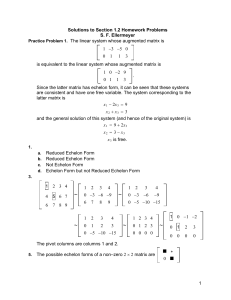
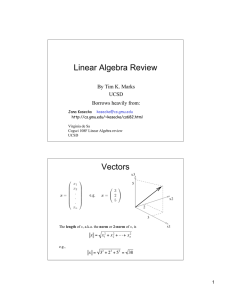
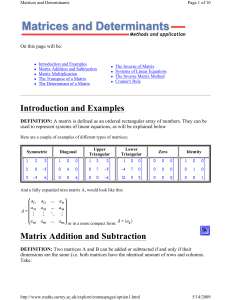
Methods of Mathematical Physics – Graphs of solutions to wk 6 HW
... dy Recall the problem we did in class: p qy 0 can be rewritten: ...
... dy Recall the problem we did in class: p qy 0 can be rewritten: ...
Chapter 2 Introduction to Finite Field
... Definition 2.1 (Finite field and Order of finite field). A finite field is a field F which has a finite number of elements, this number being called the order of the field, denoted by |F |. Theorem 2.1 (Subfield Isomorphic to Zp ). Every finite field has the order of a power of a prime number p and ...
... Definition 2.1 (Finite field and Order of finite field). A finite field is a field F which has a finite number of elements, this number being called the order of the field, denoted by |F |. Theorem 2.1 (Subfield Isomorphic to Zp ). Every finite field has the order of a power of a prime number p and ...
.pdf
... (4) The group of integers modulo n under +. These are the sets of equivalence classes of integers, where a ∼ b if and only if a−b is divisible by n. This group is denoted Z/nZ. (5) The set of 2 × 2 matrices with entries in Z/2Z (i.e. “even” and “odd”) with the usual rules of multiplication and addit ...
... (4) The group of integers modulo n under +. These are the sets of equivalence classes of integers, where a ∼ b if and only if a−b is divisible by n. This group is denoted Z/nZ. (5) The set of 2 × 2 matrices with entries in Z/2Z (i.e. “even” and “odd”) with the usual rules of multiplication and addit ...
Section 4.2 - Gordon State College
... A linear transformation T: Rn → Rm is said to be one-to-one if T maps distinct vectors (points) in Rn to distinct vectors (points) in Rm. ...
... A linear transformation T: Rn → Rm is said to be one-to-one if T maps distinct vectors (points) in Rn to distinct vectors (points) in Rm. ...






![WHEN IS F[x,y] - American Mathematical Society](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/017823178_1-6801a801f234da9ec7275765b0565209-300x300.png)