Seconds Before the Big One: Progress in Earthquake Alarms
... magnitude 5.0 earthquakes a mile or two of the fault plane ruptures; humans can easily feel movement, but modern buildings can withstand it. At magnitude 8.0 the rupture propagates for hundreds of miles across the fault plane, and the tear can extend up to the surface. It will rip a building in two. ...
... magnitude 5.0 earthquakes a mile or two of the fault plane ruptures; humans can easily feel movement, but modern buildings can withstand it. At magnitude 8.0 the rupture propagates for hundreds of miles across the fault plane, and the tear can extend up to the surface. It will rip a building in two. ...
File
... Locating an Earthquake Distance to an Earthquake – The earthquake could have occurred anywhere on a circle around the seismic station. – The radius of the circle is equal to the epicentral ...
... Locating an Earthquake Distance to an Earthquake – The earthquake could have occurred anywhere on a circle around the seismic station. – The radius of the circle is equal to the epicentral ...
Earthquake Revision - Priory Ruskin Academy
... Where do earthquakes occur? Earthquakes occur along faults, which are large cracks in the earth's crust. Most of these are associated with the larger plate boundaries. Usually on or around Plate boundaries. What causes earthquakes? They are caused by sudden jerking movements of the fault, either lat ...
... Where do earthquakes occur? Earthquakes occur along faults, which are large cracks in the earth's crust. Most of these are associated with the larger plate boundaries. Usually on or around Plate boundaries. What causes earthquakes? They are caused by sudden jerking movements of the fault, either lat ...
More Ohio Earthquakes Linked to Fracking
... wastewater injection wells that have spawned a huge uptick in earthquakes across the central and eastern U.S. in recent years. Those wells dispose of the wastewater resulting from what is called “enhanced ...
... wastewater injection wells that have spawned a huge uptick in earthquakes across the central and eastern U.S. in recent years. Those wells dispose of the wastewater resulting from what is called “enhanced ...
NAME - Thomas C. Cario Middle School
... 10.) What is the name of the spot on the Earth’s surface directly above where the earthquake takes place? Epicenter 11.) How many seismograph stations are needed to locate an epicenter? 3 12.) What information is needed in order to use a graph to find out how far away an earthquake is from a seismo ...
... 10.) What is the name of the spot on the Earth’s surface directly above where the earthquake takes place? Epicenter 11.) How many seismograph stations are needed to locate an epicenter? 3 12.) What information is needed in order to use a graph to find out how far away an earthquake is from a seismo ...
8.1 / 8.2 Fun Sheet NAME 8.1 What is an Earthquake? Earthquakes
... - The point on Earth’s surface directly above the Earthquake is the - Large cracks in Earth’s crust are called , and earthquakes occur along them when occurs Cause of Earthquakes - In the 1906 San Francisco quake, the Earth moved meters or about feet compared to the land on the other side of the fau ...
... - The point on Earth’s surface directly above the Earthquake is the - Large cracks in Earth’s crust are called , and earthquakes occur along them when occurs Cause of Earthquakes - In the 1906 San Francisco quake, the Earth moved meters or about feet compared to the land on the other side of the fau ...
File
... Locating Earthquakes • Because P waves and S waves travel at different speeds, the difference in their arrival times can be used to determine the DISTANCE away an earthquake occurred. ...
... Locating Earthquakes • Because P waves and S waves travel at different speeds, the difference in their arrival times can be used to determine the DISTANCE away an earthquake occurred. ...
Earthquake Lesson
... Locating Earthquakes • Because P waves and S waves travel at different speeds, the difference in their arrival times can be used to determine the DISTANCE away an earthquake occurred. ...
... Locating Earthquakes • Because P waves and S waves travel at different speeds, the difference in their arrival times can be used to determine the DISTANCE away an earthquake occurred. ...
topic #10 - earthquakes and tsunamis
... shaking) received 100 km from epicenter • Largest quake ever recorded = 8.9 (rocks not strong enough for more). • Earthquakes less than M = 2 are not felt by people. ...
... shaking) received 100 km from epicenter • Largest quake ever recorded = 8.9 (rocks not strong enough for more). • Earthquakes less than M = 2 are not felt by people. ...
Chapter 8 Review Test - Bismarck Public Schools
... 10. One way to forecast earthquakes in a place is to observe their past a. strength and intensity. c. frequency and intensity. b. strength and frequency. d. magnitude. ...
... 10. One way to forecast earthquakes in a place is to observe their past a. strength and intensity. c. frequency and intensity. b. strength and frequency. d. magnitude. ...
Earth Movements
... There was a time – some 225 million years ago -when the continents were not separated by oceans. The earth’s surface knew only one massive continent, called Panagea. The some 200 million years ago, Pan agea split into two major continents, one of them Gondwana-land (which contains Africa, South Amer ...
... There was a time – some 225 million years ago -when the continents were not separated by oceans. The earth’s surface knew only one massive continent, called Panagea. The some 200 million years ago, Pan agea split into two major continents, one of them Gondwana-land (which contains Africa, South Amer ...
PPT
... • where 2 plates are pulling apart by tension forces • mid ocean ridge has central crack called a rift zone • at times the ridge opens to release basaltic magma forming new oceanic crust • moves 2.5 cm per year • quiet volcanic activity ...
... • where 2 plates are pulling apart by tension forces • mid ocean ridge has central crack called a rift zone • at times the ridge opens to release basaltic magma forming new oceanic crust • moves 2.5 cm per year • quiet volcanic activity ...
File - singhscience
... Detecting earthquakes • Earthquakes are detected using a seismometer – a piece of equipment that picks up the vibrations in the earth. A scientist can work out the location of an earthquake by calculating the time difference between the arrival of the S and P waves. Information from three different ...
... Detecting earthquakes • Earthquakes are detected using a seismometer – a piece of equipment that picks up the vibrations in the earth. A scientist can work out the location of an earthquake by calculating the time difference between the arrival of the S and P waves. Information from three different ...
Earthquake Vocabulary Part 2
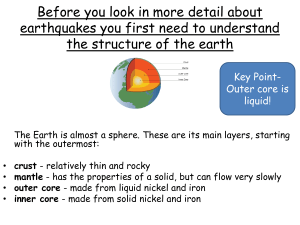
... The cool, solid outer shell of the earth. It consists of the crust and the rigid uppermost part of the mantle and is broken up into segments, or plates ...
... The cool, solid outer shell of the earth. It consists of the crust and the rigid uppermost part of the mantle and is broken up into segments, or plates ...
Real Time Weather Forecasting
... structures and household goods Increase public awareness of the earthquake hazard Create and distribute ‘Earthquake Preparedness Campaign’ among the students and nearby community Conduct Mock Drills in the schools at regular intervals ...
... structures and household goods Increase public awareness of the earthquake hazard Create and distribute ‘Earthquake Preparedness Campaign’ among the students and nearby community Conduct Mock Drills in the schools at regular intervals ...
developed
... Preparing for Earthquakes • People living in earthquake zones need to know what they should do in the event of a quake. Training people my involve holding earthquake drills and educating people via TV or radio. • People may put together emergency kits and store them in their homes. An emergency kit ...
... Preparing for Earthquakes • People living in earthquake zones need to know what they should do in the event of a quake. Training people my involve holding earthquake drills and educating people via TV or radio. • People may put together emergency kits and store them in their homes. An emergency kit ...
Geosphere in Motion Pre-Post Test
... _____ 4. Most injuries and deaths due to earthquakes are caused by the movement of the ground. (E3.4C) _____ 5. Volcanic eruptions may have a negative effect on air quality. (E3.4C) _____ 6. In comparison to continental crust, oceanic crust is younger, thinner, and denser. (E3.2C) _____ 7. The conti ...
... _____ 4. Most injuries and deaths due to earthquakes are caused by the movement of the ground. (E3.4C) _____ 5. Volcanic eruptions may have a negative effect on air quality. (E3.4C) _____ 6. In comparison to continental crust, oceanic crust is younger, thinner, and denser. (E3.2C) _____ 7. The conti ...
Tips for success
... the crust. The crust is also split up into sections called plates and these plates move very slowly (only a few millimetres a year) as they float on top of the mantle. The movements of these plates causes earthquakes to occur as the plates rub against each other. The more pressure that is built up b ...
... the crust. The crust is also split up into sections called plates and these plates move very slowly (only a few millimetres a year) as they float on top of the mantle. The movements of these plates causes earthquakes to occur as the plates rub against each other. The more pressure that is built up b ...
9th grade ch 3 notes simplified..
... the less dense continental plate, producing a subduction zone and a trench. If both are continents, the rock will fold, fault, and lead to mountain-building – like the Himalayas! 2. Transform: 2 plates slide past each other – like at the San Andreas fault. 3. Divergent: This causes a rift – new cr ...
... the less dense continental plate, producing a subduction zone and a trench. If both are continents, the rock will fold, fault, and lead to mountain-building – like the Himalayas! 2. Transform: 2 plates slide past each other – like at the San Andreas fault. 3. Divergent: This causes a rift – new cr ...
Volcanoes and Earthquakes
... when they get stuck in one spot until the point where they slip past each other releasing all the energy from the friction being released ...
... when they get stuck in one spot until the point where they slip past each other releasing all the energy from the friction being released ...
The Earth`s Crust - Red Hook Central Schools
... vibrating, shaking, or rapid motion of the Earth’s crust. Most occur when stress builds along a zone of weakness or a break in the rock known as a fault. When the crust shifts, energy is released. The energy radiates in all directions through vibrations. ...
... vibrating, shaking, or rapid motion of the Earth’s crust. Most occur when stress builds along a zone of weakness or a break in the rock known as a fault. When the crust shifts, energy is released. The energy radiates in all directions through vibrations. ...
The Earth`s Crust - mrgsearthsciencepage
... vibrating, shaking, or rapid motion of the Earth’s crust. Most occur when stress builds along a zone of weakness or a break in the rock known as a fault. When the crust shifts, energy is released. The energy radiates in all directions through vibrations. ...
... vibrating, shaking, or rapid motion of the Earth’s crust. Most occur when stress builds along a zone of weakness or a break in the rock known as a fault. When the crust shifts, energy is released. The energy radiates in all directions through vibrations. ...
Earthquake

An earthquake (also known as a quake, tremor or temblor) is the perceptible shaking of the surface of the Earth, which can be violent enough to destroy major buildings and kill thousands of people. The severity of the shaking can range from barely felt to violent enough to toss people around. Earthquakes have destroyed whole cities. They result from the sudden release of energy in the Earth's crust that creates seismic waves. The seismicity, seismism or seismic activity of an area refers to the frequency, type and size of earthquakes experienced over a period of time.Earthquakes are measured using observations from seismometers. The moment magnitude is the most common scale on which earthquakes larger than approximately 5 are reported for the entire globe. The more numerous earthquakes smaller than magnitude 5 reported by national seismological observatories are measured mostly on the local magnitude scale, also referred to as the Richter magnitude scale. These two scales are numerically similar over their range of validity. Magnitude 3 or lower earthquakes are mostly almost imperceptible or weak and magnitude 7 and over potentially cause serious damage over larger areas, depending on their depth. The largest earthquakes in historic times have been of magnitude slightly over 9, although there is no limit to the possible magnitude. The most recent large earthquake of magnitude 9.0 or larger was a 9.0 magnitude earthquake in Japan in 2011 (as of March 2014), and it was the largest Japanese earthquake since records began. Intensity of shaking is measured on the modified Mercalli scale. The shallower an earthquake, the more damage to structures it causes, all else being equal.At the Earth's surface, earthquakes manifest themselves by shaking and sometimes displacement of the ground. When the epicenter of a large earthquake is located offshore, the seabed may be displaced sufficiently to cause a tsunami. Earthquakes can also trigger landslides, and occasionally volcanic activity.In its most general sense, the word earthquake is used to describe any seismic event — whether natural or caused by humans — that generates seismic waves. Earthquakes are caused mostly by rupture of geological faults, but also by other events such as volcanic activity, landslides, mine blasts, and nuclear tests. An earthquake's point of initial rupture is called its focus or hypocenter. The epicenter is the point at ground level directly above the hypocenter.