Document
... • The first segment in the lower section, occasionally called the brain stem, consisting of structures such as the medulla (controlling breathing, heart rate and digestion) and the cerebellum (coordinating senses and muscle movement). • The second segment appears as a insignificant inflammation in l ...
... • The first segment in the lower section, occasionally called the brain stem, consisting of structures such as the medulla (controlling breathing, heart rate and digestion) and the cerebellum (coordinating senses and muscle movement). • The second segment appears as a insignificant inflammation in l ...
The Brain - Misty Cherie
... • This was sometimes knows as “split brain” surgery, because patients experienced a dissociation of the left and right sides of their brains • This created peculiar problems for some patients in which one side of the brain seemed not to know what the other side of the brain was doing ...
... • This was sometimes knows as “split brain” surgery, because patients experienced a dissociation of the left and right sides of their brains • This created peculiar problems for some patients in which one side of the brain seemed not to know what the other side of the brain was doing ...
Nervous System
... for special sense organs. There are 12 pair of cranial nerves. They are identified by their location and function. Spinal Nerves- these are mixed nerves that extend from left to right. There are 31 pair of spinal nerves. These are split into groups: 8 pair of cervical nerves, 12 pair of thoracic ner ...
... for special sense organs. There are 12 pair of cranial nerves. They are identified by their location and function. Spinal Nerves- these are mixed nerves that extend from left to right. There are 31 pair of spinal nerves. These are split into groups: 8 pair of cervical nerves, 12 pair of thoracic ner ...
Peripheral Nervous System - UBC Psychology`s Research Labs
... Allows researchers to determine the functions of distinct brain regions (i.e., functional localization). Involves artificially stimulating distinct regions and assessing changes in behaviour. Electrical stimulation is delivered through electrodes; the electrical current increases the firing of ...
... Allows researchers to determine the functions of distinct brain regions (i.e., functional localization). Involves artificially stimulating distinct regions and assessing changes in behaviour. Electrical stimulation is delivered through electrodes; the electrical current increases the firing of ...
Psychology Chapter 3
... Brain Scans and Type Medical Note: A CT Scan (or CAT Scan) and an MRI operate differently and are better suited for different types of diagnoses. An MRI suited for examining soft tissue, (e.g. ligament and tendon injury, spinal cord injury, brain tumors etc.) while a CT scan is better suited for b ...
... Brain Scans and Type Medical Note: A CT Scan (or CAT Scan) and an MRI operate differently and are better suited for different types of diagnoses. An MRI suited for examining soft tissue, (e.g. ligament and tendon injury, spinal cord injury, brain tumors etc.) while a CT scan is better suited for b ...
NERVOUS SYSTEM CNS-Central Nervous System PNS
... 2. While he could be confused with having prion-related disorders or Alzheimer’s disease because of his symptoms, he is actually suffering from something else. What neurovascular condition is he suffering from? Explain what this condition is. ...
... 2. While he could be confused with having prion-related disorders or Alzheimer’s disease because of his symptoms, he is actually suffering from something else. What neurovascular condition is he suffering from? Explain what this condition is. ...
module 6 The Cerebral Cortex and Our Divided Brain Module
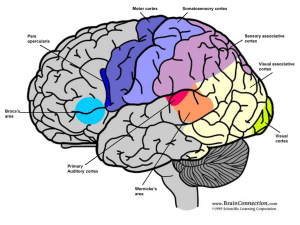
... The cerebral cortex, representing the highest level of brain development, is responsible for our most complex functions. Each hemisphere of the cerebral cortex has four geographical areas: the frontal, parietal, occipital, and temporal lobes. Although small, welldefined regions within these lobes co ...
... The cerebral cortex, representing the highest level of brain development, is responsible for our most complex functions. Each hemisphere of the cerebral cortex has four geographical areas: the frontal, parietal, occipital, and temporal lobes. Although small, welldefined regions within these lobes co ...
BIO 202 Human Anatomy and Physiology II
... Written examinations B. Written quizzes C. Laboratory work D. Comprehensive final E. Grades will be given based upon A = 90 – 100%, B = 80 – 89%, C = 70 – 79%, D = 60 – 69%, and F = below 60%. ...
... Written examinations B. Written quizzes C. Laboratory work D. Comprehensive final E. Grades will be given based upon A = 90 – 100%, B = 80 – 89%, C = 70 – 79%, D = 60 – 69%, and F = below 60%. ...
In the brain, most excitatory communication in synapses occurs by
... In the brain, most excitatory communication in synapses occurs by way of glutamate and most inhibitory communication occurs by way of gamma-aminobutyric acid. In general terms, describe what the other neurotransmitters do. ...
... In the brain, most excitatory communication in synapses occurs by way of glutamate and most inhibitory communication occurs by way of gamma-aminobutyric acid. In general terms, describe what the other neurotransmitters do. ...
This newsletter is for your information only and is not a substitute for
... between Nature (heredity, genetics, biology) and Nurture (environment, parenting, education, experiences). The brain's programmed genetic development and our environmental life experiences interplay causing brain cells (neurons) to grow, to die, to form new connections, to lose connections, to turn ...
... between Nature (heredity, genetics, biology) and Nurture (environment, parenting, education, experiences). The brain's programmed genetic development and our environmental life experiences interplay causing brain cells (neurons) to grow, to die, to form new connections, to lose connections, to turn ...
Biology Lesson 1 Keeping Healthy Learning Objectives: In this
... Biology (6th ed.); EP Solomon, LR Berg & DW Martin; Thomas Learning Inc.; ...
... Biology (6th ed.); EP Solomon, LR Berg & DW Martin; Thomas Learning Inc.; ...
The Brain Game: Adopted from Rod Plotnik: Table created by Mary
... 15. Grandma Mary—Broca’s Area—the part of the language system located in the frontal lobe (left hemisphere) is most important for producing speech. 16. The suprachiasmatic nucleus of the hypothalamus regulates our natural biorhythms. 17. Michael J. Fox—the substantia nigra of the midbrain. 18. Gwen— ...
... 15. Grandma Mary—Broca’s Area—the part of the language system located in the frontal lobe (left hemisphere) is most important for producing speech. 16. The suprachiasmatic nucleus of the hypothalamus regulates our natural biorhythms. 17. Michael J. Fox—the substantia nigra of the midbrain. 18. Gwen— ...
Science of Addiction WebquestKEY
... Neurons communicate via the synapse 6. Define synapse: Information from one neuron flows to another neuron across a small gap called a synapse Click the “Back” button and return to the page titled “The New Science of Addiction: Genetics and the Brain”. Follow the link, “Drugs alter the Brain’s Rewar ...
... Neurons communicate via the synapse 6. Define synapse: Information from one neuron flows to another neuron across a small gap called a synapse Click the “Back” button and return to the page titled “The New Science of Addiction: Genetics and the Brain”. Follow the link, “Drugs alter the Brain’s Rewar ...
Chapter1
... 2. Representation and algorithm: How can this computational theory be implemented? In particular, what is the representation for the input and output, and what is the algorithm for the transformation? 3. Hardware implementation: How can the representation and algorithm be realized physically? Marr p ...
... 2. Representation and algorithm: How can this computational theory be implemented? In particular, what is the representation for the input and output, and what is the algorithm for the transformation? 3. Hardware implementation: How can the representation and algorithm be realized physically? Marr p ...
Introduction to Cognitive Development 2012
... – Linguistics: to understand the structure of language – Anthropology: to help separate characteristics of the mind from characteristics of culture – Researchers often collaborate and/or work across these disciplines 6. Note that cognitive psychology refers to theories of information processing and ...
... – Linguistics: to understand the structure of language – Anthropology: to help separate characteristics of the mind from characteristics of culture – Researchers often collaborate and/or work across these disciplines 6. Note that cognitive psychology refers to theories of information processing and ...
Neuroplasticity
... • Results: They realised that the hand map in the brain that was expected to be jumbled was nearly normal. Merzenich concluded that if the brain map could normalize its structure in response to abnormal input, the prevailing view that we are born with a hardwired system had to be wrong, therefore th ...
... • Results: They realised that the hand map in the brain that was expected to be jumbled was nearly normal. Merzenich concluded that if the brain map could normalize its structure in response to abnormal input, the prevailing view that we are born with a hardwired system had to be wrong, therefore th ...
Biological Psychology Modules 3 & 4
... Norepinephrine • Plays a role in attention and arousal • Used by sympathetic nervous system to ...
... Norepinephrine • Plays a role in attention and arousal • Used by sympathetic nervous system to ...
09. Assessment of Neurologic System
... Deep tendon reflexes – responses to stimulation of a tendon that stretches neuromuscular spindles of a muscle group Strike a deep tendon reflex – stimulates sensory neuron that travels to spinal cord – stimulates interneuron – stimulates motor neuron to create movement ...
... Deep tendon reflexes – responses to stimulation of a tendon that stretches neuromuscular spindles of a muscle group Strike a deep tendon reflex – stimulates sensory neuron that travels to spinal cord – stimulates interneuron – stimulates motor neuron to create movement ...
Nervous System Formative Study Guide File
... 1. Identify the “job” of each of the following: a. Motor neurons Motor neurons are efferent nerves (also called effector neurons), that carry signals from the spinal cord to the muscles to produce (effect) movement. b. Sensory neurons Sensory neurons are nerve cells that transmit sensory information ...
... 1. Identify the “job” of each of the following: a. Motor neurons Motor neurons are efferent nerves (also called effector neurons), that carry signals from the spinal cord to the muscles to produce (effect) movement. b. Sensory neurons Sensory neurons are nerve cells that transmit sensory information ...
Objective 1 | Explain why psychologists are concerned with human
... best-understood neurotransmitters, affects muscle action, learning, and memory. The endorphins are natural opiates released in response to pain and exercise. Pages: 58-59 ...
... best-understood neurotransmitters, affects muscle action, learning, and memory. The endorphins are natural opiates released in response to pain and exercise. Pages: 58-59 ...
Name - ReillyPsychology
... 13. Which of the following statements best describes how researchers use case studies of accidental brain injuries (like the Phineas Gage case) to study the brain? A) Researchers use brain surgeries such as lobotomies to temporarily disable certain parts of the brain and observe the effects. B) Rese ...
... 13. Which of the following statements best describes how researchers use case studies of accidental brain injuries (like the Phineas Gage case) to study the brain? A) Researchers use brain surgeries such as lobotomies to temporarily disable certain parts of the brain and observe the effects. B) Rese ...
Haemodynamic response
In haemodynamics, the body must respond to physical activities, external temperature, and other factors by homeostatically adjusting its blood flow to deliver nutrients such as oxygen and glucose to stressed tissues and allow them to function. Haemodynamic response (HR) allows the rapid delivery of blood to active neuronal tissues. Since higher processes in the brain occur almost constantly, cerebral blood flow is essential for the maintenance of neurons, astrocytes, and other cells of the brain.