Nervous and Endocrine Systems
... o as wide as your thumb around and about 43 cm long protected by skull and vertebrae and 3 membrane layers with cerebrospinal fluid in between Aim: PNS 12 pairs of cranial nerves and 31 pairs of spinal nerves Somatic – _____ Autonomic – _____ ...
... o as wide as your thumb around and about 43 cm long protected by skull and vertebrae and 3 membrane layers with cerebrospinal fluid in between Aim: PNS 12 pairs of cranial nerves and 31 pairs of spinal nerves Somatic – _____ Autonomic – _____ ...
title of video - Discovery Education
... A neuron is a specialized cell for the transmission of information to other nerve cells, muscles or glands. ...
... A neuron is a specialized cell for the transmission of information to other nerve cells, muscles or glands. ...
Neurotox I
... There is massive death of neurons, neuroprogenitors, and oligodendroglia in normal vertebrate development. This is largely regulated by access to limiting supplies of exogenous survival-promoting trophic factors. Survival is promoted largely by activation of Akt as well as Erks, and involves blockad ...
... There is massive death of neurons, neuroprogenitors, and oligodendroglia in normal vertebrate development. This is largely regulated by access to limiting supplies of exogenous survival-promoting trophic factors. Survival is promoted largely by activation of Akt as well as Erks, and involves blockad ...
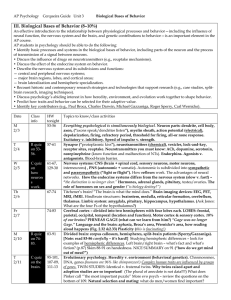
Scanning the Brain AK.rtf
... subject's head. The brain's measures the very faint timing of nerve cell activity -magnetic field induces a current magnetic fields that down to the millisecond (most in the coils, which in turn induces emanate from the head accurate of all brain scanning a magnetic field in a special, as a result o ...
... subject's head. The brain's measures the very faint timing of nerve cell activity -magnetic field induces a current magnetic fields that down to the millisecond (most in the coils, which in turn induces emanate from the head accurate of all brain scanning a magnetic field in a special, as a result o ...
The human brain contains approximately - Lake
... The first place winner receives $400, a $1000 scholarship to the University of Scranton and an invitation to the International Brain Bee, March 17 & 18 in Baltimore, MD. Second and third place winners each receive $50. ...
... The first place winner receives $400, a $1000 scholarship to the University of Scranton and an invitation to the International Brain Bee, March 17 & 18 in Baltimore, MD. Second and third place winners each receive $50. ...
Your Brain and What It Does
... body’s hormonal system interact, the hypothalamus maintains the body’s status quo. It monitors numerous bodily functions such as blood pressure and body temperature, as well as controlling body weight and appetite. ...
... body’s hormonal system interact, the hypothalamus maintains the body’s status quo. It monitors numerous bodily functions such as blood pressure and body temperature, as well as controlling body weight and appetite. ...
Review Senses and Nervous System Test
... Review Senses and Nervous System Test *(This is only an outline there is much more you should look over) CH 8 SENSES 1. What are the functions of the parts of eye? 2. What is blind spot, photoreceptors, rods, cones? 3. Read p 258, 262 4. What is colorblindness, cataracts, pink eye, glaucoma 5. What ...
... Review Senses and Nervous System Test *(This is only an outline there is much more you should look over) CH 8 SENSES 1. What are the functions of the parts of eye? 2. What is blind spot, photoreceptors, rods, cones? 3. Read p 258, 262 4. What is colorblindness, cataracts, pink eye, glaucoma 5. What ...
Nervous System
... • What are the major functions of the nervous system? • What are the 3 major organs in the nervous system? • Which part of the brain controls thought? • Which part of the nervous system control arms and legs? ...
... • What are the major functions of the nervous system? • What are the 3 major organs in the nervous system? • Which part of the brain controls thought? • Which part of the nervous system control arms and legs? ...
AP_Chapter_2[1] - HopewellPsychology
... injuries/disease affect the brain and its functions. 2. Manipulating the Brain: Electrically, chemically, or magnetically stimulate various parts of the brain and note the effects. a. Lesion: destroying specific parts of the brain to study its effects. ...
... injuries/disease affect the brain and its functions. 2. Manipulating the Brain: Electrically, chemically, or magnetically stimulate various parts of the brain and note the effects. a. Lesion: destroying specific parts of the brain to study its effects. ...
Puzzle 2A: The Neuron and Nervous System
... 2. A neuron has only one of these 4. This medication is used to treat Parkinson's disease 7. Electrically charged particles 8. Synaptic space between two neurons 11. When the neuron is sufficiently stimulated, this process occurs and triggers the action potential 12. Communication point between two ...
... 2. A neuron has only one of these 4. This medication is used to treat Parkinson's disease 7. Electrically charged particles 8. Synaptic space between two neurons 11. When the neuron is sufficiently stimulated, this process occurs and triggers the action potential 12. Communication point between two ...
Secrets of the Teen Brain
... developed by 12 years of age. • Piaget research in cognitive development, stages and ~12 years was start of formal ...
... developed by 12 years of age. • Piaget research in cognitive development, stages and ~12 years was start of formal ...
The Nervous System allows communication
... radioactive substances to produce three-dimensional colored images of those substances functioning within the body. These images are called PET scans and the technique is termed PET scanning. PET scanning provides information about the body's chemistry not available through other procedures. Unlike ...
... radioactive substances to produce three-dimensional colored images of those substances functioning within the body. These images are called PET scans and the technique is termed PET scanning. PET scanning provides information about the body's chemistry not available through other procedures. Unlike ...
Nervous System
... – The size and weight of the brain decreases – The senses gradually decline because the number of neurons in this area declines – The functions of all other neurons decreases because the number of neurons decline as well ...
... – The size and weight of the brain decreases – The senses gradually decline because the number of neurons in this area declines – The functions of all other neurons decreases because the number of neurons decline as well ...
Nervous System Student Notes
... a. Define: _______________________________________________________ b. Stages of _______________________ event: i. Action potential (electrical signal reaches axon ______________________ ii. Vesicle fuses with membrane and ruptures releasing ...
... a. Define: _______________________________________________________ b. Stages of _______________________ event: i. Action potential (electrical signal reaches axon ______________________ ii. Vesicle fuses with membrane and ruptures releasing ...
glossary - HBO.com
... compound used during a PET (see Positron emission tomography) scan of the brain to show beta-amyloid deposits. Positron emission tomography (PET)—an imaging technique using radioisotopes that allows researchers to observe and measure activity in different parts of the brain by monitoring blood flow ...
... compound used during a PET (see Positron emission tomography) scan of the brain to show beta-amyloid deposits. Positron emission tomography (PET)—an imaging technique using radioisotopes that allows researchers to observe and measure activity in different parts of the brain by monitoring blood flow ...
Spinal nerves
... Initially it was believed that the glia had only structural support functions, but recently has emerged that this is just one of many functions. It has been demonstrated that the Glia can send signals to each other and to the neurons, altering the neural transmission mechanisms. ...
... Initially it was believed that the glia had only structural support functions, but recently has emerged that this is just one of many functions. It has been demonstrated that the Glia can send signals to each other and to the neurons, altering the neural transmission mechanisms. ...
Assignment 2 - Gordon State College
... 31. The ___________________ is known as the “brain’s sensory switchboard” because information from all the senses except smell goes through here to be relayed to the appropriate part of the brain. 32. In the limbic system, the _______________________ plays a large role in the ability to form and pro ...
... 31. The ___________________ is known as the “brain’s sensory switchboard” because information from all the senses except smell goes through here to be relayed to the appropriate part of the brain. 32. In the limbic system, the _______________________ plays a large role in the ability to form and pro ...
Unit 3 Cerqueira guide
... III. Biological Bases of Behavior (8–10%) An effective introduction to the relationship between physiological processes and behavior—including the influence of neural function, the nervous system and the brain, and genetic contributions to behavior—is an important element in the AP course. AP studen ...
... III. Biological Bases of Behavior (8–10%) An effective introduction to the relationship between physiological processes and behavior—including the influence of neural function, the nervous system and the brain, and genetic contributions to behavior—is an important element in the AP course. AP studen ...
2/13/17 AP - Lemon Bay High School
... Write a story of someone riding a bike a suffering a head injury using at least 10 of this week’s BW words. ...
... Write a story of someone riding a bike a suffering a head injury using at least 10 of this week’s BW words. ...
File
... 3) List and describe the protective structures found in the CNS. 4) Describe the pathway of light through the eyeball and the process of light refraction. 5) Explain the meaning of an "odor snapshot" and its relevance to human beings. 6) Discuss the age-related disorders presbyopia and presbycusis. ...
... 3) List and describe the protective structures found in the CNS. 4) Describe the pathway of light through the eyeball and the process of light refraction. 5) Explain the meaning of an "odor snapshot" and its relevance to human beings. 6) Discuss the age-related disorders presbyopia and presbycusis. ...
Why Study Neuroscience?
... See what disabilities result from specific physical damage In humans wait for accident In animals do damage deliberately ...
... See what disabilities result from specific physical damage In humans wait for accident In animals do damage deliberately ...
Nervous System
... metabolism. Lack of oxygen for more than 5 minutes can kill brain cells. • The brain requires glucose for metabolism. Lack of glucose for more than 15 minutes kills brain cells. • Neurons cannot undergo mitosis. ...
... metabolism. Lack of oxygen for more than 5 minutes can kill brain cells. • The brain requires glucose for metabolism. Lack of glucose for more than 15 minutes kills brain cells. • Neurons cannot undergo mitosis. ...
Chapter 1 Lecture Outline
... Homeostasis is essential for survival and function of all cells Each cell contributes to maintenance of a relatively stable internal environment - Most cells are not in direct contact with the external environment - Cell survival depends on maintenance of a relatively stable internal fluid environme ...
... Homeostasis is essential for survival and function of all cells Each cell contributes to maintenance of a relatively stable internal environment - Most cells are not in direct contact with the external environment - Cell survival depends on maintenance of a relatively stable internal fluid environme ...
Haemodynamic response
In haemodynamics, the body must respond to physical activities, external temperature, and other factors by homeostatically adjusting its blood flow to deliver nutrients such as oxygen and glucose to stressed tissues and allow them to function. Haemodynamic response (HR) allows the rapid delivery of blood to active neuronal tissues. Since higher processes in the brain occur almost constantly, cerebral blood flow is essential for the maintenance of neurons, astrocytes, and other cells of the brain.








![AP_Chapter_2[1] - HopewellPsychology](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/008569681_1-9cf3b4caa50d34e12653d8840c008c05-300x300.png)