Tinnitus: What You Need to Know
... right-sided foramen Spinosum (yellow circle) and normal left foramen Spinosum (yellow arrow). (B) -Coronal demonstrating small tympanic mass adjacent to the tympanic portion of the right facial nerve canal corresponding to the Persistent Stapedial Artery (red arrow). Angiogram (C) showing intratympa ...
... right-sided foramen Spinosum (yellow circle) and normal left foramen Spinosum (yellow arrow). (B) -Coronal demonstrating small tympanic mass adjacent to the tympanic portion of the right facial nerve canal corresponding to the Persistent Stapedial Artery (red arrow). Angiogram (C) showing intratympa ...
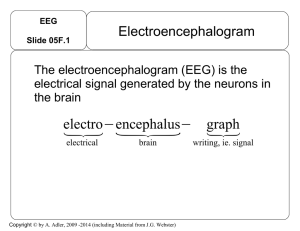
EEG - OCIBME
... (a) Different types of normal EEG waves. (b) Replacement of alpha rhythm by an asynchronous discharge when patient opens eyes. (c) Representative abnormal EEG waveforms in different types of epilepsy. Copyright © by A. Adler, 2009 -2014 (including Material from J.G. Webster) ...
... (a) Different types of normal EEG waves. (b) Replacement of alpha rhythm by an asynchronous discharge when patient opens eyes. (c) Representative abnormal EEG waveforms in different types of epilepsy. Copyright © by A. Adler, 2009 -2014 (including Material from J.G. Webster) ...
Chapter 8 Nervous System
... • Components of the extrapyramidal system provide subconscious control of skeletal muscle tone and coordinates learned movement patterns and other somatic motor activities. • They function in the control of voluntary movement and assist in the pattern and rhythm (especially for trunk and proximal li ...
... • Components of the extrapyramidal system provide subconscious control of skeletal muscle tone and coordinates learned movement patterns and other somatic motor activities. • They function in the control of voluntary movement and assist in the pattern and rhythm (especially for trunk and proximal li ...
Cardiovascular System, Respiratory System
... Cardiovascular system Embryology: development of the heart, the blood vessels and the foetal circulation. Anatomy: heart structure, course of the aorta and its branches, pulmonary arteries, systematics of the veins, portal circulation, lymphatic system. Histology: general structure of the blood vess ...
... Cardiovascular system Embryology: development of the heart, the blood vessels and the foetal circulation. Anatomy: heart structure, course of the aorta and its branches, pulmonary arteries, systematics of the veins, portal circulation, lymphatic system. Histology: general structure of the blood vess ...
GFR - gserianne.com
... Target Cell Activation By Hormones • Target cells must have specific receptors to be activated by hormones • Magnitude of target cell activation depends upon – Blood levels of the hormone • Rate of release from producing organ • Rate of degradation (target cells, kidney, liver) • Half-life – Relati ...
... Target Cell Activation By Hormones • Target cells must have specific receptors to be activated by hormones • Magnitude of target cell activation depends upon – Blood levels of the hormone • Rate of release from producing organ • Rate of degradation (target cells, kidney, liver) • Half-life – Relati ...
Neurology-Extrapyramidal Disorders
... Differentiate between Pyramidal vs. Extrapyramidal structures + functions Pyramid tract- Both the corticospinal and corticobulbar tracts. The corticospinal tract is a collection of axons that travel between the cerebral cortex of the brain and the SC. It contains mostly motor axons. It consists of 2 ...
... Differentiate between Pyramidal vs. Extrapyramidal structures + functions Pyramid tract- Both the corticospinal and corticobulbar tracts. The corticospinal tract is a collection of axons that travel between the cerebral cortex of the brain and the SC. It contains mostly motor axons. It consists of 2 ...
Cognitive impairment and associated loss in brain white
... inhibitors of the enzyme aceylcholinesterase, (Chen 2012) we also investigated brain neurometabolism with proton MR spectroscopy (1H-MRS) including choline (Cho)-containing compounds. In Alzheimer’s disease (AD), loss of cholinergic neurons results in increased levels of free Cho on 1H-MRS, and peop ...
... inhibitors of the enzyme aceylcholinesterase, (Chen 2012) we also investigated brain neurometabolism with proton MR spectroscopy (1H-MRS) including choline (Cho)-containing compounds. In Alzheimer’s disease (AD), loss of cholinergic neurons results in increased levels of free Cho on 1H-MRS, and peop ...
Magnetic resonance imaging indicators of blood
... Results: In nonhydrocephalic rats, water content decreased progressively from age 3 to 7 weeks. T1 and T2 and apparent diffusion coefficients did not exhibit parallel changes and there was no evidence of BBB permeability to tracers. The cerebral ventricles enlarged progressively in the weeks followi ...
... Results: In nonhydrocephalic rats, water content decreased progressively from age 3 to 7 weeks. T1 and T2 and apparent diffusion coefficients did not exhibit parallel changes and there was no evidence of BBB permeability to tracers. The cerebral ventricles enlarged progressively in the weeks followi ...
Make Life Visible
... Most of the world’s health care systems are focused on patients after they present with disease, and not before. While precision medicine uses personalized information to more effectively treat disease, the emerging field of precision health is situated to help assess disease risks, perform customiz ...
... Most of the world’s health care systems are focused on patients after they present with disease, and not before. While precision medicine uses personalized information to more effectively treat disease, the emerging field of precision health is situated to help assess disease risks, perform customiz ...
BRAIN SIMULATION PLATFORM
... behaviours. The Platform will make it possible to reconstruct and simulate models at different levels of description (abstract computational models, point neuron models, detailed cellular level models of neuronal circuitry, molecular level models of small areas of the brain, multiscale models that s ...
... behaviours. The Platform will make it possible to reconstruct and simulate models at different levels of description (abstract computational models, point neuron models, detailed cellular level models of neuronal circuitry, molecular level models of small areas of the brain, multiscale models that s ...
Description of Potential Projects for Research Semester, Fall 2014
... involvement of CGRP in migraine. The aim of this/the project is to determine the expression of Cgrp in CA77 cells after exposure to potential migraine provoking food compounds. The cell line used for research is thyroid C-cell line, CA77 that is derived from calcitonin secreting endocrine cells of ...
... involvement of CGRP in migraine. The aim of this/the project is to determine the expression of Cgrp in CA77 cells after exposure to potential migraine provoking food compounds. The cell line used for research is thyroid C-cell line, CA77 that is derived from calcitonin secreting endocrine cells of ...
Skeletal Muscle
... such as those which affect the gland secretion or smooth muscle of the cardiac system to contract. The main purpose of the visceral reflexes is to ensure that the involuntary process of the body are in full operating condition and can be tailored to react to a given situation. Heart rate, respirator ...
... such as those which affect the gland secretion or smooth muscle of the cardiac system to contract. The main purpose of the visceral reflexes is to ensure that the involuntary process of the body are in full operating condition and can be tailored to react to a given situation. Heart rate, respirator ...
Biology and Behavior note frame
... a. The state of a neuron when it is at _______________ and capable of _______________ an action potential b. The neuron is set and _______________ _______________ _______________ 4. All-or-None Principle a. The principle stating that ___________________________________________ ______________________ ...
... a. The state of a neuron when it is at _______________ and capable of _______________ an action potential b. The neuron is set and _______________ _______________ _______________ 4. All-or-None Principle a. The principle stating that ___________________________________________ ______________________ ...
This Week in The Journal
... schizophrenia patients, and neurons in mice carrying a deletion in the dysbindin gene have fewer dendritic spines. Hence, dysbindin might contribute to the spine pathology of schizophrenia, which manifests as a decrease in the number of dendritic spines. The development of dendritic spines is a dyna ...
... schizophrenia patients, and neurons in mice carrying a deletion in the dysbindin gene have fewer dendritic spines. Hence, dysbindin might contribute to the spine pathology of schizophrenia, which manifests as a decrease in the number of dendritic spines. The development of dendritic spines is a dyna ...
A plastic axonal hotspot
... is restricted to developmental and pathological conditions, or whether it is a normal physiological mechanism that could dynamically regulate excitability. The studies identify distinct mechanisms for modulating neuronal excitability — either displacement or extension of the AIS (Fig. 1 a, b). It wi ...
... is restricted to developmental and pathological conditions, or whether it is a normal physiological mechanism that could dynamically regulate excitability. The studies identify distinct mechanisms for modulating neuronal excitability — either displacement or extension of the AIS (Fig. 1 a, b). It wi ...
The Brain (Handout)
... cords join and finish in a single central stretch. These lines of ganglia are sometimes called the sympathetic trunks (used by the sympathetic nervous system). Not all ganglia are located in the sympathetic trunks. Some are not; and it is possible for a preganglionic fiber to go right through, makin ...
... cords join and finish in a single central stretch. These lines of ganglia are sometimes called the sympathetic trunks (used by the sympathetic nervous system). Not all ganglia are located in the sympathetic trunks. Some are not; and it is possible for a preganglionic fiber to go right through, makin ...
From circuits to behavior: a bridge too far?
... circuit. These computations depend on multiple circuits and mechanisms acting in combination, which may vary from region to region and species to species. In this respect, they resemble a set of instructions in a computer language, which does not map uniquely onto a specific set of transistors or ...
... circuit. These computations depend on multiple circuits and mechanisms acting in combination, which may vary from region to region and species to species. In this respect, they resemble a set of instructions in a computer language, which does not map uniquely onto a specific set of transistors or ...
Chapter 21: Attention
... What happens to attention under normal conditions? Assumption: Attention changes location prior to eye movement Wurtz, Goldberg, and Robinson Record neural activity from several brain regions Slide 14 Neuroscience: Exploring the Brain, 3rd Ed, Bear, Connors, and Paradiso Copyright © 2007 Lippincott ...
... What happens to attention under normal conditions? Assumption: Attention changes location prior to eye movement Wurtz, Goldberg, and Robinson Record neural activity from several brain regions Slide 14 Neuroscience: Exploring the Brain, 3rd Ed, Bear, Connors, and Paradiso Copyright © 2007 Lippincott ...
Lund University Publications
... Activation and recovery of breathing Within the rostral ventrolateral medullary reticular formation, the retrotrapezoid nucleus (RTN) contains propriobulbar neurons, which are suspected to express central respiratory chemoreceptors working as generators for breathing. To selecti ...
... Activation and recovery of breathing Within the rostral ventrolateral medullary reticular formation, the retrotrapezoid nucleus (RTN) contains propriobulbar neurons, which are suspected to express central respiratory chemoreceptors working as generators for breathing. To selecti ...
Modeling the Cardiovascular System using STELLA A module for
... capillaries are small ones called venules. These merge to make larger veins and so on. Veins typically have a greater diameter than corresponding arteries. Their walls are more flaccid so they do not contain pressure. After passing through arterioles and capillary beds, blood has little pressure any ...
... capillaries are small ones called venules. These merge to make larger veins and so on. Veins typically have a greater diameter than corresponding arteries. Their walls are more flaccid so they do not contain pressure. After passing through arterioles and capillary beds, blood has little pressure any ...
8.2 Structure of skeletal muscle
... a synapse - Neurons communicate with the cell through neurotransmitters, which are a chemical signal ...
... a synapse - Neurons communicate with the cell through neurotransmitters, which are a chemical signal ...
Haemodynamic response
In haemodynamics, the body must respond to physical activities, external temperature, and other factors by homeostatically adjusting its blood flow to deliver nutrients such as oxygen and glucose to stressed tissues and allow them to function. Haemodynamic response (HR) allows the rapid delivery of blood to active neuronal tissues. Since higher processes in the brain occur almost constantly, cerebral blood flow is essential for the maintenance of neurons, astrocytes, and other cells of the brain.