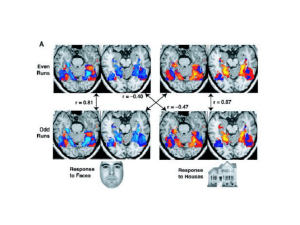
Chaper 1. A Brief History of Cognitive Neuroscience
... Chomsky: the complexity of language is built into the brain, runs on rules and principles (a grammar) that are universal. Simon & Newell: simulated cognitive processes. Hebb: neuropsychological theory of cell assemblies, which suggested that any set of neurons can learn anything. The field gradually ...
... Chomsky: the complexity of language is built into the brain, runs on rules and principles (a grammar) that are universal. Simon & Newell: simulated cognitive processes. Hebb: neuropsychological theory of cell assemblies, which suggested that any set of neurons can learn anything. The field gradually ...
brain development - EDUC111ChildGrowthDevelopment
... One factor in this increase in brain weight is the production of new synapses, which are the connections that form between neurons (brain cells). In the first few months of life, the number of synapses increases twenty times over. Daily experiences and stimulation drive the production of new synapse ...
... One factor in this increase in brain weight is the production of new synapses, which are the connections that form between neurons (brain cells). In the first few months of life, the number of synapses increases twenty times over. Daily experiences and stimulation drive the production of new synapse ...
ppt - IISER Pune
... Carries information from cerebral cortex to cerebellum Also controls a number of vital functions like breathing, ...
... Carries information from cerebral cortex to cerebellum Also controls a number of vital functions like breathing, ...
Smell - Brain Day Association of U of T
... We may be able to live without ice cream, but without a lobe, life just would not be the same! For example, if your occipital lobe is damaged you could be blind even though your eyes are in perfect condition! The brain is where our perception of the world around us comes together! ...
... We may be able to live without ice cream, but without a lobe, life just would not be the same! For example, if your occipital lobe is damaged you could be blind even though your eyes are in perfect condition! The brain is where our perception of the world around us comes together! ...
Brain - HMS - Harvard University
... Another study, led by neurophysiologist Vera Novak, an HMS associate professor of medicine and a neurophysiologist at Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center, identified a key mechanism that can lead to memory loss, depression, and other types of cognitive impairment in older adults with type 2 diabete ...
... Another study, led by neurophysiologist Vera Novak, an HMS associate professor of medicine and a neurophysiologist at Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center, identified a key mechanism that can lead to memory loss, depression, and other types of cognitive impairment in older adults with type 2 diabete ...
File
... • The central nervous system is the control center of the body. It includes the brain and spinal cord. • The thick column of nerve tissue that links the brain to most of the nerves is the spinal cord. • The brain controls most functions in the body. • The brain is located in the head and is protecte ...
... • The central nervous system is the control center of the body. It includes the brain and spinal cord. • The thick column of nerve tissue that links the brain to most of the nerves is the spinal cord. • The brain controls most functions in the body. • The brain is located in the head and is protecte ...
An Artificial Neural Network for Data Mining
... There is wide availability of huge amount of data and there is an imminent need for turning such data into useful information and knowledge. The information and knowledge gained can be used for applications ranging from market analysis, fraud detection, and customer retention, to production control ...
... There is wide availability of huge amount of data and there is an imminent need for turning such data into useful information and knowledge. The information and knowledge gained can be used for applications ranging from market analysis, fraud detection, and customer retention, to production control ...
There are about 3 million miles of axons in the human brain. The
... important for the rapid-eye movements of REM sleep (one of the 5 stages of sleep and usually makes up 90-120 minutes of an adult’s sleep) and may be important for turning REM sleep on and off. • Functions of the MIDBRAIN include controlling responses to sight, eye Movement, pupil dilation, hearing a ...
... important for the rapid-eye movements of REM sleep (one of the 5 stages of sleep and usually makes up 90-120 minutes of an adult’s sleep) and may be important for turning REM sleep on and off. • Functions of the MIDBRAIN include controlling responses to sight, eye Movement, pupil dilation, hearing a ...
Brain
... Species below the line have less brain for their body than average. Species on the line have an average amount of brain for their body size. ...
... Species below the line have less brain for their body than average. Species on the line have an average amount of brain for their body size. ...
Powerpoint version
... How do hormones signal cells? Steroid and thyroid hormones activate genes Diffuse freely into and out of cells Receptor proteins are in cytoplasm. Hormone binds and moves inside nucleus ...
... How do hormones signal cells? Steroid and thyroid hormones activate genes Diffuse freely into and out of cells Receptor proteins are in cytoplasm. Hormone binds and moves inside nucleus ...
Structure of the Nervous System
... reduces the net weight of the brain on the base of the skull, and acts to protect the brain from blows to the head. The brain is also protected by the relative impermeability of blood vessels that supply it. The supply of blood to the brain is a relatively closed system in which most substances cann ...
... reduces the net weight of the brain on the base of the skull, and acts to protect the brain from blows to the head. The brain is also protected by the relative impermeability of blood vessels that supply it. The supply of blood to the brain is a relatively closed system in which most substances cann ...
Biological Bases of Behavior - Mrs. Short`s AP Psychology Class
... – related to onset of lactation in new mothers – related to attachment/emotional bonds ...
... – related to onset of lactation in new mothers – related to attachment/emotional bonds ...
news and views - Cortical Plasticity
... information storage. To show this, he used a combination of analytical mathematics and computer simulations with the assumption that the cortical microcircuit can be viewed as an attractor network that operates at maximum information storage capacity. In symmetrically connected recurrent neural netw ...
... information storage. To show this, he used a combination of analytical mathematics and computer simulations with the assumption that the cortical microcircuit can be viewed as an attractor network that operates at maximum information storage capacity. In symmetrically connected recurrent neural netw ...
PowerPoint Presentation - Physiological Psychology
... forms of neurotransmitters are introduced. Recording Technique- Measures the activity of neurons. Recorder is inserted into axon. Electrode stimulates cell’s activity. Example-EEGelectroencephalogram. ...
... forms of neurotransmitters are introduced. Recording Technique- Measures the activity of neurons. Recorder is inserted into axon. Electrode stimulates cell’s activity. Example-EEGelectroencephalogram. ...
Slide 1
... Disease, Stage (e.g. cell, animal, individual, community), Discipline e.g. nanotechnology, clinical trials, community research, computational modeling, economic modeling, etc. Similar activities/levels may involve critical resource sharing ...
... Disease, Stage (e.g. cell, animal, individual, community), Discipline e.g. nanotechnology, clinical trials, community research, computational modeling, economic modeling, etc. Similar activities/levels may involve critical resource sharing ...
ppt - BIAC – Duke
... In this period of intense research in the neurosciences, nothing is more promising than functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) and positron emission tomography (PET) methods, which localize brain activities. These functional imaging methodologies map neurophysiological responses to cognitive, ...
... In this period of intense research in the neurosciences, nothing is more promising than functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) and positron emission tomography (PET) methods, which localize brain activities. These functional imaging methodologies map neurophysiological responses to cognitive, ...
2nd class Nervous System
... Paragraph 1: What are the parts of the Nervous system and how do they work? Paragraph 2: What parts of the body need the nervous system? Paragraph 3: What are problems of the nervous system? Paragraph 4: What are some of the ways to care for the nervous system? Also the crossword puzzle Control Cent ...
... Paragraph 1: What are the parts of the Nervous system and how do they work? Paragraph 2: What parts of the body need the nervous system? Paragraph 3: What are problems of the nervous system? Paragraph 4: What are some of the ways to care for the nervous system? Also the crossword puzzle Control Cent ...
Biopsychology
... Uinervtisy, it deosn't mttaer in waht oredr the ltteers in a wrod are, the olny iprmoatnt tihng is taht the frist and lsat ltteer be in the rghit pclae. The rset can be a taotl mses and you can sitll raed it wouthit porbelm. Tihs is bcuseae the huamn mnid deos not raed ervey lteter by istlef, but th ...
... Uinervtisy, it deosn't mttaer in waht oredr the ltteers in a wrod are, the olny iprmoatnt tihng is taht the frist and lsat ltteer be in the rghit pclae. The rset can be a taotl mses and you can sitll raed it wouthit porbelm. Tihs is bcuseae the huamn mnid deos not raed ervey lteter by istlef, but th ...
More Mind Bogglers!
... cells (neurons). Glial cells are the “support cells” of the nervous system; they perform a number of important jobs that help keep the nervous system running smoothly. Neurons are specialized to receive and transmit information. In fact, almost all functions of the nervous system are based on electr ...
... cells (neurons). Glial cells are the “support cells” of the nervous system; they perform a number of important jobs that help keep the nervous system running smoothly. Neurons are specialized to receive and transmit information. In fact, almost all functions of the nervous system are based on electr ...
How does the Teenage Brain Work? (Teacher Version)
... The more environmental input there is to guide that pruning the better. P20: “In adolescents given a medium or large reward, a centre in the brain called the ...
... The more environmental input there is to guide that pruning the better. P20: “In adolescents given a medium or large reward, a centre in the brain called the ...
Forebrain
... olfaction, and homeostasis. • Amygdala is especially important for attaching emotional significance to various stimuli perceived by the association cortex. In animals where both amygdalas have been ablated, behavior is very placid, tame, and nonaggressive. ...
... olfaction, and homeostasis. • Amygdala is especially important for attaching emotional significance to various stimuli perceived by the association cortex. In animals where both amygdalas have been ablated, behavior is very placid, tame, and nonaggressive. ...
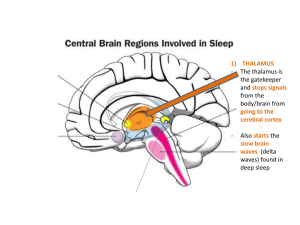
Sleep Brain Labelling
... - where the hormone melatonin is produced - Melatonin helps regulate the circadian clock - melatonin is stimulated by darkness ...
... - where the hormone melatonin is produced - Melatonin helps regulate the circadian clock - melatonin is stimulated by darkness ...
USC Brain Project Specific Aims
... non-maximal stimulus s2 so that it becomes larger than the previously largest stimulus s1, yet not switch activity to the corresponding element. In neural networks with loops - an internal state resists dependence on input: buildup of excitation and inhibition precludes the system's quick response t ...
... non-maximal stimulus s2 so that it becomes larger than the previously largest stimulus s1, yet not switch activity to the corresponding element. In neural networks with loops - an internal state resists dependence on input: buildup of excitation and inhibition precludes the system's quick response t ...
10 - Karmayog .org
... This is the state of unconsciousness that we go into once in 24 hours and it is brought about when all inputs through our five senses are cut out or brought to a minimum. It is an important state for it helps in repair and renew body functions for the tasks of the next day. You will spend about a th ...
... This is the state of unconsciousness that we go into once in 24 hours and it is brought about when all inputs through our five senses are cut out or brought to a minimum. It is an important state for it helps in repair and renew body functions for the tasks of the next day. You will spend about a th ...
How your Brain Works - Muncy School District
... Your volume of synapses is constantly changing, too, and some are stronger than others. Weak synapses become stronger through practice and learning. No matter how many synapses a neuron has, it still has the potential to grow more. Scientific proof that “practice makes perfect”! The brain is constan ...
... Your volume of synapses is constantly changing, too, and some are stronger than others. Weak synapses become stronger through practice and learning. No matter how many synapses a neuron has, it still has the potential to grow more. Scientific proof that “practice makes perfect”! The brain is constan ...