encounters a target cell it releases cytotoxic granules containing perforin and granzymes. Perforin forms pores in the membrane of the target cell allowing granzymes to enter the cell. ...
... organs and differentiate into CTL effector cells. CTLs can kill targets independently of costimulation. Once a CTL encounters a target cell it releases cytotoxic granules containing perforin and granzymes. Perforin forms pores in the membrane of the target cell allowing granzymes to enter the cell. ...
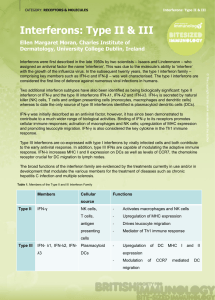
Interferon Type II & III - Bite
... whereas to date the only source of type III interferons identified is plasmacytoid dendritic cells (DCs). IFN-γ was initially described as an antiviral factor, however, it has since been demonstrated to contribute to a much wider range of biological activities. Binding of IFN-γ to its receptors prom ...
... whereas to date the only source of type III interferons identified is plasmacytoid dendritic cells (DCs). IFN-γ was initially described as an antiviral factor, however, it has since been demonstrated to contribute to a much wider range of biological activities. Binding of IFN-γ to its receptors prom ...
Immune System Powerpoint
... White Blood Cells ~T-Cells~ • T-Cells, often called “natural killer” cells, recognize infected human cells and cancer cells • T-cells will attack these infected cells, quickly kill them, and then continue to search for more cells to kill ...
... White Blood Cells ~T-Cells~ • T-Cells, often called “natural killer” cells, recognize infected human cells and cancer cells • T-cells will attack these infected cells, quickly kill them, and then continue to search for more cells to kill ...
Lymphopoiesis
Lymphopoiesis (lĭm'fō-poi-ē'sĭs) (or lymphocytopoiesis) is the generation of lymphocytes, one of the five types of white blood cell (WBC). It is more formally known as lymphoid hematopoiesis.Pathosis in lymphopoiesis leads to any of various lymphoproliferative disorders, such as the lymphomas and lymphoid leukemias.