ENDOCRINE SYSTEM ENDOCRINE SYSTEM ENDOCRINE SYSTEM
... Interface of Endocrine & Nervous Systems • Nervous system induces – nor- & epinephrine release • which stimulate ...
... Interface of Endocrine & Nervous Systems • Nervous system induces – nor- & epinephrine release • which stimulate ...
(1125) Catalytic Dehydration Reactions for Green Synthesis of
... Phosphoric acid monoesters are some of the most important substances in materials chemistry, medicinal chemistry, and so on. Many phosphoric acid monoesters have been synthesized on an industrial scale and are used as necessities in our daily life [13, 14]. From the perspective of green chemistry, t ...
... Phosphoric acid monoesters are some of the most important substances in materials chemistry, medicinal chemistry, and so on. Many phosphoric acid monoesters have been synthesized on an industrial scale and are used as necessities in our daily life [13, 14]. From the perspective of green chemistry, t ...
Spring 2014
... (8 pts) If it takes 4.184 J of energy to raise the temperature of exactly one gram of water one degree Celcius, how many photons from this LED are needed to raise the temperature of 250 g of water (about one cup) one degree Celcius? ...
... (8 pts) If it takes 4.184 J of energy to raise the temperature of exactly one gram of water one degree Celcius, how many photons from this LED are needed to raise the temperature of 250 g of water (about one cup) one degree Celcius? ...
Digestion of starch - Pearson Schools and FE Colleges
... The reduced level of oxygen entering the blood makes a person short of breath and means that the heart must work harder to deliver oxygen to the cells for respiration to take place. Goblet cells in the lungs manufacture mucus. The mucus traps dust and bacteria. Microscopic hairs called cilia then wa ...
... The reduced level of oxygen entering the blood makes a person short of breath and means that the heart must work harder to deliver oxygen to the cells for respiration to take place. Goblet cells in the lungs manufacture mucus. The mucus traps dust and bacteria. Microscopic hairs called cilia then wa ...
Electron transfer from aromatic amino acids to guanine and adenine
... passing from one conformation to another. ET rates Using the calculated values of DE and V , and the reorganization energy l = 1 eV, we estimated the rate of electron transfer N+ + X → N + X+ in the dimers. Fig. 6 shows the ET rates faster than 106 s-1 . We remind that eqn (2) can be applied only to ...
... passing from one conformation to another. ET rates Using the calculated values of DE and V , and the reorganization energy l = 1 eV, we estimated the rate of electron transfer N+ + X → N + X+ in the dimers. Fig. 6 shows the ET rates faster than 106 s-1 . We remind that eqn (2) can be applied only to ...
Oxidative Phosphorylation accompanying Oxidation of
... phate/min. at 380. Ketone-body production was estimated by the method of Bird & Symons (1959), with the subsequent modifications by Bird & Weidemann (1964), and fatty acid disappearance was estimated by steam-distilla. tion and titration under C02-free conditions as described by Pennington (1952). M ...
... phate/min. at 380. Ketone-body production was estimated by the method of Bird & Symons (1959), with the subsequent modifications by Bird & Weidemann (1964), and fatty acid disappearance was estimated by steam-distilla. tion and titration under C02-free conditions as described by Pennington (1952). M ...
Beijerinckia derxii releases plant growth regulato
... ethylene itself, through different biochemical mechanisms (McKeon et al. 1995), including auto-inhibition. Exogenous ethylene is also effective in stimulating plant development (Taiz and Zeiger 1998). Ethylene and IAA may act together to stimulate the development of the cortical cell layer (Grichko ...
... ethylene itself, through different biochemical mechanisms (McKeon et al. 1995), including auto-inhibition. Exogenous ethylene is also effective in stimulating plant development (Taiz and Zeiger 1998). Ethylene and IAA may act together to stimulate the development of the cortical cell layer (Grichko ...
Department of Chemistry University of Manitoba Undergraduate
... and to WileyPlus/Catalyst online assignment system, and (2) a copy of the Wiley Canada customized “Course Material for CHEM 0900 Preparatory Chemistry” document (provided separately to students). Subscription to Late Nite Labs REACTOR® system: This system is an online Laboratory Simulation Website ( ...
... and to WileyPlus/Catalyst online assignment system, and (2) a copy of the Wiley Canada customized “Course Material for CHEM 0900 Preparatory Chemistry” document (provided separately to students). Subscription to Late Nite Labs REACTOR® system: This system is an online Laboratory Simulation Website ( ...
Final Exam Practice Questions for General Chemistry NOTICE TO
... These exact questions will not appear on your exam. These example questions are provided to you help you review the material and become familiar with the TYPES of questions that are generally presented on the final exam. This is not a complete list of the ideas, concepts, principles, or questions co ...
... These exact questions will not appear on your exam. These example questions are provided to you help you review the material and become familiar with the TYPES of questions that are generally presented on the final exam. This is not a complete list of the ideas, concepts, principles, or questions co ...
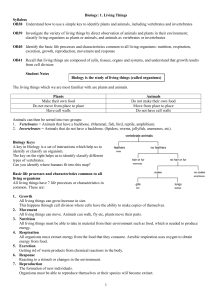
Biology 1 to 4 - Dominican
... Basic life processes and characteristics common to all living organisms All living things have 7 life processes or characteristics in common. These are: 1. Growth All living things can grow/increase in size. This happens through cell division where cells have the ability to make copies of themselves ...
... Basic life processes and characteristics common to all living organisms All living things have 7 life processes or characteristics in common. These are: 1. Growth All living things can grow/increase in size. This happens through cell division where cells have the ability to make copies of themselves ...
Lactic Acid Bacteria and Lactic Fermentations
... Presence of other sources of pyruvate, most notably CITRATE. Pyruvate is a major source of carbon for building cell structures. If it is plentiful, then more of it can be diverted into side reactions producing flavor compounds such as diacetyl. Citrate is a source of pyruvate in milk (milk contains ...
... Presence of other sources of pyruvate, most notably CITRATE. Pyruvate is a major source of carbon for building cell structures. If it is plentiful, then more of it can be diverted into side reactions producing flavor compounds such as diacetyl. Citrate is a source of pyruvate in milk (milk contains ...
Chapter 4 Reactions in Aqueous Solutions
... – A common reaction: active metal replaces (displaces) a metal ion from a solution Mg(s) + CuCl2(aq) Cu(s) + MgCl2(aq) ...
... – A common reaction: active metal replaces (displaces) a metal ion from a solution Mg(s) + CuCl2(aq) Cu(s) + MgCl2(aq) ...
7A REVIEW Circulatory, Respiratory & Excretory Systems
... 10. During gas exchange where does the oxygen and carbon dioxide go? • Oxygen diffuses into capillaries while carbon dioxide diffuses out of capillaries into the alveoli. 11. The ______ is a long straight tube that carries air from the back of the throat to the lungs. ...
... 10. During gas exchange where does the oxygen and carbon dioxide go? • Oxygen diffuses into capillaries while carbon dioxide diffuses out of capillaries into the alveoli. 11. The ______ is a long straight tube that carries air from the back of the throat to the lungs. ...
Sample 112 Final
... Which of the following shows the greatest increase in disorder? a) NH4Br(s) ! NH3(g) + HBr(g) b) C2H4(g) + HBr(g) ! C2H5Br(g) c) CO2(s) ! CO2 (g) d) C(s) + ½ O2(g) ! CO(g) e) C(graphite) + 2H2(g) !CH4(g) ...
... Which of the following shows the greatest increase in disorder? a) NH4Br(s) ! NH3(g) + HBr(g) b) C2H4(g) + HBr(g) ! C2H5Br(g) c) CO2(s) ! CO2 (g) d) C(s) + ½ O2(g) ! CO(g) e) C(graphite) + 2H2(g) !CH4(g) ...
E2 and E11 Acid Deposition Past Paper Questions
... (1) neutralization reaction produces an ammonium salt: 2 NH3 + H2SO4 (NH4)2SO4 OR 2 NH3 + H2SO3 (NH4)2SO3 OR 2 NH3 + HNO3 NH4NO3 ...
... (1) neutralization reaction produces an ammonium salt: 2 NH3 + H2SO4 (NH4)2SO4 OR 2 NH3 + H2SO3 (NH4)2SO3 OR 2 NH3 + HNO3 NH4NO3 ...
Unit 1: Sig. Figs, Compounds, Elements, Homo/Hetero mixtures
... 1. What is the name of Dalton’s model of the atom? a. Plum pudding model b. Quantum mechanical model c. Nuclear model d. Solid sphere model 2. What is the name of J.J. Thompson’s model of the atom? a. Plum pudding model b. Quantum mechanical model c. Nuclear model d. Solid sphere model 3. What is th ...
... 1. What is the name of Dalton’s model of the atom? a. Plum pudding model b. Quantum mechanical model c. Nuclear model d. Solid sphere model 2. What is the name of J.J. Thompson’s model of the atom? a. Plum pudding model b. Quantum mechanical model c. Nuclear model d. Solid sphere model 3. What is th ...
Surprising variety in energy metabolism within Trypanosomatidae
... A) Aerobic energy metabolism is defined as the complete oxidation of substrates to carbon dioxide and water. The majority of ATP in aerobic energy metabolism is produced via the mitochondrial respiratory chain and oxidative phosphorylation. Oxygen acts as the final electron acceptor to re-oxidise th ...
... A) Aerobic energy metabolism is defined as the complete oxidation of substrates to carbon dioxide and water. The majority of ATP in aerobic energy metabolism is produced via the mitochondrial respiratory chain and oxidative phosphorylation. Oxygen acts as the final electron acceptor to re-oxidise th ...
Practice problem chap3 1. The atomic mass of 35Cl (75.53%) and
... 4. Chemical analysis shows the composition of a compound containing carbon and hydrogen, to be 80.00% carbon and 20% hydrogen and the molar mass is 30 g. What is its molecular formula? (a) CH (b) C2H4 (c) C2H6 (d) C6H12 (e) C10H22 5. Balance the equation a) N2O5 N2O4 +O2 f) P4O10 + H2O H3PO4 h) ...
... 4. Chemical analysis shows the composition of a compound containing carbon and hydrogen, to be 80.00% carbon and 20% hydrogen and the molar mass is 30 g. What is its molecular formula? (a) CH (b) C2H4 (c) C2H6 (d) C6H12 (e) C10H22 5. Balance the equation a) N2O5 N2O4 +O2 f) P4O10 + H2O H3PO4 h) ...
Joint Symposium of Waseda University and Peking University
... electrode and covered it with an organic (or an aqueous) solution. In this manner, a conventional three-electrode potentiostat can be used to study ionizable drugs transfer process at a liquid /liquid interface. Physicochemical parameters such as the formal transfer potential, the Gibbs energy of tr ...
... electrode and covered it with an organic (or an aqueous) solution. In this manner, a conventional three-electrode potentiostat can be used to study ionizable drugs transfer process at a liquid /liquid interface. Physicochemical parameters such as the formal transfer potential, the Gibbs energy of tr ...
Evolution & organisation of metabolic Pathways
... Kooijman, S. A. L. M. and Segel, L. A. (2004) How growth affects the fate of cellular substrates. Bull. Math. Biol. (to appear) ...
... Kooijman, S. A. L. M. and Segel, L. A. (2004) How growth affects the fate of cellular substrates. Bull. Math. Biol. (to appear) ...
Beer
... • Generally, the barley spends about 40 hours in tanks of fresh, clean water, with three intervals during which the water is allowed to drain. • Draining is done to remove dissolved carbon dioxide and to reintroduce oxygen-rich water. • Steeping is complete when the white tips of the rootlets emerge ...
... • Generally, the barley spends about 40 hours in tanks of fresh, clean water, with three intervals during which the water is allowed to drain. • Draining is done to remove dissolved carbon dioxide and to reintroduce oxygen-rich water. • Steeping is complete when the white tips of the rootlets emerge ...
LIQUIDS
... an element into smaller and smaller pieces you would eventually come to a piece that could not be divided any further - a single ATOM of the element. Atoms are therefore very small. We can see this if we dilute a solution of potassium manganate(VI) many times. It is still coloured even when it is ve ...
... an element into smaller and smaller pieces you would eventually come to a piece that could not be divided any further - a single ATOM of the element. Atoms are therefore very small. We can see this if we dilute a solution of potassium manganate(VI) many times. It is still coloured even when it is ve ...
Biochemistry
_and_Carl_Ferdinand_Cori.jpg?width=300)
Biochemistry, sometimes called biological chemistry, is the study of chemical processes within and relating to living organisms. By controlling information flow through biochemical signaling and the flow of chemical energy through metabolism, biochemical processes give rise to the complexity of life. Over the last decades of the 20th century, biochemistry has become so successful at explaining living processes that now almost all areas of the life sciences from botany to medicine to genetics are engaged in biochemical research. Today, the main focus of pure biochemistry is in understanding how biological molecules give rise to the processes that occur within living cells, which in turn relates greatly to the study and understanding of whole organisms.Biochemistry is closely related to molecular biology, the study of the molecular mechanisms by which genetic information encoded in DNA is able to result in the processes of life. Depending on the exact definition of the terms used, molecular biology can be thought of as a branch of biochemistry, or biochemistry as a tool with which to investigate and study molecular biology.Much of biochemistry deals with the structures, functions and interactions of biological macromolecules, such as proteins, nucleic acids, carbohydrates and lipids, which provide the structure of cells and perform many of the functions associated with life. The chemistry of the cell also depends on the reactions of smaller molecules and ions. These can be inorganic, for example water and metal ions, or organic, for example the amino acids which are used to synthesize proteins. The mechanisms by which cells harness energy from their environment via chemical reactions are known as metabolism. The findings of biochemistry are applied primarily in medicine, nutrition, and agriculture. In medicine, biochemists investigate the causes and cures of disease. In nutrition, they study how to maintain health and study the effects of nutritional deficiencies. In agriculture, biochemists investigate soil and fertilizers, and try to discover ways to improve crop cultivation, crop storage and pest control.