The Civil War
... • In the same year the Romans destroy Carthage, and thus they complete the subjugation of their two ancient rivals for the supremacy of the Mediterranean. ...
... • In the same year the Romans destroy Carthage, and thus they complete the subjugation of their two ancient rivals for the supremacy of the Mediterranean. ...
A form of government in which the people choose some of the officials
... applied to citizens was called … ...
... applied to citizens was called … ...
Greece and Rome Study Guide
... 7. What common enemy did Athens and Sparta unite against? The Persians 8. What was the name of the war when Sparta finally defeated Athens? Peloponnesian War 9. What Macedonian ruler created an empire extending from Egypt to India? Alexander the Great 10. Other than his military ability, what else i ...
... 7. What common enemy did Athens and Sparta unite against? The Persians 8. What was the name of the war when Sparta finally defeated Athens? Peloponnesian War 9. What Macedonian ruler created an empire extending from Egypt to India? Alexander the Great 10. Other than his military ability, what else i ...
Document
... merchants, and artisans, who made up the majority of the population. At first had little power in making decisions. In time they gained more rights such as the veto, tribunes, and the Twelve Tables. ...
... merchants, and artisans, who made up the majority of the population. At first had little power in making decisions. In time they gained more rights such as the veto, tribunes, and the Twelve Tables. ...
Social Studies Study Guide
... Name _________________________________________ Date _________________________ 6 - ___ ...
... Name _________________________________________ Date _________________________ 6 - ___ ...
Chapter 4 - morganhighhistoryacademy.org
... these were, I may say, the root of all evils. For greed destroyed honor, integrity, and all other noble qualities. Ambition drove many men to become false; to have one thought locked in the breast, another ready on the tongue; to value friendships and enmities not on their merits but by the standard ...
... these were, I may say, the root of all evils. For greed destroyed honor, integrity, and all other noble qualities. Ambition drove many men to become false; to have one thought locked in the breast, another ready on the tongue; to value friendships and enmities not on their merits but by the standard ...
the roman invasion in england
... Claudio. They left Britain in 410 A.C. because the Saxons invaded Britain. ...
... Claudio. They left Britain in 410 A.C. because the Saxons invaded Britain. ...
Unit Three Test Study Guide
... 22. Who elected the representatives in the assembly? 23. How long could a dictator rule? In what circumstances? 24. What was the most powerful governing body? 25. What is an aqueduct? Vocabulary 26. most powerful 27. of great importance 28. “high city” in Greek 29. deadly infectious disease 30. a fe ...
... 22. Who elected the representatives in the assembly? 23. How long could a dictator rule? In what circumstances? 24. What was the most powerful governing body? 25. What is an aqueduct? Vocabulary 26. most powerful 27. of great importance 28. “high city” in Greek 29. deadly infectious disease 30. a fe ...
The Collapse of Rome: Marius, Sulla and the First Civil
... By the early first century BC, the Roman Republic had already carved itself a massive empire and was easily the most powerful state in the Mediterranean. Roman armies had marched victoriously over enemies far and wide, but the Roman heartland was soon to feel the tramp of armies on campaign as the R ...
... By the early first century BC, the Roman Republic had already carved itself a massive empire and was easily the most powerful state in the Mediterranean. Roman armies had marched victoriously over enemies far and wide, but the Roman heartland was soon to feel the tramp of armies on campaign as the R ...
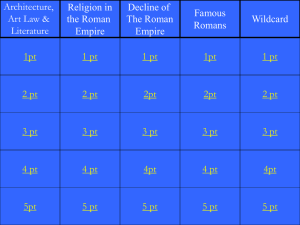
Jeopardy Example
... Gold coins were replaced with copper coins with only a thin layer of gold thus these coins were worth less ...
... Gold coins were replaced with copper coins with only a thin layer of gold thus these coins were worth less ...
Section II Study Guide I. Vocabulary: Be able to define these terms
... republic: a form of government in which its citizens vote for its leader Apennines: the mountain range that runs the length of Italy ...
... republic: a form of government in which its citizens vote for its leader Apennines: the mountain range that runs the length of Italy ...
Roman Society
... answer the following questions 1. Describe the early settlements of Rome 2. How did the patricians control the Roman Republic 3. Why did Marcus feel that Lucius and the other patricians had taken advantage of them? 4. What changes did Marcus and the other plebeians want to make in Roman government 5 ...
... answer the following questions 1. Describe the early settlements of Rome 2. How did the patricians control the Roman Republic 3. Why did Marcus feel that Lucius and the other patricians had taken advantage of them? 4. What changes did Marcus and the other plebeians want to make in Roman government 5 ...
Joshua C Ford Cumulative Essay: The History of Technology in the
... for the romans to effectively manage the massive amount of land it controlled. When speaking of roman engineering there is one simple shape that cannot be forgotten, the arch. Arches are seen in almost any roman construction from the great coliseum in Rome itself, to the aqueducts that ran into ever ...
... for the romans to effectively manage the massive amount of land it controlled. When speaking of roman engineering there is one simple shape that cannot be forgotten, the arch. Arches are seen in almost any roman construction from the great coliseum in Rome itself, to the aqueducts that ran into ever ...
The Roman Empire
... adopted a system of government that was close to a republic… 1. Rome had a Senate that was elected, with “checks and balances” 2. All Roman male-citizens were equal under the law. 3. A system of laws was adopted that is close to what we have in the USA today: for example – you are innocent until pro ...
... adopted a system of government that was close to a republic… 1. Rome had a Senate that was elected, with “checks and balances” 2. All Roman male-citizens were equal under the law. 3. A system of laws was adopted that is close to what we have in the USA today: for example – you are innocent until pro ...
Chapter 6: The Romans
... on the nearby fertile plains and expanded the city to include seven nearby hills. This is why the city was named “Rome” and called the “city on seven hills.” ...
... on the nearby fertile plains and expanded the city to include seven nearby hills. This is why the city was named “Rome” and called the “city on seven hills.” ...
World History 234
... What were the main internal causes of the empire’s decline? How did Diocletian succeed in preserving the empire? Why did so many Germanic tribes begin invading the Roman Empire? Section 5 pp.178-183 Rome and the Roots of Western Civilization Terms and Names Greco-Roman Culture Tacitus ...
... What were the main internal causes of the empire’s decline? How did Diocletian succeed in preserving the empire? Why did so many Germanic tribes begin invading the Roman Empire? Section 5 pp.178-183 Rome and the Roots of Western Civilization Terms and Names Greco-Roman Culture Tacitus ...
Ancient Roman architecture

Ancient Roman architecture developed different aspects of Ancient Greek architecture and newer technologies such as the arch and the dome to make a new architectural style. Roman architecture flourished throughout the Empire during the Pax Romana. Its use of new materials, particularly concrete, was a very important feature.Roman Architecture covers the period from the establishment of the Roman Republic in 509 BC to about the 4th century AD, after which it becomes reclassified as Late Antique or Byzantine architecture. Most of the many surviving examples are from the later period. Roman architectural style continued to influence building in the former empire for many centuries, and the style used in Western Europe beginning about 1000 is called Romanesque architecture to reflect this dependence on basic Roman forms.The Ancient Romans were responsible for significant developments in housing and public hygiene, for example their public and private baths and latrines, under-floor heating in the form of the hypocaust, mica glazing (examples in Ostia Antica), and piped hot and cold water (examples in Pompeii and Ostia).