CHEM F654
... Two exams will be given, one midterm and one final exam (50 % of final grade). These exams will be a combination of essay questions and topic reviews. Makeup exams will only be allowed with pre-approval of the instructor or with an acceptable, documented reason such as unexpected illness, family eme ...
... Two exams will be given, one midterm and one final exam (50 % of final grade). These exams will be a combination of essay questions and topic reviews. Makeup exams will only be allowed with pre-approval of the instructor or with an acceptable, documented reason such as unexpected illness, family eme ...
Answer Set 1
... If the α-C bends in each amino acid alternate in orientation, the chain forms an extended strand. Amino acids occur every 3.5 Å in opposite orientations along the extended strand, and every 7.0 Å in equivalent orientation. No H-bonds form within a signle extended strands, but two or more extended st ...
... If the α-C bends in each amino acid alternate in orientation, the chain forms an extended strand. Amino acids occur every 3.5 Å in opposite orientations along the extended strand, and every 7.0 Å in equivalent orientation. No H-bonds form within a signle extended strands, but two or more extended st ...
What meaning(s) do these two photos represent? (Hint* dna,rna
... hill.com/sites/0078802849/student_view0/unit3/chap ...
... hill.com/sites/0078802849/student_view0/unit3/chap ...
called “organic molecules”
... linking amino acids together in a chain called a “polypeptide” •Each link is created by the dehydration reaction between the amino group of one amino acid and the carboxyl group of the next amino acid in the chain. ...
... linking amino acids together in a chain called a “polypeptide” •Each link is created by the dehydration reaction between the amino group of one amino acid and the carboxyl group of the next amino acid in the chain. ...
Lecture 3
... Other factors resulting in helix deformation 1. Deformation is forced because of tertiary structure (crowding). 2. Strong H-bonding (e.g., between side chains). 3. Helix breakers inside; Pro will result in a kink for sure and Gly almost always but small polar amino acids such as Ser and Thr also c ...
... Other factors resulting in helix deformation 1. Deformation is forced because of tertiary structure (crowding). 2. Strong H-bonding (e.g., between side chains). 3. Helix breakers inside; Pro will result in a kink for sure and Gly almost always but small polar amino acids such as Ser and Thr also c ...
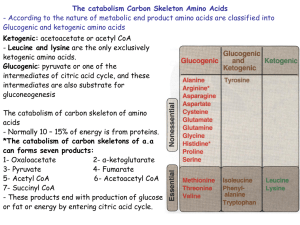
The catabolism Carbon Skeleton Amino Acids
... The catabolism Carbon Skeleton Amino Acids - According to the nature of metabolic end product amino acids are classified into Glucogenic and ketogenic amino acids Ketogenic: acetoacetate or acetyl CoA - Leucine and lysine are the only exclusively ketogenic amino acids. Glucogenic: pyruvate or one of ...
... The catabolism Carbon Skeleton Amino Acids - According to the nature of metabolic end product amino acids are classified into Glucogenic and ketogenic amino acids Ketogenic: acetoacetate or acetyl CoA - Leucine and lysine are the only exclusively ketogenic amino acids. Glucogenic: pyruvate or one of ...
Biology 12 - Biologically Important Molecules – Review Worksheet
... an enzyme that breaks down maltose to two glucose molecules an atom or molecule that has either lost or gained electrons a weak bond due to the attraction between partial charges on hydrogen, oxygen, and nitrogen atoms a polymer of glucose, used as a structural component of plant cell walls a polyme ...
... an enzyme that breaks down maltose to two glucose molecules an atom or molecule that has either lost or gained electrons a weak bond due to the attraction between partial charges on hydrogen, oxygen, and nitrogen atoms a polymer of glucose, used as a structural component of plant cell walls a polyme ...
Protein Structure and Folding
... 1. Many proteins in particular small ones are stabilized by disulfide bridges. Lysozyme contains 8 cysteine residues that form 4 four bridges. Derive expression for the number of ways N cysteins can pair with each other. Some proteins like many neutrophic factors contain odd number of cysteins. What ...
... 1. Many proteins in particular small ones are stabilized by disulfide bridges. Lysozyme contains 8 cysteine residues that form 4 four bridges. Derive expression for the number of ways N cysteins can pair with each other. Some proteins like many neutrophic factors contain odd number of cysteins. What ...
shroff srrotary institute of chemical technology
... For example, if a certain food contains 2 per cent nitrogen, on analysis its protein content would be 2x6.25=12.5 per cent. The total nitrogen content of proteins and peptides may be determined by the Dumas method or Kjeldahl method. ...
... For example, if a certain food contains 2 per cent nitrogen, on analysis its protein content would be 2x6.25=12.5 per cent. The total nitrogen content of proteins and peptides may be determined by the Dumas method or Kjeldahl method. ...
Toober variations
... Some students will randomly generate a sequence of tacks that is very difficult to fold into a shape that simultaneously satisfies all 3 (or 4) laws of chemistry. This is a good “teaching moment” in that the teacher can use these examples to emphasize that such “proteins” would not have been selecte ...
... Some students will randomly generate a sequence of tacks that is very difficult to fold into a shape that simultaneously satisfies all 3 (or 4) laws of chemistry. This is a good “teaching moment” in that the teacher can use these examples to emphasize that such “proteins” would not have been selecte ...
DNA, RNA, Proteins
... 1. Hydrogen bond: proton sharing between protondonor side chains. 2. Electrostatic interaction (salt bridge): between oppositely charged residues. 3. van der Waals bond: weak interaction between atoms (molecules) with closed electron shells. 4. Hydrophobe-hydrophobe interaction: between hydrophobic ...
... 1. Hydrogen bond: proton sharing between protondonor side chains. 2. Electrostatic interaction (salt bridge): between oppositely charged residues. 3. van der Waals bond: weak interaction between atoms (molecules) with closed electron shells. 4. Hydrophobe-hydrophobe interaction: between hydrophobic ...
Chapter 3
... – Carbonyl group—a carbon linked by a double bond to an oxygen atom – Carboxyl group—consists of a carbon double-bonded to both an oxygen and a hydroxyl group – Amino group—composed of a nitrogen bonded to two hydrogen atoms and the carbon skeleton – Phosphate group—consists of a phosphorus atom bon ...
... – Carbonyl group—a carbon linked by a double bond to an oxygen atom – Carboxyl group—consists of a carbon double-bonded to both an oxygen and a hydroxyl group – Amino group—composed of a nitrogen bonded to two hydrogen atoms and the carbon skeleton – Phosphate group—consists of a phosphorus atom bon ...
1.The general formula for amino acids, explain it term by
... The pair of hooks –NH2 and COOH- of different amino acid are used to form the peptidic bond CO-NH. 4.Describe the protein molecule. protein molecule is not a chain like, highly flexible object (think a section of chain highly flexible object) but rather a compact, well- -bundled ball of string. 5.Wh ...
... The pair of hooks –NH2 and COOH- of different amino acid are used to form the peptidic bond CO-NH. 4.Describe the protein molecule. protein molecule is not a chain like, highly flexible object (think a section of chain highly flexible object) but rather a compact, well- -bundled ball of string. 5.Wh ...
Lecture 11
... •Zymogens are inactive precursors of enzymes that are irreversibly transformed into active enzymes by cleavage of their primary structure •In other words: Your cells make an enzyme in an inactive form, but cut away a part of it to activate it when it is needed. ...
... •Zymogens are inactive precursors of enzymes that are irreversibly transformed into active enzymes by cleavage of their primary structure •In other words: Your cells make an enzyme in an inactive form, but cut away a part of it to activate it when it is needed. ...
The test will be a mixture of MCQs related to basic cell biology
... 4. Lysosomes are spherical or oval vesicles derived from the Golgi apparatus. They are membranebound organelles of varying sizes containing hydrolase enzymes capable of digesting most biological molecules. What is the function of lysosomes? a) They manufacture membrane phospholipids and make cholest ...
... 4. Lysosomes are spherical or oval vesicles derived from the Golgi apparatus. They are membranebound organelles of varying sizes containing hydrolase enzymes capable of digesting most biological molecules. What is the function of lysosomes? a) They manufacture membrane phospholipids and make cholest ...
Protein structure prediction

Protein structure prediction is the prediction of the three-dimensional structure of a protein from its amino acid sequence — that is, the prediction of its folding and its secondary, tertiary, and quaternary structure from its primary structure. Structure prediction is fundamentally different from the inverse problem of protein design. Protein structure prediction is one of the most important goals pursued by bioinformatics and theoretical chemistry; it is highly important in medicine (for example, in drug design) and biotechnology (for example, in the design of novel enzymes). Every two years, the performance of current methods is assessed in the CASP experiment (Critical Assessment of Techniques for Protein Structure Prediction). A continuous evaluation of protein structure prediction web servers is performed by the community project CAMEO3D.