Sample
... the brain gives rise to mental activity, the authors explain the fundamental concepts behind and the key discoveries that draw on neural network computer models, brain scans, and behavioral studies. Drawing on this analysis, the authors also present an intriguing theory of consciousness. In addition ...
... the brain gives rise to mental activity, the authors explain the fundamental concepts behind and the key discoveries that draw on neural network computer models, brain scans, and behavioral studies. Drawing on this analysis, the authors also present an intriguing theory of consciousness. In addition ...
Jeopardy - Zion-Benton Township High School
... Brain & Addiction B: The limbic system is involved in emotions, learning and memory, and other functions necessary for survival. The reward circuit is part of the limbic system and is activated by pleasurable activities, such as hanging out with friends and by drugs of abuse. ...
... Brain & Addiction B: The limbic system is involved in emotions, learning and memory, and other functions necessary for survival. The reward circuit is part of the limbic system and is activated by pleasurable activities, such as hanging out with friends and by drugs of abuse. ...
638965471899MyersMod_LG_03
... through the bloodstream and affect other tissues, including the brain. When they act on the brain, they influence our interest in sex, food, and aggression. Compared to the speed at which messages move through the nervous system, endocrine messages move more slowly but their effects are usually long ...
... through the bloodstream and affect other tissues, including the brain. When they act on the brain, they influence our interest in sex, food, and aggression. Compared to the speed at which messages move through the nervous system, endocrine messages move more slowly but their effects are usually long ...
Module_3vs9_Final - Doral Academy Preparatory
... • Central nervous system – Made up of neurons located in the ______________________________ ...
... • Central nervous system – Made up of neurons located in the ______________________________ ...
23mri2
... suppress signal from water. This can be done only without gradient field. Still localized measurements are possible - brain, kidneys, liver... . In addition to protons, several other nuclei are used 31P, 13C,... ...
... suppress signal from water. This can be done only without gradient field. Still localized measurements are possible - brain, kidneys, liver... . In addition to protons, several other nuclei are used 31P, 13C,... ...
Bolt IRM Mod 03
... As mentioned in the text, myelin is a fatty sheath that helps speed impulses down some neurons’ axons. Its importance for the normal transfer of information in the human nervous system is evident in the demyelinating diseases of multiple sclerosis (MS) and Guillain-Barré syndrome. It is now clear th ...
... As mentioned in the text, myelin is a fatty sheath that helps speed impulses down some neurons’ axons. Its importance for the normal transfer of information in the human nervous system is evident in the demyelinating diseases of multiple sclerosis (MS) and Guillain-Barré syndrome. It is now clear th ...
The Nervous System
... Messages travel through the cranial nerves, those which branch out from the brain and go to many places in the head such as the ears, eyes and face. ...
... Messages travel through the cranial nerves, those which branch out from the brain and go to many places in the head such as the ears, eyes and face. ...
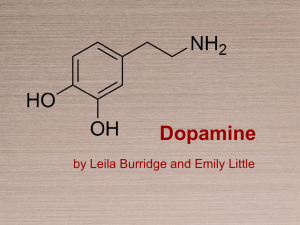
Dopamine 2013
... ● http://www.news-medical.net/health/What-is-Dopamine.aspx ● http://www.news-medical.net/health/Dopamine-Functions.aspx ● http://www.livestrong.com/article/195851-what-are-the-causes-of-lowdopamine-levels/ ● http://www.livestrong.com/article/73358-side-effects-lack-dopamine/ ● http://www.livestrong. ...
... ● http://www.news-medical.net/health/What-is-Dopamine.aspx ● http://www.news-medical.net/health/Dopamine-Functions.aspx ● http://www.livestrong.com/article/195851-what-are-the-causes-of-lowdopamine-levels/ ● http://www.livestrong.com/article/73358-side-effects-lack-dopamine/ ● http://www.livestrong. ...
The Nervous System - Hastings High School
... 3. Microglia – smallest and most rare white blood cells that have come from the capillaries engulf cell waste and pathogens 4. Ependymal cells lining of the ventricles (cavities) within the brain some areas produce cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) to bathe the brain and spinal cord also contain c ...
... 3. Microglia – smallest and most rare white blood cells that have come from the capillaries engulf cell waste and pathogens 4. Ependymal cells lining of the ventricles (cavities) within the brain some areas produce cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) to bathe the brain and spinal cord also contain c ...
The Challenge of Connecting the Dots in the B.R.A.I.N.
... the critical input to the model. For example, sleep spindles, Up and Down states, and cortical spreading depression could be described by a set of parameters including those related to subthreshold polarization, intracellular concentration of calcium in neurons and glia, blood flow, and energy consu ...
... the critical input to the model. For example, sleep spindles, Up and Down states, and cortical spreading depression could be described by a set of parameters including those related to subthreshold polarization, intracellular concentration of calcium in neurons and glia, blood flow, and energy consu ...
Sense and Control
... 2 Carefully take a small whiff of the substance. Do not breathe in too deeply. 3 Re-seal the container and wait 30 seconds before taking a similar whiff. Rate the strength of the smell from 0 (no smell) to 5 (the strength of your first smell). 4 Continue to take a whiff every 30 seconds, giving the ...
... 2 Carefully take a small whiff of the substance. Do not breathe in too deeply. 3 Re-seal the container and wait 30 seconds before taking a similar whiff. Rate the strength of the smell from 0 (no smell) to 5 (the strength of your first smell). 4 Continue to take a whiff every 30 seconds, giving the ...
System Responses to Exercise and Disease
... materials between tissues and bloodstream • Materials may move across capillary walls only by diffusion and bulk flow, with exceptions: – brain capillaries actively transport glucose into the brain ISF – Ordinarily, capillary slits are not permeable to molecules as large as plasma proteins, but in o ...
... materials between tissues and bloodstream • Materials may move across capillary walls only by diffusion and bulk flow, with exceptions: – brain capillaries actively transport glucose into the brain ISF – Ordinarily, capillary slits are not permeable to molecules as large as plasma proteins, but in o ...
Nervous System: Topic 1: Neural Tissue Objective: Students will
... The __________________ is released into the synaptic cleft by exocytosis. The neurotransmitter is soon broken down by another chemical (this is called the synaptic delay). ...
... The __________________ is released into the synaptic cleft by exocytosis. The neurotransmitter is soon broken down by another chemical (this is called the synaptic delay). ...
thoughts - Budokon MD
... dramatic wiring until we’re 5-7 years old, and they don’t fully mature until we are 20-30 years old. This means that the primitive emotional brain (limbic system) holds control over the more sophisticated adult brain for many years. Children have less control over their emotions, because the axons t ...
... dramatic wiring until we’re 5-7 years old, and they don’t fully mature until we are 20-30 years old. This means that the primitive emotional brain (limbic system) holds control over the more sophisticated adult brain for many years. Children have less control over their emotions, because the axons t ...
neurolinguistics: shakespeare and aphasia
... The brain processes information and sends instructions through an extremely complex system of nervecells, known as neurons. The travelling of information from one neuron to the other is a process called synapse, and the synapses can be chemical (indirect synapse, where messages are transferred throu ...
... The brain processes information and sends instructions through an extremely complex system of nervecells, known as neurons. The travelling of information from one neuron to the other is a process called synapse, and the synapses can be chemical (indirect synapse, where messages are transferred throu ...
Unit 6 Nervous System
... Blood Supply to the Brain One of the most metabolically active organs in the body Makes up only 2-3% of body weight but uses about 20% of available O2 at rest Well supplied with O2 and nutrients Only nutritional source for brain metabolic activity is glucose Capillaries in the brain are muc ...
... Blood Supply to the Brain One of the most metabolically active organs in the body Makes up only 2-3% of body weight but uses about 20% of available O2 at rest Well supplied with O2 and nutrients Only nutritional source for brain metabolic activity is glucose Capillaries in the brain are muc ...
Your Child`s Brain
... and rumpled cortex wherein thought and perception originate. The neural cells are so small, and the distance so great, that a neuron striking out for what will be the prefrontal cortex migrates a distance equivalent to a human's walking from New York to California, says developmental neurobiologist ...
... and rumpled cortex wherein thought and perception originate. The neural cells are so small, and the distance so great, that a neuron striking out for what will be the prefrontal cortex migrates a distance equivalent to a human's walking from New York to California, says developmental neurobiologist ...
CH 14 brain cranial nerves shortened for test 4 A and P 2016
... - BBB regulates what leaves BV and gets to brain cells and fibers - blood brain barrier has tight junctions for capillaries & ependymal - circumventricular organ in 3rd & 4th ventricles, has direct access to brain, cells here monitor glucose, pH, osmolarity, & other parameters – disease can access b ...
... - BBB regulates what leaves BV and gets to brain cells and fibers - blood brain barrier has tight junctions for capillaries & ependymal - circumventricular organ in 3rd & 4th ventricles, has direct access to brain, cells here monitor glucose, pH, osmolarity, & other parameters – disease can access b ...
4.27.05 Respiration and Nervous
... • The nervous system is divided into a central nervous system (CNS), consisting of the brain and spinal cord, and a peripheral nervous system (PNS), consisting of nerves carrying sensory and motor information between the CNS and muscles and glands. • Both systems have two types of cells: neurons tha ...
... • The nervous system is divided into a central nervous system (CNS), consisting of the brain and spinal cord, and a peripheral nervous system (PNS), consisting of nerves carrying sensory and motor information between the CNS and muscles and glands. • Both systems have two types of cells: neurons tha ...
УДК - Clinical pharmacy
... bloodstream functioning of the brain initiates a cascade of disorders of energy and plastic neuronal metabolism. Currently, a number of vascular self-regulated mechanisms are found, by which the brain can partially compensate the lack of blood supply. Significant role in the implementation of these ...
... bloodstream functioning of the brain initiates a cascade of disorders of energy and plastic neuronal metabolism. Currently, a number of vascular self-regulated mechanisms are found, by which the brain can partially compensate the lack of blood supply. Significant role in the implementation of these ...
The Nervous System and The Brain
... Increasing the stimulus above the threshold will not increase the intensity of the impulse. The neuron’s reaction is an “All or None Response” – Like firing a gun – either it fires, or it doesn’t ***Reaction Time Experiment*** http://www.bbc.co.uk/science/humanbody/sleep/sheep/ How do you know the d ...
... Increasing the stimulus above the threshold will not increase the intensity of the impulse. The neuron’s reaction is an “All or None Response” – Like firing a gun – either it fires, or it doesn’t ***Reaction Time Experiment*** http://www.bbc.co.uk/science/humanbody/sleep/sheep/ How do you know the d ...
Addiction - Biological, Not Sociological
... Genetic factors account for 40%-60% of the likelihood of developing an addiction. There are multiple genes that control various aspects of the biological response to drugs or the physiological predisposition to become an abuser. Genetic factors do not ensure addiction; just as lack of them does not ...
... Genetic factors account for 40%-60% of the likelihood of developing an addiction. There are multiple genes that control various aspects of the biological response to drugs or the physiological predisposition to become an abuser. Genetic factors do not ensure addiction; just as lack of them does not ...
File
... a disturbance of motor functions. Usually normal intelligence In certain cases there is no identifiable cause, other etiologies include problems in intrauterine development (e.g. exposure to radiation, infection), asphyxia before birth, hypoxia of the brain, and birth trauma during labor and deliver ...
... a disturbance of motor functions. Usually normal intelligence In certain cases there is no identifiable cause, other etiologies include problems in intrauterine development (e.g. exposure to radiation, infection), asphyxia before birth, hypoxia of the brain, and birth trauma during labor and deliver ...
Slide 1
... involved in learning, emotion, memory, and motivation. – Thalamus - part of the limbic system located in the center of the brain, this structure relays sensory information from the lower part of the brain to the proper areas of the cortex and processes some sensory information before sending it to i ...
... involved in learning, emotion, memory, and motivation. – Thalamus - part of the limbic system located in the center of the brain, this structure relays sensory information from the lower part of the brain to the proper areas of the cortex and processes some sensory information before sending it to i ...
Blood–brain barrier

The blood–brain barrier (BBB) is a highly selective permeability barrier that separates the circulating blood from the brain extracellular fluid (BECF) in the central nervous system (CNS). The blood–brain barrier is formed by brain endothelial cells, which are connected by tight junctions with an extremely high electrical resistivity of at least 0.1 Ω⋅m. The blood–brain barrier allows the passage of water, some gases, and lipid-soluble molecules by passive diffusion, as well as the selective transport of molecules such as glucose and amino acids that are crucial to neural function. On the other hand, the blood–brain barrier may prevent the entry of lipophilic, potential neurotoxins by way of an active transport mechanism mediated by P-glycoprotein. Astrocytes are necessary to create the blood–brain barrier. A small number of regions in the brain, including the circumventricular organs (CVOs), do not have a blood–brain barrier.The blood–brain barrier occurs along all capillaries and consists of tight junctions around the capillaries that do not exist in normal circulation. Endothelial cells restrict the diffusion of microscopic objects (e.g., bacteria) and large or hydrophilic molecules into the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF), while allowing the diffusion of small hydrophobic molecules (O2, CO2, hormones). Cells of the barrier actively transport metabolic products such as glucose across the barrier with specific proteins. This barrier also includes a thick basement membrane and astrocytic endfeet.