The Nervous System
... So how do these neurons work if someone taps you on the shoulder . . . 1. Receptors in the skin sense touch or other stimuli. 2. Sensory neurons transmit the touch message. 3. Information is sorted and interpreted in the brain. A response in determined by interneurons. 4. Motor neurons transmit a r ...
... So how do these neurons work if someone taps you on the shoulder . . . 1. Receptors in the skin sense touch or other stimuli. 2. Sensory neurons transmit the touch message. 3. Information is sorted and interpreted in the brain. A response in determined by interneurons. 4. Motor neurons transmit a r ...
sensory neurone
... a) receptor-->sensory neurone-->relay neurone-->motor neurone--> effector b) receptor--> motor neurone-->relay neurone-->sensory neurone-->effector ...
... a) receptor-->sensory neurone-->relay neurone-->motor neurone--> effector b) receptor--> motor neurone-->relay neurone-->sensory neurone-->effector ...
Chp 9: NERVOUS TISSUE
... of the eye, inner ear, olfactory area of brain ______________________________: dendrites and one axon fused together forming a continuous process that emerges from cell body; begin in embryo as bipolar neurons; most function as sensory receptors for touch, pressure, pain, or thermal stimuli. Cell ...
... of the eye, inner ear, olfactory area of brain ______________________________: dendrites and one axon fused together forming a continuous process that emerges from cell body; begin in embryo as bipolar neurons; most function as sensory receptors for touch, pressure, pain, or thermal stimuli. Cell ...
Finding Clues to Schizophrenia Outside Neurons
... be engulfed and digested. The same process occurs on parts of neurons destined for elimination. There is an “eat-me” signal that informs the microglial cell to remove a particular synaptic spine (for example, one marked by C3). There are separate “find-me” signals that draw the microglial cell close ...
... be engulfed and digested. The same process occurs on parts of neurons destined for elimination. There is an “eat-me” signal that informs the microglial cell to remove a particular synaptic spine (for example, one marked by C3). There are separate “find-me” signals that draw the microglial cell close ...
Steroids: The Brain`s Response
... They can also have a profound effect on reproductive organs and hormones. Many of the effects of steroids are brought about through their actions in the brain. Once steroids enter the brain, they are distributed to many regions, including the hypothalamus and limbic system. When a person takes stero ...
... They can also have a profound effect on reproductive organs and hormones. Many of the effects of steroids are brought about through their actions in the brain. Once steroids enter the brain, they are distributed to many regions, including the hypothalamus and limbic system. When a person takes stero ...
reflexes_lesson
... Note: A trained athlete's heart can pump more blood with each beat so his or her heart rate is slower. Lance Armstrong (famous biker) has resting heart rate of 32-34bpm! Heart rate increases during exercise During exercise, the heart rate increases in order to pump more blood (which carries oxygen) ...
... Note: A trained athlete's heart can pump more blood with each beat so his or her heart rate is slower. Lance Armstrong (famous biker) has resting heart rate of 32-34bpm! Heart rate increases during exercise During exercise, the heart rate increases in order to pump more blood (which carries oxygen) ...
Sliding Filament Theory
... (SR) to release calcium into the sarcoplasm. SR is a specialized organelle in muscle cells used to store calcium. ...
... (SR) to release calcium into the sarcoplasm. SR is a specialized organelle in muscle cells used to store calcium. ...
How is information about touch relayed to the brain?
... What are the major areas of the brain that are associated with the perception of touch? • The majority of thalamic neurons that receive touch information subsequently project the information to the primary somatosensory cortex (SI). Thereafter, information is projected to the secondary somatosensor ...
... What are the major areas of the brain that are associated with the perception of touch? • The majority of thalamic neurons that receive touch information subsequently project the information to the primary somatosensory cortex (SI). Thereafter, information is projected to the secondary somatosensor ...
Document
... • How do reflexes help newborns interact with the world? • How do we determine whether a baby is healthy and adjusting to life outside the uterus? • What behavioral states are common among newborns? • What are the different features of temperament? Do they change as children grow? ...
... • How do reflexes help newborns interact with the world? • How do we determine whether a baby is healthy and adjusting to life outside the uterus? • What behavioral states are common among newborns? • What are the different features of temperament? Do they change as children grow? ...
Chater 2 - Study Guide
... 15. Dr. Frankenstein made a mistake during neurosurgery on his monster. After the operation, the monster “saw” with his ears and “heard” with his eyes. It is likely that Dr. Frankenstein “rewired” neural connections in the monster's: A) hypothalamus. B) cerebellum. C) amygdala. D) thalamus. E) hipp ...
... 15. Dr. Frankenstein made a mistake during neurosurgery on his monster. After the operation, the monster “saw” with his ears and “heard” with his eyes. It is likely that Dr. Frankenstein “rewired” neural connections in the monster's: A) hypothalamus. B) cerebellum. C) amygdala. D) thalamus. E) hipp ...
Chapter Three - New Providence School District
... biological parents at a very early age and raised by adoptive parents. The idea behind these studies is that if the adoptive children more closely resemble their biological parents with respect to a specific trait, then i,.t,,can be assumed that plays a major role. On the other hand, if the adoptive ...
... biological parents at a very early age and raised by adoptive parents. The idea behind these studies is that if the adoptive children more closely resemble their biological parents with respect to a specific trait, then i,.t,,can be assumed that plays a major role. On the other hand, if the adoptive ...
Prémio Artigo Destaque SPN_2011 Cellular and Molecular
... between excitation and inhibition of synaptic signals is crucial for the functioning of neural circuits. An alteration of this balance can lead to pathological conditions such as epileptic states or abnormal cognitive processes. In normal brain functioning, the balance between excitation and inhibit ...
... between excitation and inhibition of synaptic signals is crucial for the functioning of neural circuits. An alteration of this balance can lead to pathological conditions such as epileptic states or abnormal cognitive processes. In normal brain functioning, the balance between excitation and inhibit ...
Introduction - Fullfrontalanatomy.com
... Surrounds the central canal and contains cell bodies of neurons and glial cells Groups of nuclei (sensory or motor) with specific functions Posterior gray horns contain somatic and visceral sensory nuclei; anterior gray horns contain somatic motor nuclei. Lateral gray horns contain visceral ...
... Surrounds the central canal and contains cell bodies of neurons and glial cells Groups of nuclei (sensory or motor) with specific functions Posterior gray horns contain somatic and visceral sensory nuclei; anterior gray horns contain somatic motor nuclei. Lateral gray horns contain visceral ...
Glial Cells: The Other Cells of the Nervous System
... receptors can cause ionic changes or activation of a secondary messenger system. In this context, changes in Ca++ levels in astrocytes have been studied extensively. Astrocyte membranes have voltage gated as well as ligand gated calcium channels. Elevation of K + concentration extracellularlly can d ...
... receptors can cause ionic changes or activation of a secondary messenger system. In this context, changes in Ca++ levels in astrocytes have been studied extensively. Astrocyte membranes have voltage gated as well as ligand gated calcium channels. Elevation of K + concentration extracellularlly can d ...
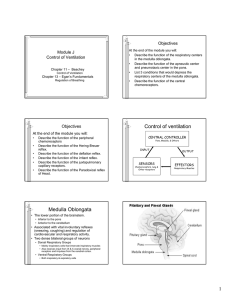
Control of ventilation Medulla Oblongata
... Depression of Medulla Oblongata • Reduced blood flow through the medulla as a result of increased pressure caused by cerebral edema or other intracerebral abnormality. • Acute poliomyelitis. • Drugs that depress CNS function. ...
... Depression of Medulla Oblongata • Reduced blood flow through the medulla as a result of increased pressure caused by cerebral edema or other intracerebral abnormality. • Acute poliomyelitis. • Drugs that depress CNS function. ...
PowerPoint Presentation - macomb
... Depression of Medulla Oblongata • Reduced blood flow through the medulla as a result of increased pressure caused by cerebral edema or other intracerebral abnormality. • Acute poliomyelitis. • Drugs that depress CNS function. ...
... Depression of Medulla Oblongata • Reduced blood flow through the medulla as a result of increased pressure caused by cerebral edema or other intracerebral abnormality. • Acute poliomyelitis. • Drugs that depress CNS function. ...
Food for Thought: Essential Fatty Acid Protects
... the postsynaptic proteins drebrin and PSD-95. While it is well known that dendrites are severely affected in AD and APP mice (Games et al., 1995; Lanz et al., 2003; Palop et al., 2003), the relationship of dendritic and postsynaptic alterations to depletion of DHA/PFAs is novel and has potential the ...
... the postsynaptic proteins drebrin and PSD-95. While it is well known that dendrites are severely affected in AD and APP mice (Games et al., 1995; Lanz et al., 2003; Palop et al., 2003), the relationship of dendritic and postsynaptic alterations to depletion of DHA/PFAs is novel and has potential the ...
Chapter 02: Neurons and Glia
... synthesized) Soma-independent (isolated axon still can transport ...
... synthesized) Soma-independent (isolated axon still can transport ...
1. A biological psychologist would be more likely to study
... 11. The brain research technique that involves monitoring the brain's usage of glucose is called (in abbreviated form) the: A) PET scan. B) CT scan. C) EEG. D) MRI. 12. The technique that uses magnetic fields and radio waves to produce computer images of structures within the brain is called: A) the ...
... 11. The brain research technique that involves monitoring the brain's usage of glucose is called (in abbreviated form) the: A) PET scan. B) CT scan. C) EEG. D) MRI. 12. The technique that uses magnetic fields and radio waves to produce computer images of structures within the brain is called: A) the ...
Nervous System
... autonomic control is movement of food through the digestive tract during sleep. The efferent portion of the autonomic system is divided into sympathetic and parasympathetic systems. The sympathetic nerves mobilize energy for the 'Fight or Flight' reaction during stress, causing increased blood press ...
... autonomic control is movement of food through the digestive tract during sleep. The efferent portion of the autonomic system is divided into sympathetic and parasympathetic systems. The sympathetic nerves mobilize energy for the 'Fight or Flight' reaction during stress, causing increased blood press ...
General design of the nervous system
... Peripheral nervous system connects the brain and spinal cord to the rest of the body. Autonomic somatic The somatic nervous system includes all nerves controlling the muscular system and external sensory receptors. External sense organs (including skin) are receptors. Muscle fibers and gland cells a ...
... Peripheral nervous system connects the brain and spinal cord to the rest of the body. Autonomic somatic The somatic nervous system includes all nerves controlling the muscular system and external sensory receptors. External sense organs (including skin) are receptors. Muscle fibers and gland cells a ...
Polarization theory of motivations, emotions and
... (Murik, 2002). Process of food consumption and the state of saturation were accompanied by repolarization processes in the mentioned structure. As our experiments showed (Fig. 1–2), activation of neurons is possible on the background of both depolarization and hyperpolarization processes, i.e. at th ...
... (Murik, 2002). Process of food consumption and the state of saturation were accompanied by repolarization processes in the mentioned structure. As our experiments showed (Fig. 1–2), activation of neurons is possible on the background of both depolarization and hyperpolarization processes, i.e. at th ...
Haemodynamic response
In haemodynamics, the body must respond to physical activities, external temperature, and other factors by homeostatically adjusting its blood flow to deliver nutrients such as oxygen and glucose to stressed tissues and allow them to function. Haemodynamic response (HR) allows the rapid delivery of blood to active neuronal tissues. Since higher processes in the brain occur almost constantly, cerebral blood flow is essential for the maintenance of neurons, astrocytes, and other cells of the brain.