the science of weight loss - Beyond
... • Used for centuries now, the Bushmen of South Africa, have been eating the Hoodia plant to not only ward off thirst but to curb appetites and eliminate hunger during long hunting trips in the wilderness. • The active compound known as P57, a steroidal glycoside, which sends a signal to the BRAIN -h ...
... • Used for centuries now, the Bushmen of South Africa, have been eating the Hoodia plant to not only ward off thirst but to curb appetites and eliminate hunger during long hunting trips in the wilderness. • The active compound known as P57, a steroidal glycoside, which sends a signal to the BRAIN -h ...
tRNA aminoacylation by arginyltRNA synthetase: induced
... linking the appropriate amino acid to the 3¢ end of the correct tRNA. In most organisms, there are 20 distinct aaRSs, each one of them being responsible for aminoacylating its cognate tRNA(s) with a unique amino acid in a two-step catalytic reaction. The ®rst step, which requires ATP and Mg2+ ions, ...
... linking the appropriate amino acid to the 3¢ end of the correct tRNA. In most organisms, there are 20 distinct aaRSs, each one of them being responsible for aminoacylating its cognate tRNA(s) with a unique amino acid in a two-step catalytic reaction. The ®rst step, which requires ATP and Mg2+ ions, ...
Catalysis
... 4. Enzyme catalysed reactions are much more sensitive to catalytic poisons such as HCN, H2S, CS2 etc. The inhibitors interact with the active functional groups present on the enzyme surface and often reduce or completely destroy the catalytic activity of the enzymes 5. The activity of certain enzym ...
... 4. Enzyme catalysed reactions are much more sensitive to catalytic poisons such as HCN, H2S, CS2 etc. The inhibitors interact with the active functional groups present on the enzyme surface and often reduce or completely destroy the catalytic activity of the enzymes 5. The activity of certain enzym ...
22. pyruvate oxidation and citric acid cycle
... been given in honour of its most illustrious proponent, Sir Hans A. Krebs, who first postulated it in 1937 and the cycle has since then been slightly modified in a form we know today. However, a third name tricarboxylic acid cycle (TCA) was given to it some years after Krebs postulated the cycle bec ...
... been given in honour of its most illustrious proponent, Sir Hans A. Krebs, who first postulated it in 1937 and the cycle has since then been slightly modified in a form we know today. However, a third name tricarboxylic acid cycle (TCA) was given to it some years after Krebs postulated the cycle bec ...
Coupling of Silicon, Carbon and Nitrogen Metabolisms in Marine
... orthosilicic acid (Si(OH)4) which then polymerizes inside the cell within a silicon-deposition vesicle (SDV). Heterogeneous nucleation and growth via autopolymerization may be subsequently induced by the surface of the SDV to forrn amorphous biogenic silica (opal). Orthosilicic acid uptake as weil a ...
... orthosilicic acid (Si(OH)4) which then polymerizes inside the cell within a silicon-deposition vesicle (SDV). Heterogeneous nucleation and growth via autopolymerization may be subsequently induced by the surface of the SDV to forrn amorphous biogenic silica (opal). Orthosilicic acid uptake as weil a ...
Pinar Tulay membrane_17
... – BUT the proteins are so large that they sometimes make up half the mass of a membrane. • Like lipids, some membrane proteins move relatively freely within the phospholipid bilayer. • The proteins in a membrane may be peripheral proteins or ...
... – BUT the proteins are so large that they sometimes make up half the mass of a membrane. • Like lipids, some membrane proteins move relatively freely within the phospholipid bilayer. • The proteins in a membrane may be peripheral proteins or ...
Organization and Synthesis of DNA
... Cross-shaped structures arise from palindromic structures, including interrupted palindromes like this example These are less stable than regular duplexes but they are common, and they do create recognition sites for DNA-binding proteins, including restriction enzymes ...
... Cross-shaped structures arise from palindromic structures, including interrupted palindromes like this example These are less stable than regular duplexes but they are common, and they do create recognition sites for DNA-binding proteins, including restriction enzymes ...
Isolation of a New Member of the $100 Protein Family: Amino Acid
... © The Rockefeller University Press, 0021-9525/89/02/569/10 $2.00 The Journal of Cell Biology, Volume 108, February 1989 569-578 ...
... © The Rockefeller University Press, 0021-9525/89/02/569/10 $2.00 The Journal of Cell Biology, Volume 108, February 1989 569-578 ...
Cholesterol Synthesis Regulation of cholesterol synthesis pathway
... fatty acids in blood stream cause gall bladder to contract releasing bile liver ...
... fatty acids in blood stream cause gall bladder to contract releasing bile liver ...
- Gondwana University, Gadchiroli
... 7)determination of zinc by complexometric titration with EDTA 8) Determination of total hardness of water (permanent and temporary) by EDTA ...
... 7)determination of zinc by complexometric titration with EDTA 8) Determination of total hardness of water (permanent and temporary) by EDTA ...
AutoMotif server: prediction of single residue post-translational
... By default the AMS identifies PTM sites of 12 types in a query protein. Users can limit the search by choosing the particular type of PTM from the drop-down list on the server’s main page (like a phosphorylation in general or by specific protein kinase). Users can also submit their own list of posit ...
... By default the AMS identifies PTM sites of 12 types in a query protein. Users can limit the search by choosing the particular type of PTM from the drop-down list on the server’s main page (like a phosphorylation in general or by specific protein kinase). Users can also submit their own list of posit ...
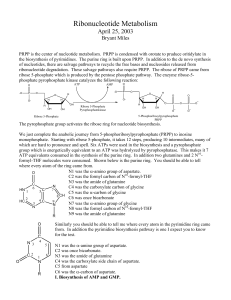
Ribonucleotide Metabolism
... Your typical cell has 5 to 10 times more RNA than DNA. Ribonucleotides have multiple metabolic roles. Deoxyribonucleotides are used for only one role, the storage of genetic information as DNA. Most of the energy expended on nucleotide biosynthesis goes into the formation of the ribonucleotides, a r ...
... Your typical cell has 5 to 10 times more RNA than DNA. Ribonucleotides have multiple metabolic roles. Deoxyribonucleotides are used for only one role, the storage of genetic information as DNA. Most of the energy expended on nucleotide biosynthesis goes into the formation of the ribonucleotides, a r ...
PDF
... demonstrated that Ae2-L-Lys-o-Ala-D-iactate and other esters and thioesters can interact with o,opeptidases and transpeptidases [12,14], which suggests that the modified precursor, once incorporated into linear peptidoglycan, could take part in the final stage of peptidoglycan synthesis. As this rea ...
... demonstrated that Ae2-L-Lys-o-Ala-D-iactate and other esters and thioesters can interact with o,opeptidases and transpeptidases [12,14], which suggests that the modified precursor, once incorporated into linear peptidoglycan, could take part in the final stage of peptidoglycan synthesis. As this rea ...
... iii) Indicate the location of the new chiral centers on the pyranose ring of glucose, what is this new center called? (2 pts) OH OH iv) Sketch, or describe, any one of the following carbohydrates (4 pts) CH OH CH OH a) lactose c) glycogen glucose galactose b) sucrose d) cellulose Choice B: In what w ...
6-Catabolism of Pyrimidine Nucleotides
... The pyrimidine ring can be completely degraded in humans. ...
... The pyrimidine ring can be completely degraded in humans. ...
Support material for lesson planning – AS content
... This information can also be used in the context of teaching the Chemistry A A Level specification from 2015 (H432). Note that the timings are suggested only, and that individual centres should always plan their schemes of work according to their individual needs. Actual teaching times for topics wi ...
... This information can also be used in the context of teaching the Chemistry A A Level specification from 2015 (H432). Note that the timings are suggested only, and that individual centres should always plan their schemes of work according to their individual needs. Actual teaching times for topics wi ...
Chemistry Revision Checklist F4 2017 (inc F3)
... Describe the concept of homologous series as a ‘family’ of similar compounds with similar chemical properties due to the presence of the same functional group Describe the general characteristics of an homologous series Recall that the compounds in a homologous series have the same general formula D ...
... Describe the concept of homologous series as a ‘family’ of similar compounds with similar chemical properties due to the presence of the same functional group Describe the general characteristics of an homologous series Recall that the compounds in a homologous series have the same general formula D ...
Lecture 3 – Secondary Structure - LCQB
... toward tertiary structure prediction • PSSP algorithms historically rely on amino acid preferences for certain types of secondary structure to infer general rules • The predictions can be refined by the use of multiple sequence alignments or some 3D-structural knowledge ...
... toward tertiary structure prediction • PSSP algorithms historically rely on amino acid preferences for certain types of secondary structure to infer general rules • The predictions can be refined by the use of multiple sequence alignments or some 3D-structural knowledge ...
Cloning, Functional Characterization and Site
... 2004). L-phenylalanine is catalyzed by PAL to form transcinnamic acid, which is further converted to p-coumaric acid by C4H. p-Coumaric acid is then activated by a member of the 4CL family (4CL; EC 6.2.1.12) into p-coumaroyl CoA. CoA-ester intermediate is subsequently hydroxylated by C2’H into umbel ...
... 2004). L-phenylalanine is catalyzed by PAL to form transcinnamic acid, which is further converted to p-coumaric acid by C4H. p-Coumaric acid is then activated by a member of the 4CL family (4CL; EC 6.2.1.12) into p-coumaroyl CoA. CoA-ester intermediate is subsequently hydroxylated by C2’H into umbel ...
Project 1: Infrared Spectra of Volcanic Plumes
... Schrödinger equation. The first is that if we are interested in the electron density of a molecule (which tells about bonding and potential reactive sites, among other things), then we can consider that the nuclei are fixed. This assumption is called the Born-Oppenheimer approximation, and it works ...
... Schrödinger equation. The first is that if we are interested in the electron density of a molecule (which tells about bonding and potential reactive sites, among other things), then we can consider that the nuclei are fixed. This assumption is called the Born-Oppenheimer approximation, and it works ...
Chemical Bonding
... P2, you can assume that third period diatomics form valence molecular orbitals similar to second period diatomics but with n=3) and the following heteronuclear diatomic species, CO, NO and BN (assume the same energy level diagram as Be2 to N2). Determine the bond order of each species. Indicate any ...
... P2, you can assume that third period diatomics form valence molecular orbitals similar to second period diatomics but with n=3) and the following heteronuclear diatomic species, CO, NO and BN (assume the same energy level diagram as Be2 to N2). Determine the bond order of each species. Indicate any ...
Immunophilins and Parvulins. Superfamily of
... Immunophilins are defined as receptors for immunosuppressive drugs including cyclosporin A, FK506, and rapamycin. The cyclosporin A receptors are referred to as cyclophilins (CYPs) and FK506- and rapamycin-binding proteins are abbreviated as FKBPs. These two groups of proteins (collectively called i ...
... Immunophilins are defined as receptors for immunosuppressive drugs including cyclosporin A, FK506, and rapamycin. The cyclosporin A receptors are referred to as cyclophilins (CYPs) and FK506- and rapamycin-binding proteins are abbreviated as FKBPs. These two groups of proteins (collectively called i ...
invisible forms
... solu3on NaCl 20% + Na-‐Acetate Buffer 1M + H2O) in 2 wells of the crystallisa3on plate (according to the volumes of each solu3on given in the table above). Pipeie 2 μl of iysozyme solu3on ( 40mg/ ...
... solu3on NaCl 20% + Na-‐Acetate Buffer 1M + H2O) in 2 wells of the crystallisa3on plate (according to the volumes of each solu3on given in the table above). Pipeie 2 μl of iysozyme solu3on ( 40mg/ ...
Biochemistry
_and_Carl_Ferdinand_Cori.jpg?width=300)
Biochemistry, sometimes called biological chemistry, is the study of chemical processes within and relating to living organisms. By controlling information flow through biochemical signaling and the flow of chemical energy through metabolism, biochemical processes give rise to the complexity of life. Over the last decades of the 20th century, biochemistry has become so successful at explaining living processes that now almost all areas of the life sciences from botany to medicine to genetics are engaged in biochemical research. Today, the main focus of pure biochemistry is in understanding how biological molecules give rise to the processes that occur within living cells, which in turn relates greatly to the study and understanding of whole organisms.Biochemistry is closely related to molecular biology, the study of the molecular mechanisms by which genetic information encoded in DNA is able to result in the processes of life. Depending on the exact definition of the terms used, molecular biology can be thought of as a branch of biochemistry, or biochemistry as a tool with which to investigate and study molecular biology.Much of biochemistry deals with the structures, functions and interactions of biological macromolecules, such as proteins, nucleic acids, carbohydrates and lipids, which provide the structure of cells and perform many of the functions associated with life. The chemistry of the cell also depends on the reactions of smaller molecules and ions. These can be inorganic, for example water and metal ions, or organic, for example the amino acids which are used to synthesize proteins. The mechanisms by which cells harness energy from their environment via chemical reactions are known as metabolism. The findings of biochemistry are applied primarily in medicine, nutrition, and agriculture. In medicine, biochemists investigate the causes and cures of disease. In nutrition, they study how to maintain health and study the effects of nutritional deficiencies. In agriculture, biochemists investigate soil and fertilizers, and try to discover ways to improve crop cultivation, crop storage and pest control.